AI Conversation
Robotics Technology
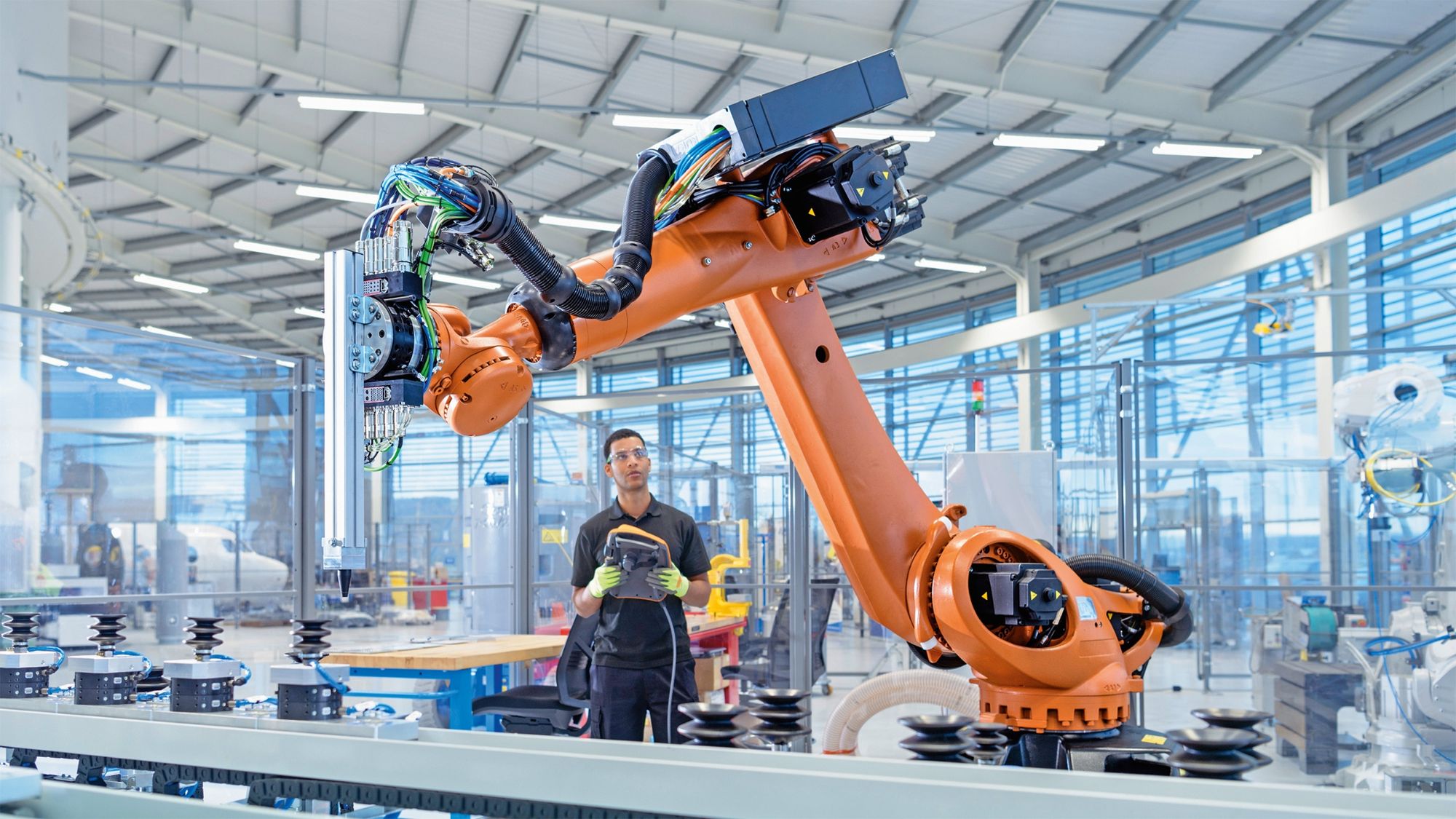

Robotics technology in engineering has advanced to the point where robots can now autonomously perform complex surgeries, significantly reducing recovery times and improving precision beyond human capabilities.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dO3Gts-gkuQ
sensors
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hm7e3ADBoRI

Sensors in robotics are crucial for perception and interaction with the environment. They provide data on position, proximity, temperature, and more, enabling robots to navigate, manipulate objects, and perform tasks autonomously. Advances in sensor technology enhance robot accuracy, efficiency, and adaptability, driving innovation in automation and artificial intelligence.
artificial intelligence

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Jky9I1ihAkg
Artificial intelligence in robotics enhances automation, enabling machines to perform complex tasks with precision and adaptability. It integrates machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing, allowing robots to learn from data, recognize patterns, and interact seamlessly with humans, revolutionizing industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics with increased efficiency and innovation.
kinematics

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s6CgomkNf-w
Kinematics in robotics focuses on the motion of robots without considering forces. It involves calculating positions, velocities, and accelerations of robot components. Essential for designing robotic systems, kinematics ensures precise movement and control, enabling tasks like manipulation, navigation, and interaction in various applications, from manufacturing to healthcare.
actuators
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XnCHWxX4eRo
Actuators are crucial components in robotics, converting electrical signals into physical movement. They enable robots to perform tasks by controlling motion, force, and positioning. Common types include electric, hydraulic, and pneumatic actuators. Their efficiency, precision, and responsiveness are vital for robotic functionality across industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and automation.
power supply
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZO4_ipwwXYc
Power supply in robotics technology is crucial for optimal performance and efficiency. It involves selecting appropriate energy sources, such as batteries or fuel cells, to ensure reliability and longevity. Advanced power management systems are essential for balancing energy consumption, enhancing mobility, and supporting complex tasks in autonomous and industrial robots.
control systems
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2BwUMk10WqI
Control systems in robotics technology manage and direct robot behavior through feedback loops, sensors, and algorithms. They ensure precision, stability, and adaptability in tasks like navigation, manipulation, and interaction. By integrating hardware and software, control systems enable robots to perform complex functions autonomously and efficiently in dynamic environments.
end effectors
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h4pMCnDv_eE
End effectors are crucial components in robotics, serving as the interface between robots and their tasks. They include grippers, tools, or sensors, enabling robots to manipulate objects, perform precise operations, and interact with environments. Advances in materials and design enhance their adaptability, precision, and functionality across diverse applications in automation and manufacturing.
programming
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9URSbTOE4YI
Programming in robotics technology involves designing algorithms to control robotic systems, enabling them to perform tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously. It integrates artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor data processing to enhance robot perception, decision-making, and adaptability, driving advancements in automation, manufacturing, healthcare, and exploration industries.

Sensors

Some sensors in engineering technology, like accelerometers, are so sensitive that they can detect the vibrations caused by footsteps or even the fluttering of a butterfly's wings.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XI49uFm5HRE
infrared sensors
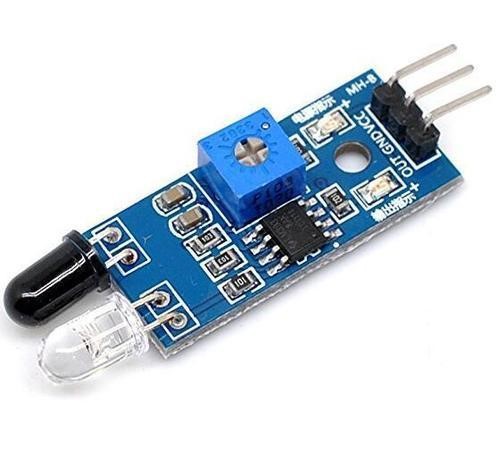

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XRCprhlz4D8
Infrared sensors detect infrared radiation to measure heat and motion, widely used in various applications like night vision, temperature sensing, and motion detection. They offer advantages in low-light conditions and are integral in security systems, industrial automation, and environmental monitoring, enhancing efficiency and safety across diverse fields.
gyroscope

A gyroscope is a sensor that measures angular velocity, crucial for detecting orientation and maintaining stability in devices. Widely used in smartphones, drones, and gaming controllers, it enhances motion sensing by providing precise rotational data, complementing accelerometers for accurate 3D motion tracking and navigation systems.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=REVp33SwwHE
proximity sensors
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tpXW6qWoJGA
Proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of objects without physical contact, using methods like infrared, ultrasonic, or electromagnetic fields. They are crucial in automation, enhancing safety and efficiency by triggering responses in machinery or systems. Their applications span industries, including automotive, manufacturing, and consumer electronics.
ultrasonic sensors

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dPZ9izkt1pY
Ultrasonic sensors use high-frequency sound waves to detect objects and measure distances. They are widely used in various applications, including robotics, automotive parking systems, and industrial automation, due to their ability to function in diverse environments and detect transparent or reflective surfaces where optical sensors might fail.
vision sensors

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IB7EtJPVj8c
Vision sensors are devices that capture and process visual information from the environment. They play a crucial role in automation, robotics, and surveillance by enabling machines to interpret and respond to visual data. These sensors enhance efficiency and accuracy in various applications, from quality control to autonomous navigation.
lidar
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FOxxqVzDaaA
Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging) is a sensor technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances, creating precise 3D maps of environments. Widely used in autonomous vehicles, drones, and topographic mapping, lidar provides high-resolution spatial data, enhancing navigation, obstacle detection, and environmental monitoring capabilities across various industries.

accelerometer

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KuekQ-m9xpw
An accelerometer is a sensor that measures acceleration forces, enabling the detection of motion, orientation, and vibration. Widely used in smartphones, wearables, and automotive systems, it provides critical data for navigation, activity tracking, and stabilization, enhancing user experience and device functionality through precise motion sensing.
force sensors
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UQBLe5H45dc
Force sensors are devices that measure the amount of force applied to an object. They play a crucial role in various applications, including robotics, manufacturing, and healthcare. By converting mechanical force into electrical signals, these sensors enable precise control and monitoring, enhancing efficiency and safety across diverse industries.
AI Report
Essay
**Title: The Impact of Robotics Technology on Modern Society**
Robotics technology has emerged as a transformative force in various sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics. The integration of robotics into these industries has not only enhanced efficiency and productivity but has also raised important questions about the future of work and human-robot collaboration. As robotics technology continues to evolve, its implications for society become increasingly significant, warranting a closer examination of its benefits and challenges.
One of the most notable advancements in robotics technology is its application in manufacturing. Industrial robots have revolutionized production processes by enabling automation and precision work. According to Bogue (2018), the use of robots in manufacturing has led to increased output, reduced operational costs, and improved product quality. These machines can perform repetitive tasks with high accuracy, minimizing human error and allowing workers to focus on more complex problem-solving tasks. As a result, companies that adopt robotics technology often experience a competitive advantage in the global market.
In addition to manufacturing, robotics technology has made significant strides in the healthcare sector. Robots are increasingly being used for surgical procedures, rehabilitation, and patient care. For instance, surgical robots allow for minimally invasive operations, which can lead to faster recovery times for patients (Yang et al., 2020). Furthermore, robotic systems are being developed to assist the elderly and individuals with disabilities, enhancing their quality of life and independence. These advancements demonstrate the potential of robotics to improve healthcare outcomes while addressing workforce challenges in the industry.
However, the integration of robotics technology also raises ethical and societal concerns. One of the primary issues is the displacement of jobs as robots take over tasks traditionally performed by humans. A report by the McKinsey Global Institute (2017) estimates that up to 800 million jobs could be displaced by automation by 2030. This potential job loss necessitates a reevaluation of workforce training and education to prepare individuals for a changing job landscape. Additionally, concerns about data privacy and security arise as robots increasingly rely on artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms.
Despite these challenges, the future of robotics technology appears promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at enhancing human-robot collaboration. Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work alongside humans, complementing their skills rather than replacing them. According to a study by Ghosh and Yadav (2021), effective collaboration between humans and robots can lead to improved productivity and job satisfaction. By fostering a synergistic relationship, organizations can harness the strengths of both humans and robots to achieve optimal outcomes.
In conclusion, robotics technology is reshaping various aspects of modern society, offering significant benefits while also posing challenges that require careful consideration. As industries continue to adopt robotic solutions, it is essential to address the ethical implications and workforce transitions that accompany this technological shift. By fostering an environment of collaboration and innovation, society can leverage the potential of robotics to enhance productivity and improve quality of life for all.
**References**
Bogue, R. (2018). Industrial robots: A review of the current state of technology and future prospects. *Industrial Robot: An International Journal*, 45(3), 311-315. https://doi.org/10.1108/IR-02-2018-0029
Ghosh, P., & Yadav, S. (2021). Human-robot collaboration: A study on the impact of collaborative robots on productivity and job satisfaction. *Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management*, 32(4), 769-786. https://doi.org/10.1108/JMTM-07-2020-0304
McKinsey Global Institute. (2017). A future that works: Automation, employment, and productivity. Retrieved from https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/future-of-work/afuture-that-works
Yang, G.-Z., Hawkes, E. W., Leal-Junior, E. C., & et al. (2020). Medical robotics: A review. *IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering*, 13, 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1109/RBME.2019.2934016
Lesson Plan
### Lesson Plan: Introduction to Robotics Technology
**Grade Level**: Technical Vocational Students
**Duration**: 2 Hours
**Subject**: Robotics Technology
**Instructor**: [Instructor's Name]
**Location**: [Classroom/Workshop]
---
#### **Objectives**
By the end of this lesson, students will be able to:
1. Define robotics and explain its key components.
2. Understand how robots work, including sensors, actuators, and controllers.
3. Identify basic maintenance procedures for robotic systems.
4. Discuss real-world applications of robotics technology.
---
### **Materials Needed**
- PowerPoint presentation on Robotics Technology
- Robotics kits (if available)
- Video clips demonstrating robotic operations
- Whiteboard and markers
- Handouts with key terminology and concepts
- Maintenance checklists for robotic systems
---
### **Lesson Outline**
#### **I. Introduction (15 minutes)**
- **A. Engage Students**
- Start with a short video showcasing various types of robots (industrial, medical, service robots).
- Ask students what they know about robotics and its applications.
- **B. Objectives Overview**
- Present the lesson objectives and what students can expect to learn.
#### **II. Understanding Robotics Technology (30 minutes)**
- **A. Definition of Robotics**
- Explain what robotics is and its significance in various industries.
- **B. Key Components of Robots**
- Discuss the following components:
- **Sensors**: Types and functions (e.g., cameras, ultrasonic sensors).
- **Actuators**: How they move and control robots (e.g., motors, servos).
- **Controllers**: The brain of the robot (e.g., microcontrollers, software).
- **C. How Robots Work**
- Explain the basic operation of a robot using the components discussed.
- Use diagrams and animations to illustrate processes.
#### **III. Maintenance of Robotics Systems (30 minutes)**
- **A. Importance of Maintenance**
- Discuss why regular maintenance is crucial for robotic systems.
- **B. Basic Maintenance Procedures**
- Review common maintenance tasks:
- Cleaning sensors and components
- Checking and replacing batteries
- Testing and calibrating sensors and actuators
- Introduce a maintenance checklist that students can use.
#### **IV. Real-World Applications of Robotics (20 minutes)**
- **A. Industry Applications**
- Discuss various applications of robotics in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and agriculture.
- **B. Group Activity**
- Divide students into small groups. Each group will choose an industry and discuss how robotics is utilized. They will present their findings to the class.
#### **V. Q&A and Discussion (15 minutes)**
- Open the floor for questions. Encourage students to share their thoughts on robotics technology and its future.
#### **VI. Conclusion and Assignment (10 minutes)**
- **A. Recap Key Points**
- Summarize the key concepts covered in the lesson.
- **B. Assignment**
- Ask students to write a short report on a specific robot they find interesting, including its components, how it works, and its applications. Reports are due by the next class.
---
### **Assessment**
- Participation in group discussions and activities.
- Quality of the short report on a robot.
- Completion of a quiz covering key concepts from the lesson (to be conducted in the following class).
---
### **Extensions**
- Organize a field trip to a local robotics company or lab.
- Invite a guest speaker who works in the robotics field to share insights with students.
---
### **Resources**
- Recommended websites and books on robotics technology.
- Access to online simulations or robotics software for hands-on practice.
---
This lesson plan provides a comprehensive introduction to robotics technology tailored for technical vocational students, blending theoretical knowledge with practical applications.
Class Syllabus Outline
# Syllabus for Robotics Technology
## Course Title: Introduction to Robotics Technology
**Course Code:** RBT101
**Semester:** Fall 2023
**Credits:** 3
**Instructor:** Dr. Jane Smith
**Email:** jane.smith@university.edu
**Office Hours:** Mondays and Wednesdays, 2 PM - 4 PM (Room 204, Engineering Building)
### Course Description:
This course provides an introduction to the fundamental concepts and technologies in robotics. Students will explore the history, design, programming, and applications of robots in various fields. The course will combine theoretical knowledge with hands-on projects to develop practical skills in robotics.
### Course Objectives:
By the end of this course, students will be able to:
1. Understand the basic components and architecture of robotic systems.
2. Analyze the role of sensors, actuators, and controllers in robotics.
3. Develop simple robotic programs using a programming language.
4. Design and build a basic robot as part of a team project.
5. Evaluate the ethical implications and future trends in robotics technology.
### Required Textbooks:
- **Introduction to Robotics: Mechanics and Control** by John J. Craig
- **Robot Operating System (ROS) for Beginners** by Aaron Martinez and Enrique Fernandez
### Course Outline:
#### Week 1: Introduction to Robotics
- Overview of robotics history and applications
- Key components of robotic systems: sensors, actuators, controllers
#### Week 2: Types of Robots
- Industrial robots, service robots, mobile robots, and humanoid robots
- Case studies of robots in various industries
#### Week 3: Kinematics and Dynamics of Robots
- Forward and inverse kinematics
- Introduction to dynamics and motion planning
#### Week 4: Sensors and Perception
- Types of sensors: vision, ultrasonic, infrared, and tactile sensors
- Data processing and sensor integration
#### Week 5: Actuators and Control Systems
- Motors and servo systems
- Control algorithms: PID control, state-space control
#### Week 6: Introduction to Programming Robots
- Overview of programming languages used in robotics (C++, Python, ROS)
- Basic programming concepts for robotics
#### Week 7: Midterm Exam
- Review of course material
- Midterm examination
#### Week 8: Robot Operating System (ROS)
- Introduction to ROS architecture
- Setting up ROS and basic commands
#### Week 9: Robot Design and Prototyping
- Design thinking and engineering principles in robotics
- Rapid prototyping techniques
#### Week 10: Robot Navigation and Mapping
- Introduction to navigation algorithms (SLAM)
- Path planning and obstacle avoidance
#### Week 11: Team Project Work
- Forming teams and brainstorming project ideas
- Initial design and planning phase for group projects
#### Week 12: Project Development
- Hands-on work on team projects
- Incorporating feedback and iterative design
#### Week 13: Presentations and Demonstrations
- Team project presentations
- Demonstration of final projects
#### Week 14: Ethical Considerations in Robotics
- Discussion on the ethical implications of robotics
- Future trends and developments in robotics technology
#### Week 15: Course Review and Final Exam Preparation
- Review key concepts and prepare for the final exam
### Assessment and Grading:
- Participation and Attendance: 10%
- Homework Assignments: 20%
- Midterm Exam: 25%
- Team Project: 30%
- Final Exam: 15%
### Policies:
- **Attendance:** Attendance is mandatory. More than three unexcused absences may result in a lower grade.
- **Late Work:** Assignments submitted late will incur a 10% penalty for each day late.
- **Academic Integrity:** Students are expected to adhere to the university’s academic integrity policy. Plagiarism and cheating will not be tolerated.
### Important Dates:
- **Midterm Exam:** Week 7
- **Team Project Due Date:** Week 13
- **Final Exam:** Scheduled by the university at the end of the semester
### Additional Resources:
- Robotics lab hours (TBA)
- Online forums and discussion boards for peer support
- Additional readings and resources provided on the course website
---
**Note:** This syllabus is subject to change at the instructor's discretion. Students will be notified of any changes in a timely manner.
Learning Objectives
### Learning Objectives for Robotics Technology Course
1. **Understanding Robotics Fundamentals**
- Identify and describe the basic components and systems of robotic technology, including sensors, actuators, controllers, and power supplies.
2. **Programming and Control Systems**
- Demonstrate proficiency in programming languages and software used for robotic applications, such as Python, C++, and ROS (Robot Operating System).
3. **Robotic System Design**
- Apply principles of engineering design to create and develop functional robotic systems tailored to specific tasks or challenges.
4. **Sensor Integration**
- Explain the role of various types of sensors in robotics, including proximity, vision, and tactile sensors, and integrate them into robotic systems for enhanced functionality.
5. **Mechanical and Electrical Systems**
- Analyze and troubleshoot mechanical and electrical systems within robots, including motors, gears, and circuit boards.
6. **Automation and Control Theory**
- Understand and apply basic concepts of automation and control theory, including feedback loops and PID control, in robotic systems.
7. **Safety and Ethics in Robotics**
- Recognize and assess safety protocols and ethical considerations in the design and deployment of robotic systems in various environments.
8. **Collaborative Robotics**
- Explore the concepts of collaborative robots (cobots) and their applications in industrial and service sectors, promoting human-robot interaction and teamwork.
9. **Project Management**
- Develop project management skills relevant to robotics projects, including planning, execution, and evaluation of robotic solutions.
10. **Emerging Trends in Robotics**
- Investigate current trends and future directions in robotics technology, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, and their impact on the industry.
11. **Hands-On Experience**
- Engage in hands-on projects that involve building, programming, and testing robotic systems, fostering practical skills and problem-solving abilities.
12. **Communication and Presentation Skills**
- Effectively communicate complex technical information related to robotics technology through presentations, reports, and discussions to diverse audiences.
By the end of the course, students will be equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to pursue further education or careers in the field of robotics technology.
Quiz Questions
Sure! Here are five multiple choice questions about Robotics Technology along with their answers:
### Question 1:
What is the primary purpose of a robotic actuator?
A) To provide power to the robot
B) To control the robot's movements
C) To process information
D) To sense the environment
**Answer:** B) To control the robot's movements
### Question 2:
Which of the following is a common programming language used in robotics?
A) HTML
B) Python
C) SQL
D) CSS
**Answer:** B) Python
### Question 3:
What kind of sensors do robots typically use to navigate their environment?
A) Temperature sensors
B) Proximity sensors
C) Sound sensors
D) All of the above
**Answer:** D) All of the above
### Question 4:
In the context of robotics, what does "SLAM" stand for?
A) Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
B) Simple Logic and Mechanics
C) Systematic Layout and Movement
D) Sequential Learning and Action Modeling
**Answer:** A) Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
### Question 5:
Which type of robot is designed to work alongside humans in a shared workspace?
A) Autonomous robot
B) Collaborative robot
C) Industrial robot
D) Humanoid robot
**Answer:** B) Collaborative robot