AI Conversation
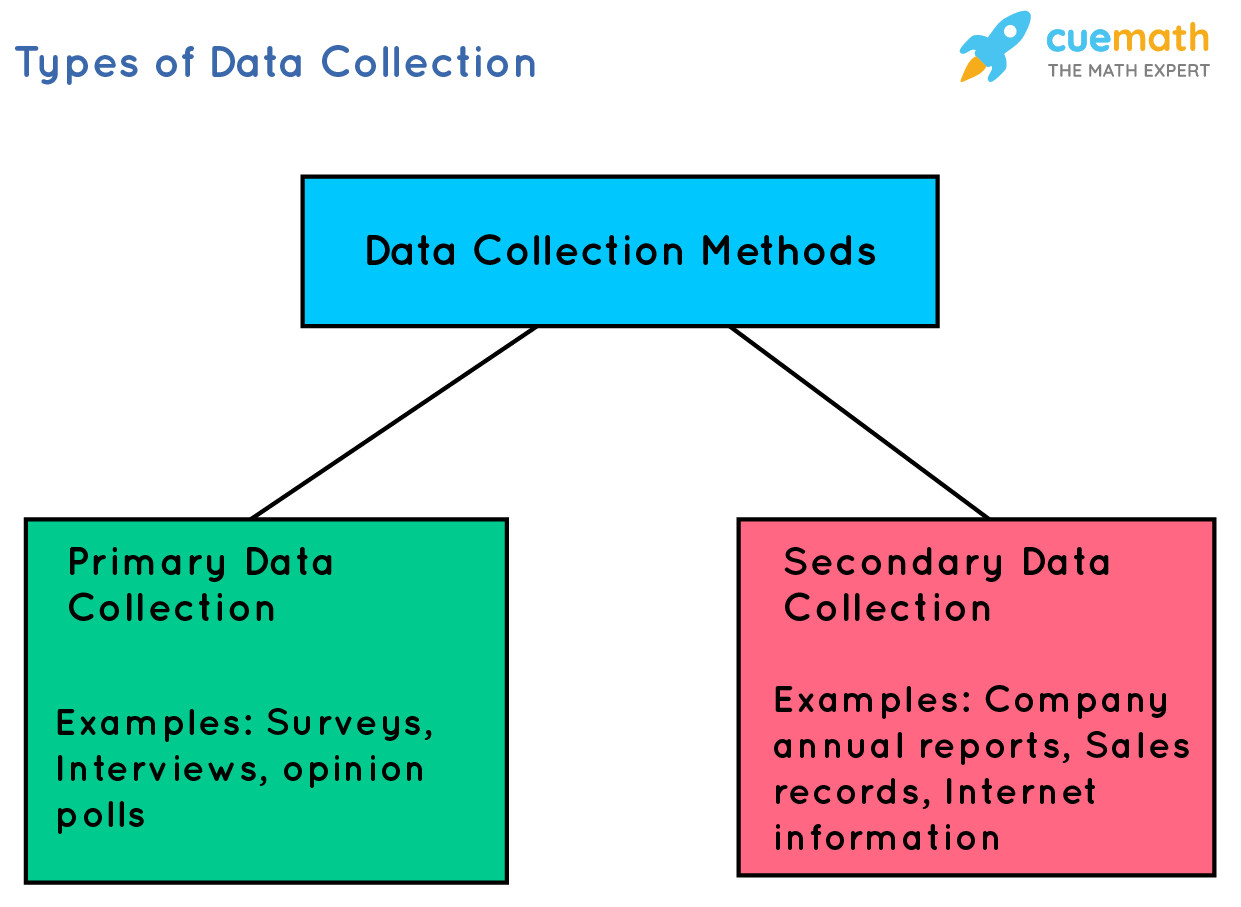
Data Collection Techniques
Crowdsourcing is a popular data collection technique where large groups of people contribute information or insights, often via the internet, enabling the gathering of diverse and extensive datasets quickly and cost-effectively.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q17s84ADGfA
surveys
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9cuOyAR-Y9I
Surveys are a data collection technique involving structured questionnaires to gather information from a target population. They can be conducted via various modes, such as online, telephone, or face-to-face. Surveys are efficient for collecting quantitative data, enabling researchers to analyze trends, opinions, and behaviors across large groups.
case studies

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kynoEFQNEq8
Case studies in data collection involve in-depth analysis of specific instances or entities to gather detailed insights. They utilize qualitative and quantitative methods, such as interviews, observations, and document reviews, to explore complex issues. This approach provides comprehensive understanding, contextual depth, and real-world applicability, enhancing data richness and validity.
online tracking
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wefD2N-GWUo
Online tracking involves collecting data on users' activities across websites and apps. Techniques include cookies, device fingerprinting, and tracking pixels. This data helps companies personalize content, target ads, and analyze user behavior. While enhancing user experience, it raises privacy concerns, prompting discussions on data protection and regulatory measures.
interviews
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7DOJ5VGpWAs
Interviews are a qualitative data collection technique involving direct, structured or unstructured conversations to gather in-depth insights. They enable researchers to explore participants' perspectives, experiences, and motivations. Interviews can be conducted face-to-face, by phone, or online, offering flexibility and rich, detailed data for analysis.
focus groups

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=65zsyaQsQBw
Focus groups are a qualitative data collection technique involving guided discussions with a small group of participants. They provide insights into attitudes, perceptions, and experiences. Facilitated by a moderator, focus groups encourage interaction and diverse viewpoints, making them valuable for exploring complex issues and generating in-depth understanding of research topics.
observations
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RVDjBPSXzS8

Observations in data collection involve systematically recording behaviors, events, or conditions as they occur. This technique provides real-time, contextual insights and is often used in qualitative research. It can be structured or unstructured, allowing researchers to capture detailed, nuanced data that might be missed through other methods like surveys or interviews.
experiments
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DcxL7hhVruk
Experiments in data collection involve controlled environments to test hypotheses, manipulating variables to observe effects. They ensure reliability and validity through randomization and replication. This method provides causal insights, enabling researchers to establish cause-and-effect relationships, crucial for scientific advancements and decision-making across various fields.

document analysis
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G8qzSIo3UHU
Document analysis is a qualitative data collection technique involving the systematic examination of documents to extract meaningful information. It helps researchers understand context, identify patterns, and gather insights from existing records, reports, or texts, complementing other methods like interviews and surveys to provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject.
AI Report
Essay
### Data Collection Techniques
Data collection is a critical aspect of research that involves gathering information to answer specific questions, test hypotheses, or evaluate outcomes. The choice of data collection technique significantly influences the quality and reliability of research findings. Various techniques exist, each with its advantages and limitations. This essay will discuss several common data collection techniques, including surveys, interviews, observations, experiments, and secondary data analysis, highlighting their applications and effectiveness in different research contexts.
Surveys are one of the most widely used data collection techniques, particularly in social sciences. They involve the systematic gathering of information from a predefined group of respondents through questionnaires or online forms. Surveys can be conducted in various formats, including face-to-face, telephone, or digital platforms (Creswell, 2014). They are valued for their ability to collect data from a large sample size, which enhances the generalizability of the findings. However, surveys can be susceptible to biases, such as self-reporting bias, where respondents may provide socially desirable answers rather than truthful ones (Fowler, 2014).
Interviews are another effective data collection method that allows for more in-depth exploration of participants' thoughts and experiences. This technique can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured, depending on the research objectives (Kvale & Brinkmann, 2009). Interviews enable researchers to probe deeper into responses, facilitating a more nuanced understanding of complex issues. However, they can be time-consuming and may involve challenges related to interviewer bias, where the interviewer’s beliefs and attitudes may inadvertently influence the responses of participants (McGrath, 2016).
Observations involve systematically watching and recording behaviors or events in their natural setting. This technique is particularly useful in qualitative research, where understanding context is essential. Observational studies can be either participant or non-participant, depending on whether the researcher engages with the subjects being studied (Angrosino, 2007). While observations can provide rich, contextual data, they also come with limitations, such as the potential for observer bias and the challenge of generalizing findings to a broader population.
Experiments are a quantitative research method that involves manipulating one or more independent variables to observe their effect on a dependent variable. This technique is highly regarded for its ability to establish cause-and-effect relationships (Field, 2013). Experiments can be conducted in controlled settings or in the field, allowing researchers to maintain control over extraneous variables. However, the artificial nature of laboratory experiments may limit their external validity, and ethical considerations often restrict the types of experiments that can be conducted (Creswell, 2014).
Finally, secondary data analysis involves using existing data collected by other researchers or organizations. This technique can save time and resources while providing access to large datasets that may not be feasible to collect independently (Boslaugh, 2007). Secondary data analysis is particularly useful in longitudinal studies where data over time can reveal trends and patterns. However, researchers must be cautious about the quality and relevance of the data, as it may not align perfectly with their specific research questions.
In conclusion, data collection techniques play a pivotal role in the research process, each contributing unique strengths and weaknesses. Surveys, interviews, observations, experiments, and secondary data analysis offer various ways to gather information, and the choice of technique depends on the research objectives and context. By carefully selecting appropriate data collection methods, researchers can enhance the reliability and validity of their findings, ultimately contributing to the advancement of knowledge in their respective fields.
### References
Angrosino, M. (2007). *Doing Ethnographic and Observational Research*. Sage Publications.
Boslaugh, S. (2007). *Secondary Data Sources for Public Health: A Practical Guide*. Cambridge University Press.
Creswell, J. W. (2014). *Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches* (4th ed.). Sage Publications.
Field, A. (2013). *Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics* (4th ed.). Sage Publications.
Fowler, F. J. (2014). *Survey Research Methods* (5th ed.). Sage Publications.
Kvale, S., & Brinkmann, S. (2009). *InterViews: Learning the Craft of Qualitative Research Interviewing* (2nd ed.). Sage Publications.
McGrath, J. (2016). *Research Methods: A Practical Guide for the Social Sciences*. Routledge.
Lesson Plan
### Lesson Plan: Data Collection Techniques
**Grade Level:** Technical Vocational Students
**Subject:** Data Collection Techniques
**Duration:** 2 hours
**Materials Needed:**
- Whiteboard and markers
- Projector and screen
- Handouts on data collection techniques
- Examples of data collection tools (surveys, software, etc.)
- Computers or tablets for students (if available)
- Internet access (optional)
---
#### **Lesson Objectives:**
By the end of this lesson, students will be able to:
1. Identify and describe various data collection techniques.
2. Understand how different data collection methods work.
3. Discuss the maintenance and ethical considerations of data collection.
4. Design a simple data collection plan for a project.
---
### **Lesson Outline**
#### **Introduction (15 minutes)**
1. **Warm-Up Activity:**
- Ask students, "What is data, and why is it important in your field?"
- Facilitate a brief discussion to gauge prior knowledge.
2. **Definition and Importance of Data Collection:**
- Define data collection.
- Explain why data collection is critical in technical and vocational fields (e.g., project planning, quality control, market research).
#### **Main Content (60 minutes)**
1. **Overview of Data Collection Techniques (30 minutes):**
- Present different data collection methods:
- **Surveys and Questionnaires:** Explain how to create effective questions.
- **Interviews:** Discuss types of interviews (structured, semi-structured, unstructured).
- **Observations:** Describe different observational methods (participant vs. non-participant).
- **Experiments:** Discuss controlled experimentation and its data collection.
- **Existing Data:** Explain how to use existing datasets.
- Use examples and visual aids to illustrate each technique.
2. **How Data Collection Techniques Work (15 minutes):**
- Discuss the process of data collection:
- Planning: Define objectives and select the appropriate method.
- Data Gathering: Techniques and tools used.
- Data Entry: Importance of accuracy and reliability.
- Demonstrate how to use one data collection tool (e.g., Google Forms for surveys).
3. **Maintenance of Data Collection (15 minutes):**
- Discuss the importance of data maintenance:
- **Data Quality:** Ensuring accuracy, consistency, and reliability.
- **Data Management:** Organizing and storing data securely.
- **Ethical Considerations:** Discuss issues of privacy, consent, and data security.
- Provide tips for maintaining data integrity.
#### **Activity (30 minutes)**
1. **Group Activity: Design a Data Collection Plan**
- Divide students into small groups and assign them a project scenario (e.g., conducting a survey for a new vocational program).
- Each group will:
- Choose a data collection technique.
- Develop a set of 5-10 questions (if applicable).
- Plan how they will collect, manage, and maintain the data.
- Groups will present their plans briefly to the class.
#### **Conclusion (15 minutes)**
1. **Recap Key Points:**
- Review the techniques covered and their importance in vocational settings.
- Highlight the significance of ethical data collection.
2. **Q&A Session:**
- Open the floor for any questions or clarifications.
#### **Assessment:**
- Collect the group data collection plans and provide feedback.
- Optional: A short quiz on data collection techniques and their applications.
#### **Homework/Extension Activity:**
- Assign students to research a specific data collection technique and prepare a one-page report on its applications in their chosen vocational field.
---
### **Notes for Instructors:**
- Adapt the lesson based on the technical background of the students.
- Encourage participation and create a supportive environment for discussions.
- Be prepared to provide additional resources for students who may want to learn more about advanced data collection tools and techniques.
Class Syllabus Outline
# Syllabus for Data Collection Techniques
## Course Information
- **Course Title**: Data Collection Techniques
- **Course Code**: DCT 101
- **Credits**: 3
- **Semester**: Fall 2023
- **Instructor**: Dr. Jane Smith
- **Email**: jane.smith@example.com
- **Office Hours**: Mondays 2:00 PM - 4:00 PM, Wednesdays 10:00 AM - 12:00 PM
## Course Description
This course provides an overview of various data collection techniques used in research and professional practice. Students will explore qualitative and quantitative methods, understand the strengths and weaknesses of each technique, and learn how to select appropriate methods for different research scenarios. The course will also cover ethical considerations, data management, and analysis strategies.
## Course Objectives
By the end of this course, students will be able to:
1. Identify and describe different data collection techniques, including surveys, interviews, observations, and experiments.
2. Evaluate the appropriateness of various data collection methods for specific research questions.
3. Design a data collection plan that incorporates ethical considerations.
4. Analyze and interpret data collected through different techniques.
5. Communicate findings effectively, using appropriate data presentation methods.
## Required Texts
- Creswell, J. W. (2014). *Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches* (4th ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Fink, A. (2013). *How to Conduct Surveys: A Step-by-Step Guide* (5th ed.). SAGE Publications.
## Course Schedule
### Week 1: Introduction to Data Collection
- Overview of data collection
- Importance of data in research
### Week 2: Qualitative vs. Quantitative Data
- Definitions and differences
- When to use each type
### Week 3: Surveys and Questionnaires
- Designing effective surveys
- Types of questions: open-ended vs. closed-ended
### Week 4: Interviews
- Structured, semi-structured, and unstructured interviews
- Best practices for conducting interviews
### Week 5: Observational Techniques
- Types of observation (participant vs. non-participant)
- Field notes and recording observations
### Week 6: Experimental Methods
- Designing experiments and control groups
- Ethical considerations in experimentation
### Week 7: Focus Groups
- Conducting and analyzing focus groups
- Group dynamics and moderation techniques
### Week 8: Mixed Methods Research
- Integrating qualitative and quantitative approaches
- Case studies and applications
### Week 9: Ethical Considerations in Data Collection
- Informed consent
- Confidentiality and data protection
### Week 10: Data Management
- Organizing and storing data
- Software tools for data collection and management
### Week 11: Data Analysis Techniques
- Analyzing qualitative data (coding, thematic analysis)
- Analyzing quantitative data (statistical methods)
### Week 12: Communicating Findings
- Writing research reports
- Data visualization techniques
### Week 13: Student Presentations
- Presentation of final projects
- Peer feedback and discussion
### Week 14: Course Review and Final Exam Preparation
- Review key concepts and techniques
- Discuss exam format and expectations
## Assessment and Grading
- Participation and Attendance: 10%
- Weekly Quizzes: 20%
- Midterm Exam: 20%
- Final Project: 30%
- Final Exam: 20%
## Policies
- **Attendance**: Regular attendance is expected. More than two unexcused absences may affect your grade.
- **Late Assignments**: Late submissions will incur a penalty of 10% per day unless prior arrangements are made with the instructor.
- **Academic Integrity**: Cheating and plagiarism will not be tolerated. All work must be original.
## Additional Resources
- University Writing Center: [website link]
- Library Resources: [website link]
- Online Data Collection Tools: SurveyMonkey, Google Forms, Qualtrics
## Conclusion
This course aims to equip students with the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively collect and analyze data in various contexts. Active participation and engagement in discussions will enhance the learning experience.
---
Feel free to adjust any sections of this syllabus to better fit the specific needs of your course or institution.
Learning Objectives
### Learning Objectives for Data Collection Techniques Course
1. **Understand Data Collection Principles**:
- Define key concepts related to data collection, including types of data, data sources, and the importance of accurate data collection in technical fields.
2. **Identify Data Collection Methods**:
- Compare and contrast various data collection methods (quantitative vs. qualitative), including surveys, interviews, observations, and experiments, and determine their appropriate applications in vocational contexts.
3. **Design Data Collection Instruments**:
- Develop effective data collection instruments (e.g., questionnaires, interview guides) that align with specific research objectives and ensure reliability and validity.
4. **Implement Data Collection Procedures**:
- Execute data collection processes following established protocols, ensuring ethical considerations and adherence to best practices in data gathering.
5. **Utilize Technology in Data Collection**:
- Explore and apply technological tools and software (e.g., online survey platforms, data management systems) to streamline data collection and enhance accuracy.
6. **Analyze Collected Data**:
- Employ basic statistical techniques and data analysis tools to interpret collected data, drawing meaningful conclusions relevant to technical vocational applications.
7. **Present Data Findings**:
- Communicate data findings effectively through written reports and oral presentations, utilizing appropriate visual aids (e.g., charts, graphs) to support conclusions.
8. **Evaluate Data Quality**:
- Assess the quality and integrity of collected data, identifying potential biases, errors, and limitations that may affect the results and recommendations.
9. **Apply Ethical Standards**:
- Recognize and apply ethical standards and legal requirements related to data collection, including informed consent, confidentiality, and data protection.
10. **Reflect on Data Collection Experiences**:
- Critically reflect on personal experiences with data collection in vocational settings, identifying strengths, areas for improvement, and the impact of data-driven decisions in technical fields.
By the end of this course, students will be equipped with the foundational skills and knowledge necessary to effectively collect, analyze, and present data relevant to their technical vocational careers.
Quiz Questions
Sure! Here are five multiple-choice questions about data collection techniques, along with their correct answers:
### Question 1:
Which of the following is a qualitative data collection technique?
A) Surveys with closed-ended questions
B) Structured interviews
C) Observational studies
D) Experiments
**Answer:** C) Observational studies
---
### Question 2:
What is the primary purpose of using a survey in data collection?
A) To manipulate variables
B) To gather quantitative data from a large number of respondents
C) To observe behaviors in real-time
D) To conduct in-depth case studies
**Answer:** B) To gather quantitative data from a large number of respondents
---
### Question 3:
Which of the following data collection techniques involves the researcher interacting directly with participants?
A) Secondary data analysis
B) Focus groups
C) Literature review
D) Content analysis
**Answer:** B) Focus groups
---
### Question 4:
In which scenario would observational data collection be most appropriate?
A) When measuring customer satisfaction through a questionnaire
B) When assessing the effectiveness of a new marketing strategy
C) When studying the behavior of consumers in a retail environment
D) When analyzing historical sales data
**Answer:** C) When studying the behavior of consumers in a retail environment
---
### Question 5:
What is a disadvantage of using online surveys for data collection?
A) They can reach a wide audience quickly.
B) They are cost-effective compared to face-to-face interviews.
C) Respondents may not provide thoughtful answers due to anonymity.
D) They allow for easy data analysis.
**Answer:** C) Respondents may not provide thoughtful answers due to anonymity.
---
Feel free to use or adapt these questions as needed!