Lesson AI Summary
Lesson has no AI Report
AI Conversation
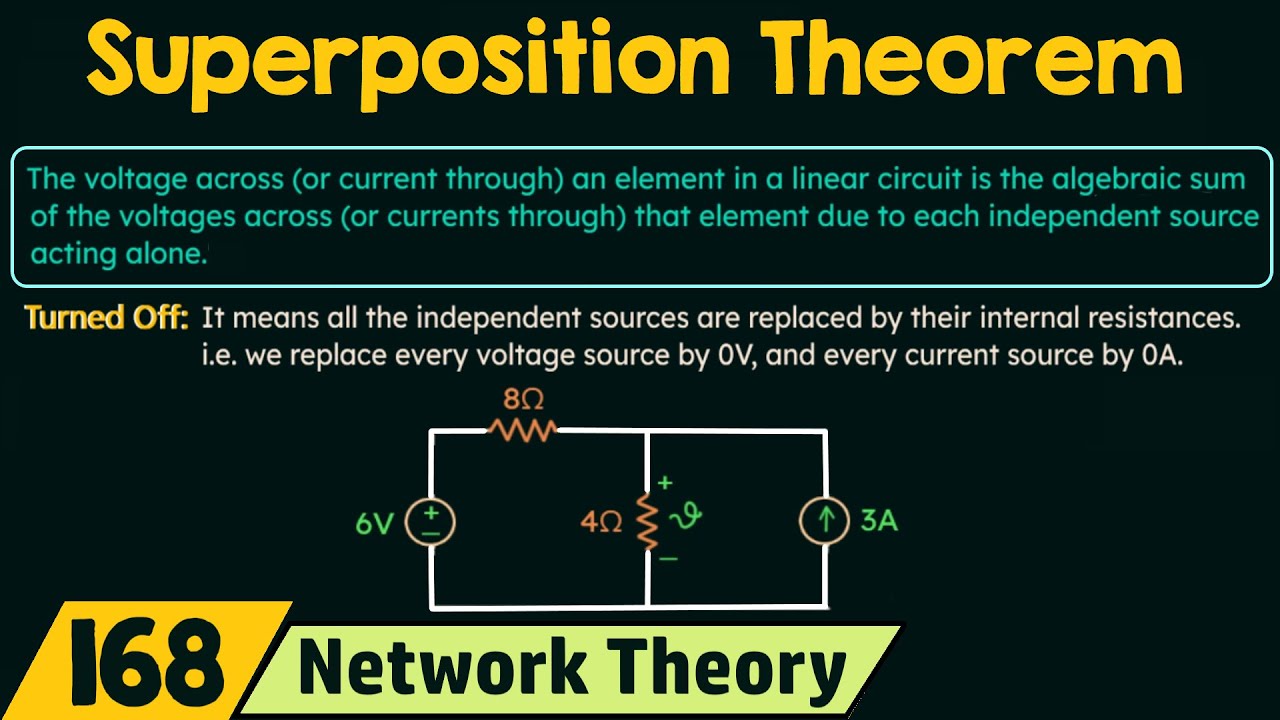
Superposition Theorem
The Superposition Theorem states that in a linear circuit with multiple sources, the response (voltage or current) is the sum of the responses from each source acting independently. This principle aids in simplifying the analysis of circuits with multiple power sources.
nodal analysis
Nodal Analysis is a method used to determine the voltage at various nodes in a circuit. By applying KCL at each node, it simplifies the process of solving complex circuits with multiple components.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f-sbANgw4fo
kirchhoff's current law (kcl)
KCL asserts that the total current entering a junction equals the total current leaving it. This law is crucial for analyzing current flow in complex circuits, ensuring that charge is conserved at every node.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q39xQUlTGew
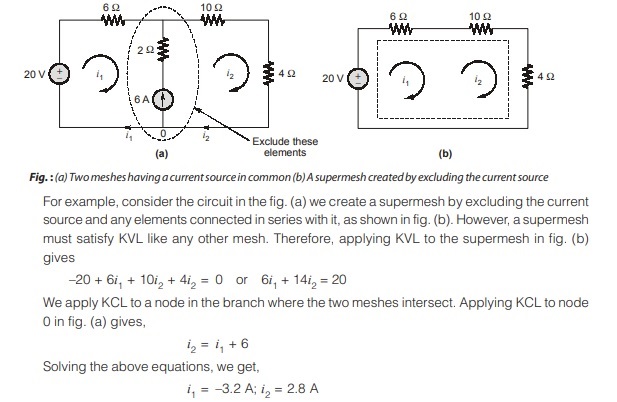
mesh analysis
Mesh Analysis involves applying KVL to find the current in each mesh of a circuit. This technique is particularly useful for planar circuits, where it simplifies the process of solving for unknown currents.
kirchhoff's voltage law (kvl)
KVL states that the sum of all electrical voltages around any closed network is zero. This principle helps in analyzing the voltage distribution in a circuit, ensuring that energy is conserved as it circulates through the loop.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6F_rmZ1nXFQ
ohm's law
Ohm's Law relates voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit, expressed as V=IR. It is fundamental for calculating the relationship between these quantities and designing circuits with desired electrical characteristics.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HsLLq6Rm5tU
norton's theorem
Norton's Theorem is similar to Thevenin's but reduces a circuit to a current source in parallel with a resistance. It provides an alternative method for simplifying and analyzing circuits, particularly useful for parallel configurations.

introduction to network theory
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-ckaLBsCoxo
Introduction to Network Theory in Electrical Engineering involves understanding the principles governing electrical circuits. Learn the basics of network theory, including Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL), which are fundamental for analyzing complex circuits and ensuring efficient electrical system design and operation.

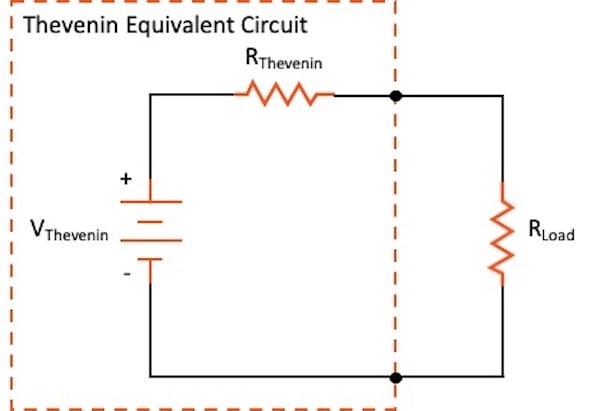
thevenin's theorem
Thevenin's Theorem simplifies a complex circuit to a single voltage source and series resistance. This reduction makes it easier to analyze and understand the behavior of the circuit, especially when examining load variations.