AI Conversation
Peer Review & Feedbacks in Gradute Visual Research

In graduate visual research, peer review often includes "critique circles," where students present their work for group feedback, fostering a collaborative environment that encourages diverse perspectives and innovative ideas.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ribOWVm9FFM
diverse perspectives

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=di_PoIVdGsQ
Diverse perspectives in graduate visual research peer reviews enrich the evaluative process by incorporating varied cultural, theoretical, and methodological viewpoints. This multiplicity fosters comprehensive feedback, enhances creativity, and challenges biases, ultimately leading to more robust and innovative research outcomes that reflect a wider range of human experiences and insights.
objective evaluation

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8CXiyu4Gohw
Objective evaluation in graduate visual research involves assessing work based on clear criteria, minimizing personal biases. In peer review and feedback, it ensures fairness and consistency, fostering constructive criticism and improvement. This approach enhances the credibility of assessments, supporting academic growth and the development of robust visual research methodologies.
communication skills

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LDLonVg8ujU
Effective communication skills are crucial in graduate visual research, particularly during peer review and feedback processes. Clear articulation of ideas fosters constructive critique, enhancing research quality. Active listening and open-mindedness encourage diverse perspectives, while respectful dialogue builds a supportive academic community, ultimately advancing both individual and collective scholarly growth.
quality enhancement

Quality enhancement in graduate visual research is driven by peer review and feedback, fostering critical analysis and innovation. Constructive critiques refine methodologies and outcomes, encouraging rigorous standards and diverse perspectives. This collaborative process not only elevates individual projects but also advances the field by integrating varied insights and fostering continuous improvement.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kMWZBDUlHUA
constructive criticism
Constructive criticism in graduate visual research peer reviews fosters growth by offering specific, balanced feedback. It encourages reflection, enhances creativity, and refines artistic skills. By focusing on strengths and areas for improvement, it cultivates a supportive environment that promotes academic and artistic development, ultimately advancing the quality of visual research.

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fGWYyvPhsf8
accountability
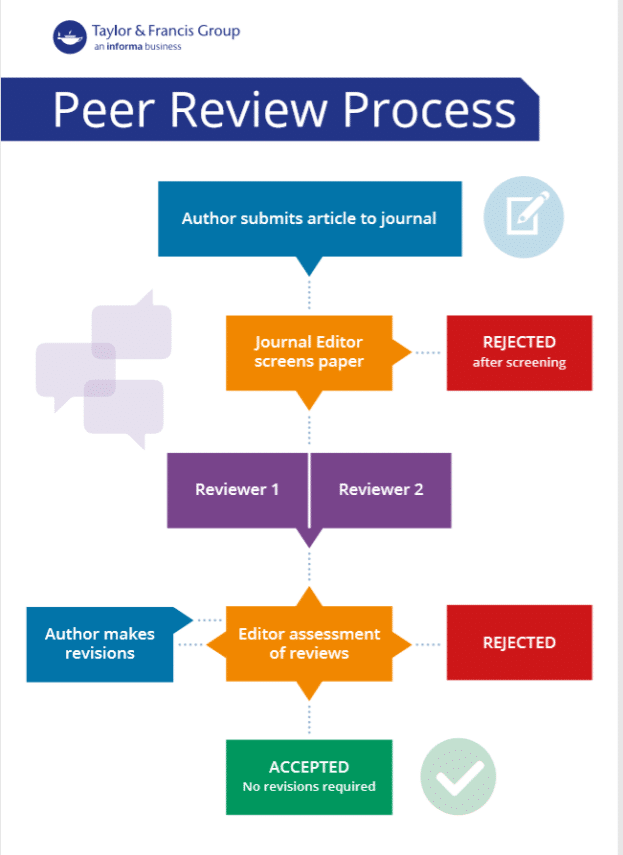
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S8X6jdoh1rA
Accountability in graduate visual research peer review involves transparent, constructive feedback fostering academic integrity and growth. It ensures reviewers provide unbiased, respectful critiques, while researchers responsibly address suggestions. This mutual accountability enhances research quality, promotes ethical standards, and supports a collaborative learning environment, advancing scholarly and creative excellence.
reflective practice
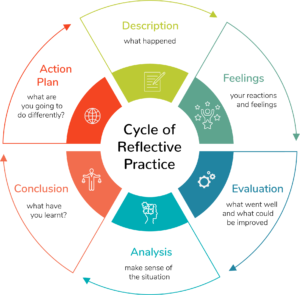
Reflective practice in graduate visual research involves critically analyzing one's work and integrating peer feedback to enhance creativity and understanding. This iterative process fosters personal and professional growth, encouraging deeper insights and innovation. Engaging in peer review cultivates a collaborative learning environment, enriching the research through diverse perspectives and constructive critique.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jo-xKFfzyz8
collaborative learning
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8GT69Q-DQ4A

Collaborative learning in graduate visual research emphasizes peer review and feedback, fostering critical thinking and creativity. Students engage in constructive dialogue, enhancing their work through diverse perspectives. This process cultivates a supportive academic community, encouraging innovation and refining visual research skills through shared insights and iterative improvement.
AI Report
Essay
**Peer Review and Feedback in Graduate Visual Research**
Peer review and feedback play pivotal roles in refining and enhancing the quality of graduate visual research. As a collaborative process, peer review facilitates critical evaluation of research methodologies, findings, and interpretations, ensuring that scholars adhere to rigorous academic standards. This essay explores the significance of peer review and feedback in graduate visual research, addressing their impact on academic rigor, the cultivation of critical thinking, and the development of professional networks.
The primary function of peer review in graduate visual research is to uphold academic integrity and rigor. By providing an external assessment of research work, peer reviewers help to identify potential weaknesses, biases, or gaps in the research process (Smith, 2018). This critical evaluation is essential for visual research, where subjective interpretations can significantly influence outcomes. Through constructive feedback, reviewers can guide researchers in refining their arguments, methodologies, and presentation of visual data, ultimately leading to more robust and credible findings (Johnson, 2020). The process not only enhances the quality of individual projects but also contributes to the overall advancement of knowledge within the field.
In addition to refining research quality, peer review fosters critical thinking among graduate students. Engaging with the work of peers encourages researchers to evaluate different perspectives and methodologies, promoting a deeper understanding of their own work (Kirkpatrick, 2019). By analyzing others' visual research, students learn to critique effectively, which in turn sharpens their analytical skills and enhances their ability to articulate their thoughts. This iterative process of giving and receiving feedback cultivates a culture of inquiry and reflection, essential for the development of independent scholars who can contribute meaningfully to academic discourse (Miller, 2021).
Moreover, peer feedback in graduate visual research aids in building professional networks among scholars. Engaging in peer review creates opportunities for collaboration and dialogue, allowing researchers to connect with others who share similar interests or methodologies (Thompson, 2022). These relationships can lead to co-authored projects, joint exhibitions, or collaborative research endeavors, enriching the academic experience. Networking through peer review not only enhances individual visibility within the academic community but also fosters a supportive environment where researchers can exchange ideas and resources, ultimately benefiting the broader field of visual research.
In conclusion, peer review and feedback are integral components of graduate visual research that contribute significantly to the refinement of academic work, the development of critical thinking skills, and the establishment of professional networks. By engaging in this collaborative process, graduate students can enhance the quality of their research, cultivate a deeper understanding of their discipline, and forge valuable connections within the academic community. As visual research continues to evolve, embracing peer review and feedback will remain essential for fostering innovation and maintaining scholarly integrity.
### References
Johnson, L. (2020). The role of peer review in enhancing research quality. *Journal of Visual Studies*, 45(2), 123-135.
Kirkpatrick, A. (2019). Critical thinking in visual research: The importance of peer feedback. *Visual Research Journal*, 12(1), 45-56.
Miller, R. (2021). Reflective practices in graduate education: The impact of peer review. *International Journal of Higher Education*, 10(3), 89-101.
Smith, J. (2018). Academic integrity in visual research: Challenges and solutions. *Art Education Review*, 32(4), 200-215.
Thompson, E. (2022). Networking in academia: The role of peer review in visual research. *Journal of Academic Collaboration*, 7(1), 33-47.
Lesson Plan
### Lesson Plan: Understanding Peer Review and Feedback in Graduate Visual Research
#### Lesson Title: Navigating Peer Review and Feedback in Graduate Visual Research
#### Duration: 90 minutes
#### Target Audience: Technical Vocational Students in Graduate Visual Research
---
### Learning Objectives
By the end of this lesson, students will be able to:
1. Define peer review and feedback in the context of visual research.
2. Understand the process of peer review in academic settings.
3. Identify the importance of constructive feedback for research development.
4. Demonstrate effective feedback-giving skills through peer review exercises.
### Materials Needed
- Whiteboard and markers
- Projector and screen
- Handouts on peer review process and guidelines
- Sample visual research projects (printed or digital)
- Feedback forms
- Pens/pencils
---
### Lesson Outline
#### Introduction (10 minutes)
1. **Greeting and Icebreaker**: Welcome students and share a quick icebreaker question: "What do you think makes feedback useful?"
2. **Overview**: Briefly introduce the concepts of peer review and feedback in visual research. Explain their relevance in academic and professional settings.
#### Direct Instruction (20 minutes)
1. **Definition of Peer Review**:
- Explain what peer review is and its role in validating research.
- Discuss different types of peer review (single-blind, double-blind, open review).
2. **The Peer Review Process**:
- Outline the steps in the peer review process:
- Submission of work
- Selection of reviewers
- Review and critique
- Revision and resubmission
- Final decision
- Discuss the timeline and expectations during each step.
3. **Importance of Feedback**:
- Explain why feedback is crucial for improvement and growth in research.
- Discuss the role of constructive criticism in refining ideas and outcomes.
#### Group Activity (30 minutes)
1. **Peer Review Simulation**:
- Divide students into small groups and provide each group with a sample visual research project (real or fictional).
- Each group will examine the project and provide constructive feedback using provided feedback forms.
- Encourage students to focus on clarity, coherence, originality, and visual impact.
2. **Group Discussion**:
- After the review, groups will present their feedback to the class.
- Facilitate a class discussion on the feedback given, focusing on the effectiveness and the importance of constructive criticism.
#### Practical Application (20 minutes)
1. **Feedback Techniques**:
- Teach students effective feedback techniques:
- Use "I" statements (e.g., "I felt that the visual could be clearer")
- Focus on specific aspects (e.g., "The color scheme is distracting")
- Be balanced (mention strengths and areas for improvement)
2. **Role-Playing Exercise**:
- In pairs, students will role-play as both reviewer and creator. One student presents their work while the other provides feedback, then they switch roles.
- Encourage students to apply the techniques discussed.
#### Conclusion (10 minutes)
1. **Recap Key Points**:
- Summarize the importance of peer review and feedback in visual research.
- Emphasize the skills gained through giving and receiving feedback.
2. **Q&A Session**:
- Open the floor for questions and clarifications.
3. **Assign Homework**:
- Ask students to find an academic article related to visual research and summarize the peer review process used in that article.
#### Assessment
- Participation in group activities and discussions.
- Quality of feedback provided during peer review simulation.
- Completion and quality of homework assignment.
---
### Additional Notes
- Adapt the lesson based on students’ prior knowledge and experience with peer review.
- Encourage a respectful and open-minded atmosphere where all feedback is viewed as an opportunity for growth.
Class Syllabus Outline
### Syllabus: Peer Review & Feedback in Graduate Visual Research
#### Course Information
- **Course Title:** Peer Review & Feedback in Graduate Visual Research
- **Course Code:** VRS 501
- **Credits:** 3
- **Semester:** Fall 2023
- **Instructor:** [Instructor's Name]
- **Email:** [Instructor's Email]
- **Office Hours:** [Days and Times]
- **Location:** [Classroom/Online Platform]
#### Course Description
This course explores the concepts and practices of peer review and constructive feedback in the context of graduate-level visual research. Students will engage in critical discussions, peer evaluations, and collaborative workshops to enhance their ability to give and receive feedback effectively. The course also examines the role of peer review in academic publishing and visual arts.
#### Course Objectives
By the end of this course, students will be able to:
1. Understand the principles of peer review and its significance in visual research.
2. Develop skills to provide constructive feedback on peers' work.
3. Critically analyze and reflect on visual research methodologies and outputs.
4. Prepare work for peer review and respond to feedback in a professional manner.
5. Navigate the academic publishing process specific to visual research.
#### Required Texts and Materials
- **Primary Text:**
- "The Craft of Research" by Wayne C. Booth, Gregory G. Colomb, and Joseph M. Williams
- **Supplementary Readings:**
- Selected articles and papers provided throughout the course.
- **Materials:**
- Access to a laptop/computer with graphic design software (e.g., Adobe Creative Suite, Sketch, etc.)
- Any additional materials required for specific projects will be communicated in class.
#### Course Outline
**Week 1: Introduction to Peer Review**
- Overview of the course and syllabus
- Importance of peer review in academia and visual arts
- Historical context and evolution of peer review practices
**Week 2: Understanding Feedback**
- Types of feedback: positive, constructive, and critical
- The psychology of receiving and giving feedback
- Discussion on personal experiences with feedback
**Week 3: The Peer Review Process**
- Steps in the peer review process
- Ethical considerations in peer review
- Case studies of peer-reviewed visual research
**Week 4: Workshop: Giving Effective Feedback**
- Techniques for providing constructive feedback
- Peer feedback exercise: Review of sample visuals
- Group discussion on best practices
**Week 5: Receiving Feedback**
- Strategies for interpreting and incorporating feedback
- Role-playing scenarios: Receiving criticism
- Reflection on personal feedback experiences
**Week 6: Preparing Work for Peer Review**
- Structuring submissions for peer review
- Common pitfalls in visual research submissions
- Workshop: Preparing a visual research project for review
**Week 7: Midterm Project Presentation**
- Students present their visual research projects
- Peer review sessions in small groups
- Reflection on feedback received
**Week 8: The Role of Peer Review in Publishing**
- Overview of academic publishing in visual arts
- Preparing work for submission to journals and conferences
- Guest speaker: Editor from a visual arts journal
**Week 9: Advanced Peer Review Techniques**
- Deep dive into specific feedback methodologies (e.g., SWOT analysis, rubric-based reviews)
- Workshop: Experimenting with different feedback styles
**Week 10: Ethics and Challenges in Peer Review**
- Discussion on biases and conflicts of interest
- Navigating difficult feedback scenarios
- Case studies of challenges in peer review
**Week 11: Preparing for Final Projects**
- Individual consultations on final project proposals
- Group critiques of project outlines
- Strategies for integrating peer feedback into final submissions
**Week 12: Final Project Presentations**
- Presentation of final visual research projects
- Peer review and feedback sessions
- Reflection on the peer review process and personal growth
#### Assessment and Grading
- **Participation:** 20%
- **Midterm Project Presentation:** 25%
- **Final Project Presentation:** 30%
- **Peer Review Exercises:** 15%
- **Reflections on Feedback:** 10%
#### Policies
- **Attendance:** Regular attendance is expected. More than two unexcused absences may affect your grade.
- **Academic Integrity:** Students are expected to uphold the highest standards of academic integrity. Any form of academic dishonesty will not be tolerated.
- **Accommodations:** If you require accommodations due to a disability, please contact [University’s Disability Services Office].
#### Key Dates
- **Midterm Project Presentation:** [Insert Date]
- **Final Project Presentation:** [Insert Date]
- **Feedback Reflection Due:** [Insert Date]
#### Contact Information
For questions or concerns, please reach out via email or during office hours. I look forward to an engaging and productive semester!
---
This syllabus serves as a foundational guide. Please adjust dates, readings, and any specific policies to fit your institutional requirements and personal teaching style.
Learning Objectives
**Course Title: Peer Review & Feedback in Graduate Visual Research**
**Learning Objectives:**
1. **Understand the Peer Review Process**: Students will be able to articulate the purpose and significance of peer review in the context of visual research, including its role in enhancing academic rigor and fostering collaborative learning.
2. **Evaluate Visual Research Projects**: Students will develop the skills to critically assess visual research projects by applying established criteria for quality, originality, and relevance, ensuring constructive and objective feedback.
3. **Provide Constructive Feedback**: Students will learn techniques for delivering effective and respectful feedback that promotes growth and improvement in their peers' work, focusing on both strengths and areas for development.
4. **Incorporate Feedback into Research**: Students will demonstrate the ability to integrate feedback received from peers into their visual research projects, illustrating an iterative approach to refining their work based on constructive critique.
5. **Facilitate Peer Review Sessions**: Students will practice organizing and leading peer review sessions, employing strategies that encourage open dialogue, enhance participation, and foster a positive learning environment.
6. **Reflect on Personal Growth**: Students will engage in reflective practices to evaluate their own contributions to peer review processes, identifying personal strengths and areas for improvement in giving and receiving feedback.
7. **Explore Ethical Considerations**: Students will understand the ethical dimensions of peer review in visual research, including issues of confidentiality, intellectual property, and the responsibilities of peer reviewers.
8. **Develop Communication Skills**: Students will enhance their verbal and written communication skills, enabling them to articulate their critiques clearly and persuasively, both in formal presentations and written feedback.
9. **Utilize Digital Tools for Feedback**: Students will become proficient in using various digital platforms and tools to facilitate peer review and feedback processes, enhancing collaboration and accessibility in visual research.
10. **Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement**: Students will cultivate an appreciation for ongoing learning and improvement through peer feedback, recognizing its value in both academic and professional contexts within the visual research field.
Quiz Questions
Sure! Here are five multiple-choice questions about peer review and feedback in graduate visual research, along with their answers:
### Question 1:
What is the primary purpose of peer review in graduate visual research?
A) To ensure originality of the visual content
B) To validate the research methodology and findings
C) To improve the aesthetic quality of visual materials
D) To increase the number of citations
**Answer:** B) To validate the research methodology and findings
---
### Question 2:
Which of the following is a common benefit of receiving feedback during the peer review process?
A) It guarantees publication in a journal
B) It helps identify strengths and weaknesses in the research
C) It eliminates the need for revisions
D) It provides a platform for personal promotion
**Answer:** B) It helps identify strengths and weaknesses in the research
---
### Question 3:
In the context of visual research, which aspect is most important for reviewers to focus on?
A) The technical quality of the visuals
B) The relevance of the visuals to the research question
C) The reviewer's personal preferences for art
D) Both A and B
**Answer:** D) Both A and B
---
### Question 4:
How can constructive feedback improve the quality of visual research?
A) By providing a platform for debate among peers
B) By highlighting areas for improvement and suggesting solutions
C) By discouraging collaboration among researchers
D) By focusing solely on the visual appeal of the work
**Answer:** B) By highlighting areas for improvement and suggesting solutions
---
### Question 5:
What is a common challenge faced by researchers when receiving peer feedback on visual work?
A) The feedback is always positive
B) The feedback may be subjective and vary by reviewer
C) The feedback process is usually very quick
D) Reviewers often have no expertise in visual research
**Answer:** B) The feedback may be subjective and vary by reviewer
---
Feel free to use or adapt these questions for your needs!