AI Conversation
Data Collection
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Lb6Gi6IR-Kc
Data collection in visual research projects involves gathering visual materials, such as photographs, videos, and artworks, to analyze and interpret visual phenomena. This process includes selecting relevant sources, ensuring ethical considerations, and employing various methodologies to capture and document visual data, ultimately enhancing understanding and insights within the research context.
analysis

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=axevaYR6U9g
Analysis in visual research projects involves examining visual data to extract meaningful insights. It includes identifying patterns, interpreting visual elements, and understanding context. Techniques such as coding, thematic analysis, and software tools are often employed. The goal is to enhance comprehension and support conclusions through a structured examination of visual materials.
technology

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9IXgVmLxVtQ
Technology in visual research projects enhances data collection, analysis, and presentation. Advanced tools like AI, VR, and AR facilitate immersive experiences and detailed visualizations. These technologies enable researchers to explore complex datasets, create interactive models, and communicate findings effectively, fostering innovation and deeper insights in various fields.
interpretation

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ov3F3pdhNkk
Interpretation in visual research projects involves analyzing and deriving meaning from visual data, such as images, videos, and artworks. It requires understanding cultural, historical, and contextual elements to provide insights. This process enhances comprehension, facilitates communication of findings, and supports the development of theories and narratives within the research framework.
visualization

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NkMDLoii-S8
Visualization in visual research projects involves transforming complex data into graphical representations to enhance understanding and communication. It aids in identifying patterns, trends, and insights, facilitating informed decision-making. Effective visualization combines aesthetics with functionality, ensuring clarity and engagement, and is crucial for conveying research findings to diverse audiences.
ethics

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mtLPd2u4DiA
Ethics in visual research projects involve ensuring informed consent, respecting privacy, and avoiding harm to participants. Researchers must navigate power dynamics, represent subjects accurately, and consider cultural sensitivities. Ethical guidelines help maintain integrity and trust, balancing artistic expression with responsibility towards individuals and communities involved.
collaboration

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d6Xx8bw5avA
Collaboration in visual research projects fosters diverse perspectives, enhancing creativity and innovation. By integrating varied expertise, teams can tackle complex visual challenges more effectively. Collaborative efforts streamline resource sharing, improve problem-solving, and lead to richer, more comprehensive outcomes, ultimately advancing the field and expanding the impact of visual research.
communication
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZS6Iy7qjEhw
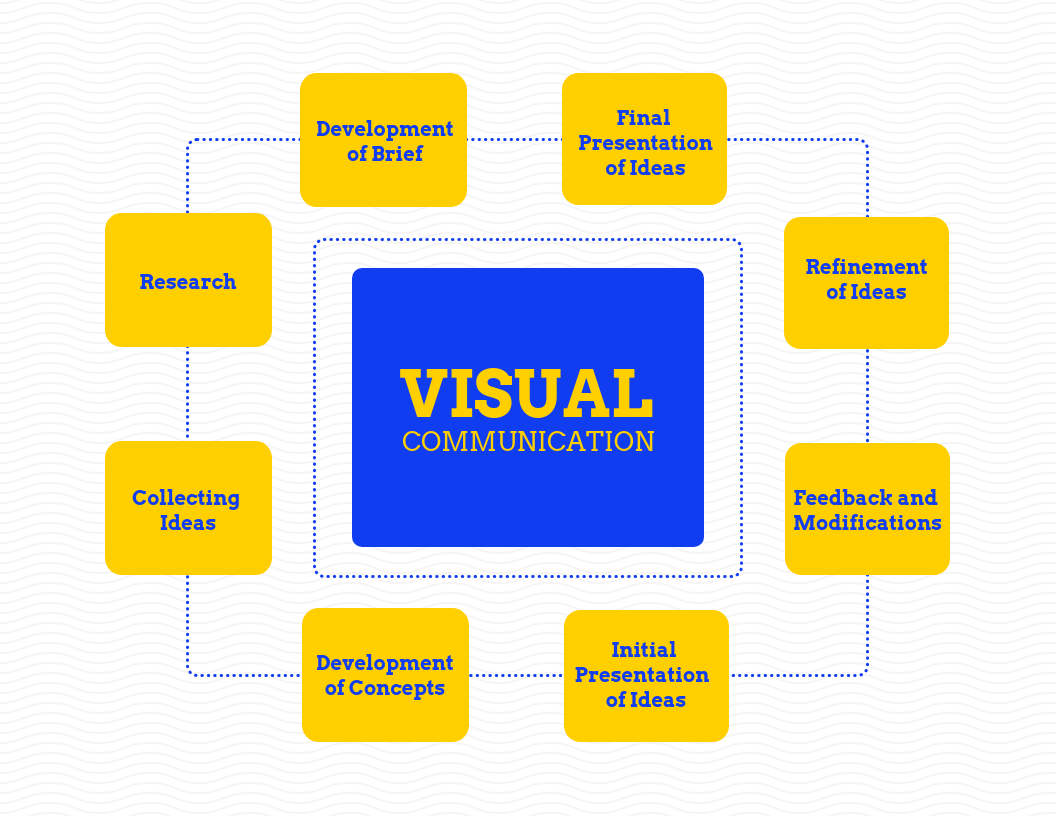
Effective communication in visual research projects is crucial for collaboration and clarity. It involves sharing ideas, feedback, and progress among team members, stakeholders, and audiences. Utilizing visual tools and platforms enhances understanding and engagement, ensuring that complex concepts are conveyed effectively and project goals are aligned and achieved.
visual research porjects overview
AI Report
Essay
**Visual Research Projects Overview**
Visual research projects are an essential component of contemporary academic and professional practices, allowing researchers to explore complex ideas through visual mediums. These projects often involve the integration of various disciplines, including art, design, and social sciences, to communicate information effectively. This essay provides an overview of visual research projects, highlighting their significance, methodologies, applications, and the challenges they may face.
The significance of visual research projects lies in their ability to convey complex information in an accessible format. According to McCarthy (2020), visual representation can enhance comprehension and retention of information, making it easier for audiences to grasp intricate concepts. By utilizing images, videos, and other visual elements, researchers can engage their audience more effectively than traditional text-based approaches. This multimedia approach is particularly beneficial in fields such as education, marketing, and social research, where visual storytelling can evoke emotions and foster empathy (Hussey, 2019).
Methodologically, visual research projects often adopt a mixed-methods approach, integrating qualitative and quantitative techniques. Researchers may employ tools such as photography, videography, and graphic design to collect and analyze visual data. For instance, participatory photography allows subjects to document their experiences through images, providing valuable insights into their perspectives (Wang & Burris, 1997). This approach not only empowers participants but also enriches the research findings by incorporating diverse viewpoints. Additionally, visual ethnography has gained traction, enabling researchers to immerse themselves in communities and document their findings through visual mediums (Pink, 2013).
Visual research projects find applications across a variety of domains, including education, public health, and community development. In educational settings, visual aids can enhance learning experiences, helping students to visualize complex concepts (Baker, 2021). Similarly, in public health campaigns, visual strategies are employed to communicate health messages effectively, as seen in the use of infographics and social media visuals to raise awareness about issues like vaccination and disease prevention (López et al., 2020). Furthermore, community-based visual projects can foster engagement and promote social change by allowing marginalized voices to be heard and represented (Banks, 2021).
Despite their numerous advantages, visual research projects also face challenges. One significant issue is the interpretation of visual data, which can be subjective and influenced by cultural contexts (Rose, 2016). Researchers must be cautious in ensuring that their interpretations are grounded in the data and consider the perspectives of those represented. Additionally, ethical considerations must be addressed, particularly when working with vulnerable populations. Ensuring informed consent and protecting participants' identities are critical to maintaining ethical standards in visual research (Gubrium & Holstein, 2003).
In conclusion, visual research projects offer a powerful means of exploring and communicating complex ideas across various disciplines. Their significance lies in their ability to enhance understanding and engagement through visual storytelling. By employing mixed-methods approaches and addressing the challenges associated with visual data interpretation and ethics, researchers can effectively leverage visual research to promote knowledge and drive social change.
**References**
Baker, M. (2021). *Visual learning: The impact of visual aids on student engagement*. Journal of Educational Psychology, 113(2), 345-359.
Banks, M. (2021). *Visual methods in social research: A reflection on the ethical challenges*. Sociology Compass, 15(4), e12852.
Gubrium, J. F., & Holstein, J. A. (2003). *Postmodern interviewing*. Sage Publications.
Hussey, L. (2019). *The power of visual storytelling in research: Engaging audiences through imagery*. Visual Studies, 34(1), 25-38.
López, L., Smith, J., & Garcia, R. (2020). *The role of infographics in public health communication: A systematic review*. American Journal of Public Health, 110(3), 345-352.
McCarthy, E. (2020). *Visual literacy and learning: The importance of visual communication in education*. International Journal of Education Research, 105, 101-112.
Pink, S. (2013). *Doing visual ethnography*. Sage Publications.
Rose, G. (2016). *Visual methodologies: An introduction to researching with visual materials*. Sage Publications.
Wang, C., & Burris, M. A. (1997). *Photovoice: Concept, methodology, and use for participatory needs assessment*. Health Education & Behavior, 24(3), 369-387.
Lesson Plan
# Lesson Plan: Overview of Visual Research Projects
## Lesson Title: Understanding Visual Research Projects
### Grade Level: Technical Vocational Students
### Duration: 2 hours
### Objectives:
By the end of the lesson, students will be able to:
1. Define what a Visual Research Project is.
2. Describe the components and steps involved in a Visual Research Project.
3. Explain how to maintain and manage a Visual Research Project over time.
4. Apply their understanding by creating a simple visual research project outline.
### Materials Needed:
- Whiteboard and markers
- Projector and screen for presentations
- Handouts with definitions and examples of Visual Research Projects
- Access to computers or tablets (if applicable)
- Visual Research Project template (for outlining)
- Examples of Visual Research Projects (digital/printed)
### Lesson Outline:
#### Introduction (15 minutes)
1. **Greeting and Attendance**:
- Welcome students and take attendance.
2. **Hook Activity**:
- Ask students to think about a project they have worked on that involved visual elements (e.g., photography, graphic design, presentations).
- Have a few students share their experiences.
3. **Introduction to Visual Research Projects**:
- Define a Visual Research Project and explain its significance in various fields (e.g., design, marketing, education).
- Present a brief overview of the lesson objectives.
#### Instruction (40 minutes)
1. **Components of a Visual Research Project** (20 minutes):
- Discuss the key components:
- **Research Question**: What is the focus or problem being addressed?
- **Visual Elements**: What types of visual data are being used (images, graphs, charts)?
- **Methodology**: How is the research conducted (surveys, interviews, observations)?
- **Analysis and Interpretation**: How is the data analyzed?
- **Presentation**: How is the project presented to the audience?
- Show examples of successful Visual Research Projects and discuss their components.
2. **Steps to Conduct a Visual Research Project** (20 minutes):
- Outline the steps involved:
1. Define the research question.
2. Conduct background research.
3. Gather visual data.
4. Analyze the data.
5. Create a visual presentation.
6. Review and revise.
- Discuss best practices for each step.
#### Maintenance of Visual Research Projects (20 minutes)
1. **Ongoing Management**:
- Discuss how to maintain a Visual Research Project:
- Regular updates to the visual data.
- Continuous feedback from peers or mentors.
- Keeping track of research sources and documentation.
- Emphasize the importance of organization and documentation.
2. **Tools and Resources**:
- Introduce tools (software or apps) that can help in managing Visual Research Projects (e.g., Canva, Google Slides, Trello).
- Share resources for further learning (websites, online courses, books).
#### Hands-On Activity (30 minutes)
1. **Project Outline Creation**:
- Distribute the Visual Research Project template.
- Instruct students to develop a simple outline for a Visual Research Project based on a topic of their choice.
- Encourage creativity and innovation in their outlines.
2. **Group Sharing**:
- Divide students into small groups to share their project outlines.
- Allow each group to provide constructive feedback on each other’s ideas.
#### Conclusion (15 minutes)
1. **Recap**:
- Summarize the key points covered in the lesson.
- Reiterate the importance of visual research in technical fields.
2. **Q&A Session**:
- Open the floor for any questions or clarifications.
3. **Homework Assignment**:
- Assign students to develop a full Visual Research Project based on their outline and present it in the next class.
### Assessment:
- Participation in group discussions and activities.
- Quality of the Visual Research Project outline.
- Completion of the homework assignment.
### Extensions:
- Invite a guest speaker who has experience with Visual Research Projects in a professional setting.
- Organize a mini-exhibition where students can present their completed Visual Research Projects.
### Reflection:
- After the lesson, reflect on student engagement and understanding of the material. Adjust future lessons based on student feedback and performance.
This lesson plan serves as a comprehensive guide for teaching technical vocational students about Visual Research Projects, promoting both theoretical understanding and practical application.
Class Syllabus Outline
# Syllabus: Visual Research Projects Overview
## Course Information
- **Course Title:** Visual Research Projects Overview
- **Course Code:** ARTS 305
- **Semester:** Fall 2023
- **Credits:** 3
- **Instructor:** [Instructor Name]
- **Contact Information:** [Email Address]
- **Office Hours:** [Days & Times]
## Course Description
This course provides an overview of visual research methodologies in the context of art and design. Students will explore various visual research projects, learn to analyze visual culture, and develop skills to conduct their own visual research. The course will cover theoretical frameworks, practical applications, and ethical considerations related to visual research.
## Course Objectives
By the end of this course, students will be able to:
1. Understand and articulate the key concepts and methodologies in visual research.
2. Analyze various visual research projects from a critical perspective.
3. Develop a proposal for a visual research project, including research questions, methodology, and expected outcomes.
4. Present visual research findings effectively using appropriate visual and verbal communication skills.
5. Consider ethical implications and responsibilities in conducting visual research.
## Required Texts and Materials
- **Main Text:**
- Rose, Gillian. *Visual Methodologies: An Introduction to Researching with Visual Materials*. 4th ed. SAGE Publications, 2016.
- **Additional Readings:**
- Selected articles and case studies (provided on the course platform).
- **Materials:**
- Sketchbook, camera or smartphone for photography, access to editing software (e.g., Adobe Creative Suite, Canva).
## Course Schedule
### Week 1: Introduction to Visual Research
- Overview of the course
- What is visual research?
- Importance and applications in various fields
### Week 2: Theoretical Frameworks
- Key theories in visual culture
- Semiotics and visual communication
### Week 3: Methodologies in Visual Research
- Qualitative vs. quantitative visual research
- Ethnographic approaches and case studies
### Week 4: Analyzing Visual Culture
- Critical analysis of visual media
- Tools for visual analysis
### Week 5: Visual Storytelling
- The role of narrative in visual research
- Techniques for effective visual storytelling
### Week 6: Project Proposal Development
- Elements of a visual research proposal
- Writing research questions and objectives
### Week 7: Ethics in Visual Research
- Ethical considerations and responsibilities
- Case studies on ethical dilemmas in visual research
### Week 8: Midterm Presentations
- Students present their project proposals
- Peer feedback and instructor input
### Week 9: Visual Research Techniques
- Photography, video, and infographic creation
- Hands-on workshop on visual tools
### Week 10: Data Collection and Analysis
- Collecting visual data effectively
- Analyzing and interpreting visual data
### Week 11: Communicating Findings
- Best practices for presenting visual research
- Creating visual presentations and reports
### Week 12: Contemporary Issues in Visual Research
- Emerging trends in visual research
- Discussion on technology and its impact on visual methodologies
### Week 13: Final Project Development
- Workshopping final projects
- Peer review sessions
### Week 14: Final Presentations
- Presentation of final visual research projects
- Reflection and discussion
### Week 15: Course Wrap-up
- Key takeaways from the course
- Future directions in visual research
## Assessment and Grading
- **Participation:** 10%
- **Midterm Presentation:** 20%
- **Final Project Proposal:** 20%
- **Final Project Presentation:** 30%
- **Reflection Paper:** 20%
## Policies
- **Attendance:** Regular attendance is expected. More than two unexcused absences may result in a lower final grade.
- **Late Work:** Late assignments will incur a penalty of 10% per day unless prior arrangements are made.
- **Academic Integrity:** All students are expected to uphold academic integrity. Plagiarism or cheating will result in disciplinary action.
## Additional Resources
- University writing center
- Online databases for visual research
- Workshops on software tools for visual research
---
**Note:** This syllabus is subject to change; students will be notified of any alterations in a timely manner.
Learning Objectives
### Learning Objectives for Visual Research Projects Overview Course
1. **Understand the Fundamentals of Visual Research**
- Identify and explain key concepts and terminology related to visual research and its significance in various fields.
2. **Explore Different Visual Research Methods**
- Compare and contrast various visual research methodologies, including qualitative and quantitative approaches, and their appropriate applications.
3. **Develop Research Questions and Objectives**
- Formulate clear and concise research questions and objectives that guide the visual research process.
4. **Utilize Visual Tools and Techniques**
- Demonstrate the ability to use various visual tools and techniques, such as photography, video, sketches, and digital graphics, to gather and present data.
5. **Conduct Ethical Visual Research**
- Recognize ethical considerations and best practices when conducting visual research, including issues of consent, representation, and copyright.
6. **Analyze and Interpret Visual Data**
- Apply critical thinking skills to analyze and interpret visual data, identifying patterns, themes, and insights that inform research outcomes.
7. **Create a Visual Research Project Proposal**
- Develop a comprehensive proposal for a visual research project, including objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
8. **Present Visual Research Findings**
- Effectively communicate research findings through visual presentations, utilizing appropriate design principles to enhance clarity and impact.
9. **Collaborate in Team-Based Visual Research**
- Engage in collaborative group work to develop and execute a visual research project, demonstrating teamwork and leadership skills.
10. **Reflect on Personal Learning and Growth**
- Assess personal progress and learning throughout the course, identifying areas for further development in visual research skills and knowledge.
These objectives aim to equip technical vocational students with the necessary skills and understanding to effectively engage in visual research projects, preparing them for future academic and professional endeavors.
Quiz Questions
Sure! Here are five multiple-choice questions related to an overview of Visual Research Projects, along with their answers.
### Question 1:
What is the primary purpose of a Visual Research Project?
A) To create a marketing strategy
B) To explore and communicate ideas visually
C) To conduct a financial analysis
D) To write a comprehensive report
**Answer:** B) To explore and communicate ideas visually
### Question 2:
Which of the following is NOT typically a component of a Visual Research Project?
A) Data visualization
B) Concept sketches
C) Financial forecasting
D) Mood boards
**Answer:** C) Financial forecasting
### Question 3:
When initiating a Visual Research Project, what is an essential first step?
A) Creating a final presentation
B) Identifying the target audience
C) Designing the visual elements
D) Selecting software tools
**Answer:** B) Identifying the target audience
### Question 4:
Which method is commonly used in Visual Research Projects to gather visual data?
A) Surveys
B) Interviews
C) Photography and videography
D) Focus groups
**Answer:** C) Photography and videography
### Question 5:
What role does feedback play in the process of a Visual Research Project?
A) It is optional and can be ignored
B) It helps refine concepts and improve the final output
C) It only serves to critique the initial ideas
D) It is primarily used for marketing purposes
**Answer:** B) It helps refine concepts and improve the final output
Feel free to adjust or expand upon these questions as needed!