AI Conversation
Question: I did uh within design thinking and why is it so important?
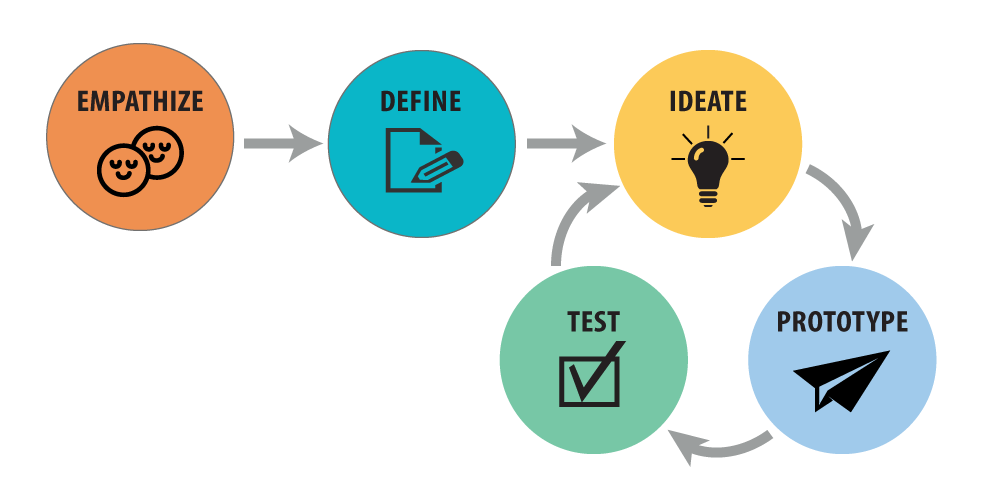
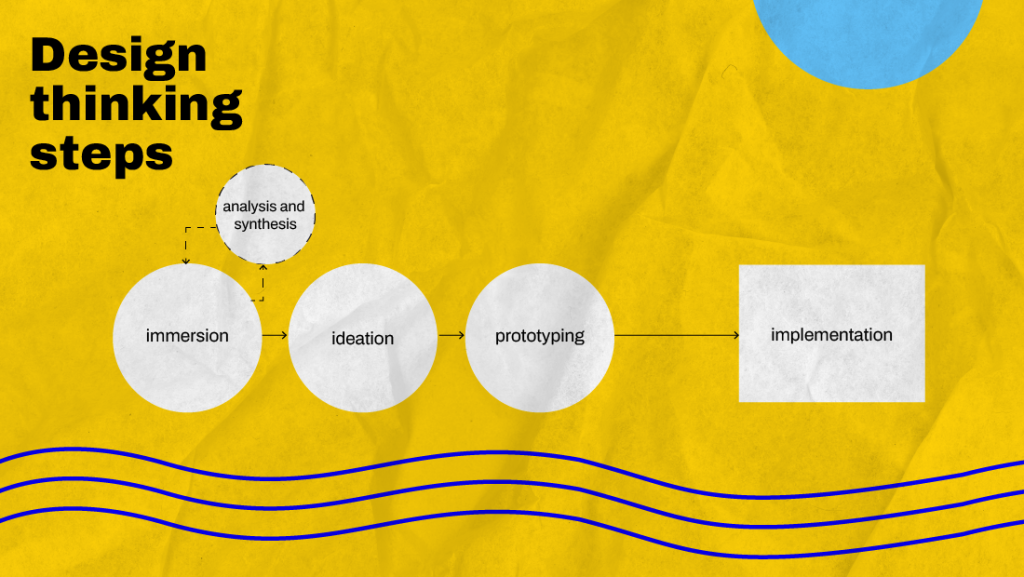
Answer: Design thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that integrates the needs of people, the possibilities of technology, and the requirements for business success. It encourages university students to tackle complex academic subjects with unparalleled clarity. SOUND: Pages of a notebook flipping softly. By fostering curiosity and inspiring learning beyond textbooks, design thinking helps students develop empathy, define problems, ideate solutions, prototype, and test them. SOUND: The gentle hum of a 3D printer starting up. This iterative process not only enhances problem-solving skills but also provides personalized learning experiences, allowing students to tailor their projects to their interests and strengths. SOUND: The click of a mouse as a student navigates design software. Incorporating design thinking into education ensures that students are better prepared for real-world challenges, making them innovative thinkers and effective problem solvers. SOUND: A soft murmur of brainstorming discussions in the background. Ultimately, design thinking is crucial because it transforms how students approach and solve problems, making learning a dynamic and engaging process.
Design thinking

Design thinking originated from the practices of designers but has been adopted by various fields, including business and education, to foster innovation and solve complex problems creatively.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_WI3B54m6SU
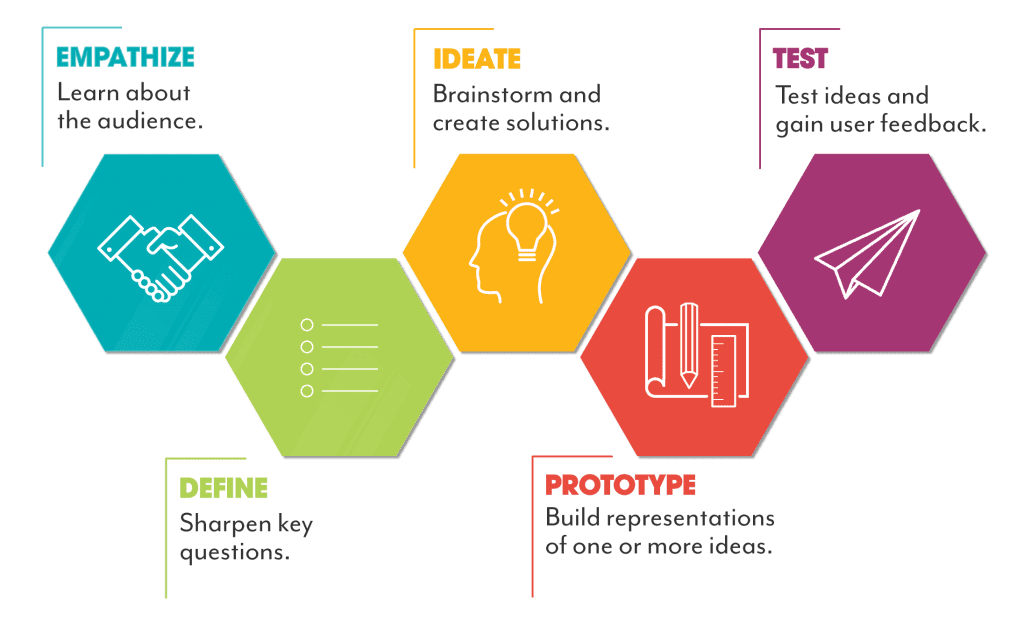
empathize

In design thinking, "empathize" involves deeply understanding users' needs, emotions, and experiences. This phase requires immersing oneself in users' environments, conducting interviews, and observing behaviors to gain insights. By fostering empathy, designers create solutions that genuinely address users' problems, leading to more effective and user-centered innovations.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q654-kmF3Pc
define
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TNAdanuvwtc
In design thinking, "Define" is the second stage where insights from the empathy phase are synthesized to articulate a clear problem statement. This stage focuses on identifying user needs and challenges, setting a foundation for ideation and solution development, ensuring the design process remains user-centered and goal-oriented.
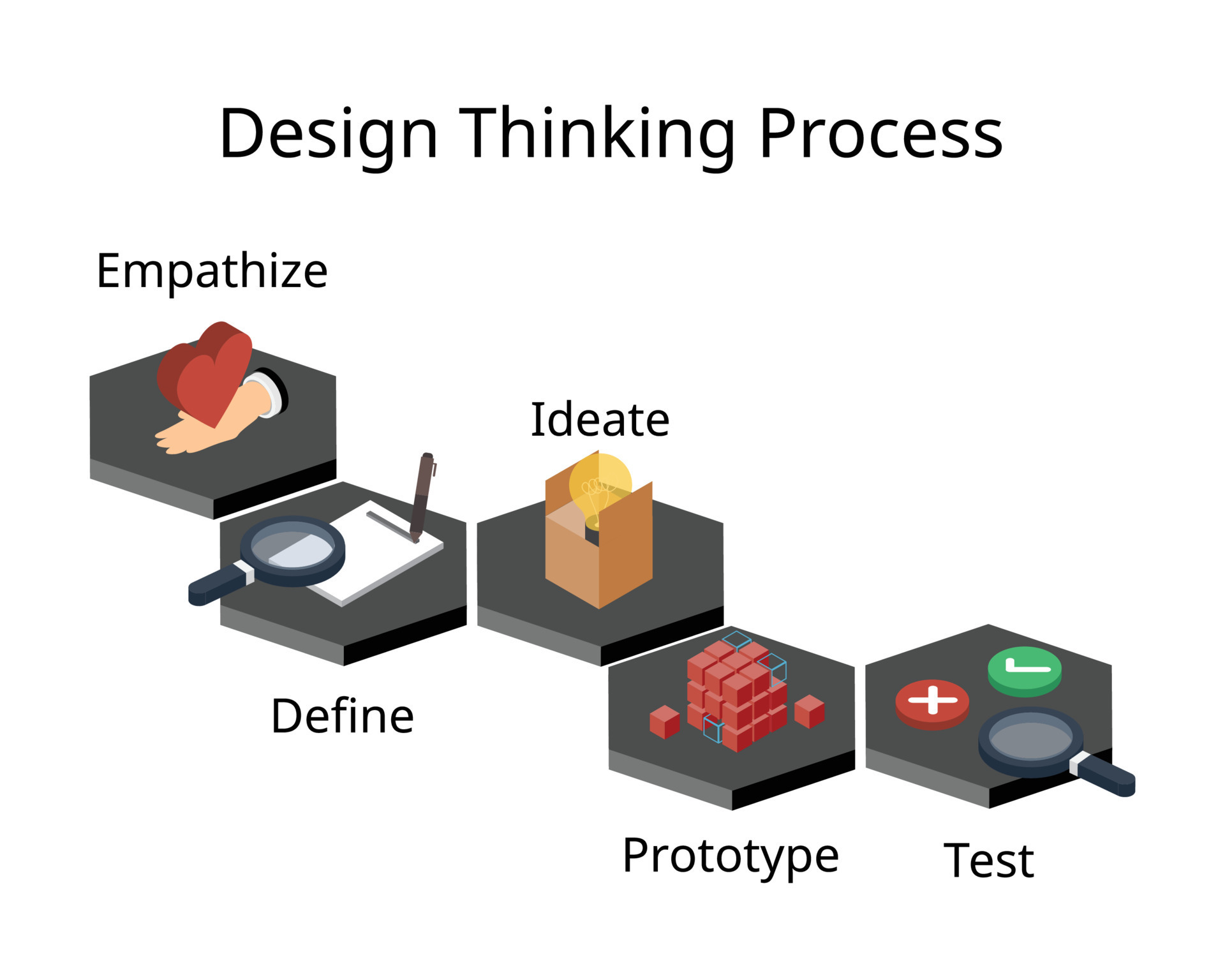
ideate
In design thinking, "ideate" is the phase where creativity flourishes. It involves brainstorming and generating a wide range of ideas and solutions. This stage encourages divergent thinking, allowing for innovative and unconventional concepts to emerge, which are later refined and tested in subsequent phases.

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zbLxs6te5to
test
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UVEQCNM6X-A
In design thinking, "test" involves evaluating prototypes with real users to gather feedback and insights. This iterative process helps identify flaws, refine solutions, and ensure the design meets user needs effectively. Testing is crucial for validating ideas and improving the final product through continuous learning and adaptation.

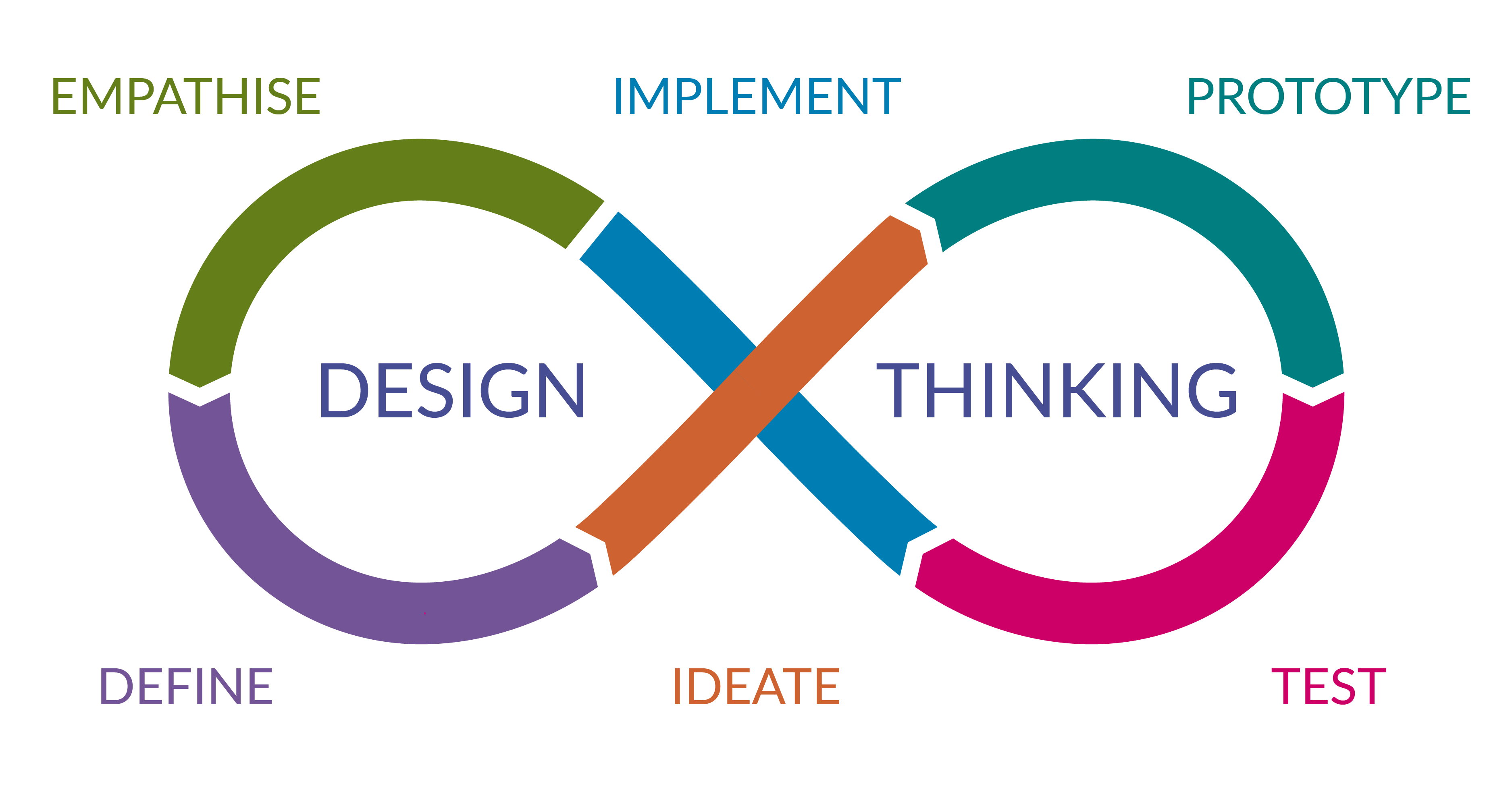
iterate
In design thinking, "iterate" refers to the cyclical process of prototyping, testing, and refining ideas. This approach emphasizes continuous improvement and user feedback, enabling designers to evolve solutions through repeated cycles. Iteration fosters innovation, ensuring that final designs are user-centric and effectively address real-world problems.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J6ioHruDko4
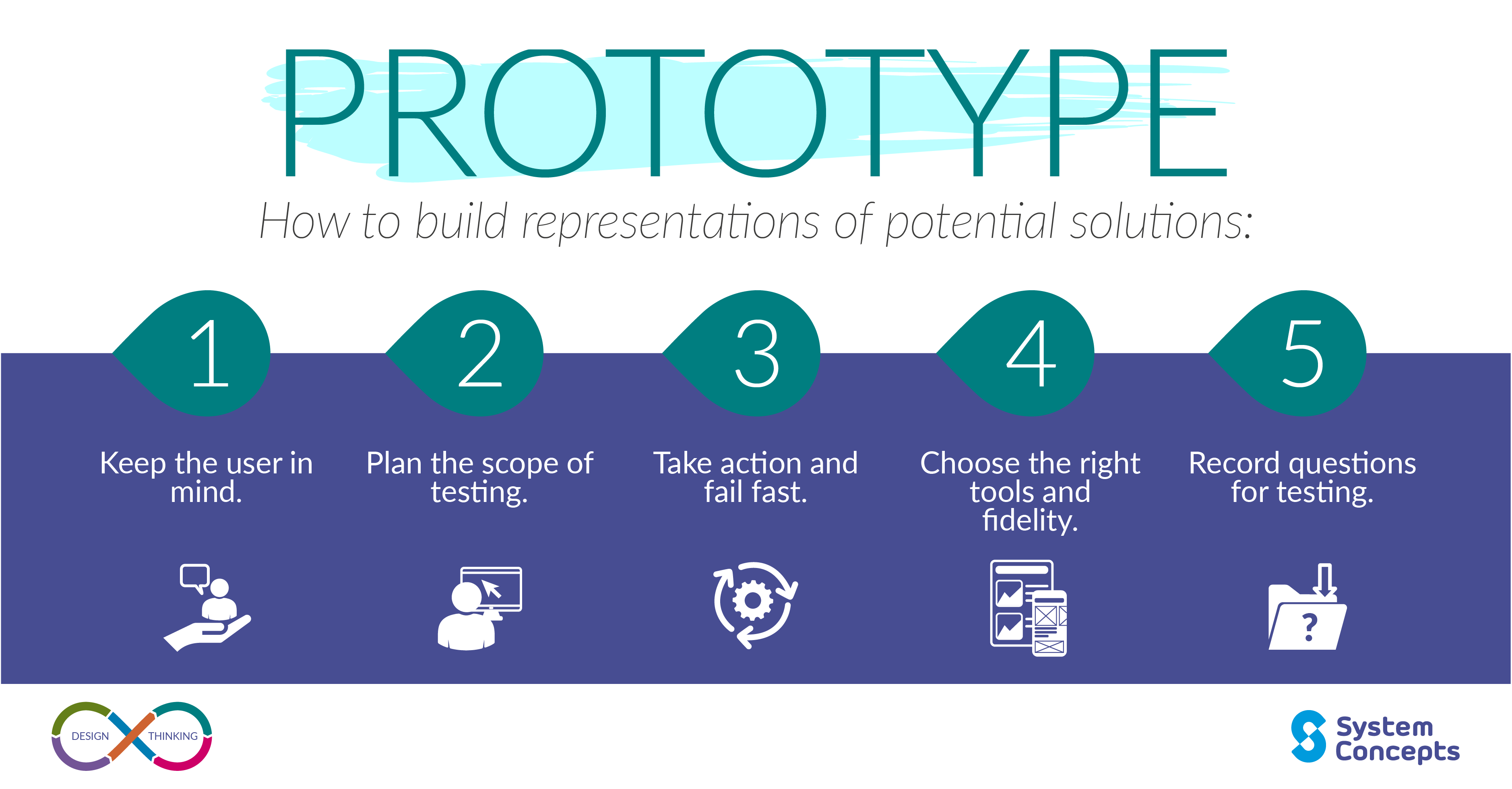
prototype
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q4MzT2MEDHA
In design thinking, a prototype is an early, tangible model of a product or solution used to visualize ideas, test functionality, and gather user feedback. It facilitates iterative development, enabling designers to refine concepts, identify issues, and enhance user experience before final production.
human-centered
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=musmgKEPY2o
Human-centered design in the context of design thinking prioritizes understanding and addressing the needs, behaviors, and experiences of users. It involves empathy, iterative prototyping, and feedback to create solutions that are both innovative and user-friendly, ensuring that the end product truly resonates with and benefits its intended audience.

collaboration
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_TXqLL8MJBY
Collaboration in design thinking involves diverse teams working together to empathize, ideate, and prototype solutions. It leverages collective creativity and interdisciplinary insights to address complex problems, fostering innovation through shared perspectives and iterative feedback. This cooperative approach enhances problem-solving and drives user-centered design outcomes.
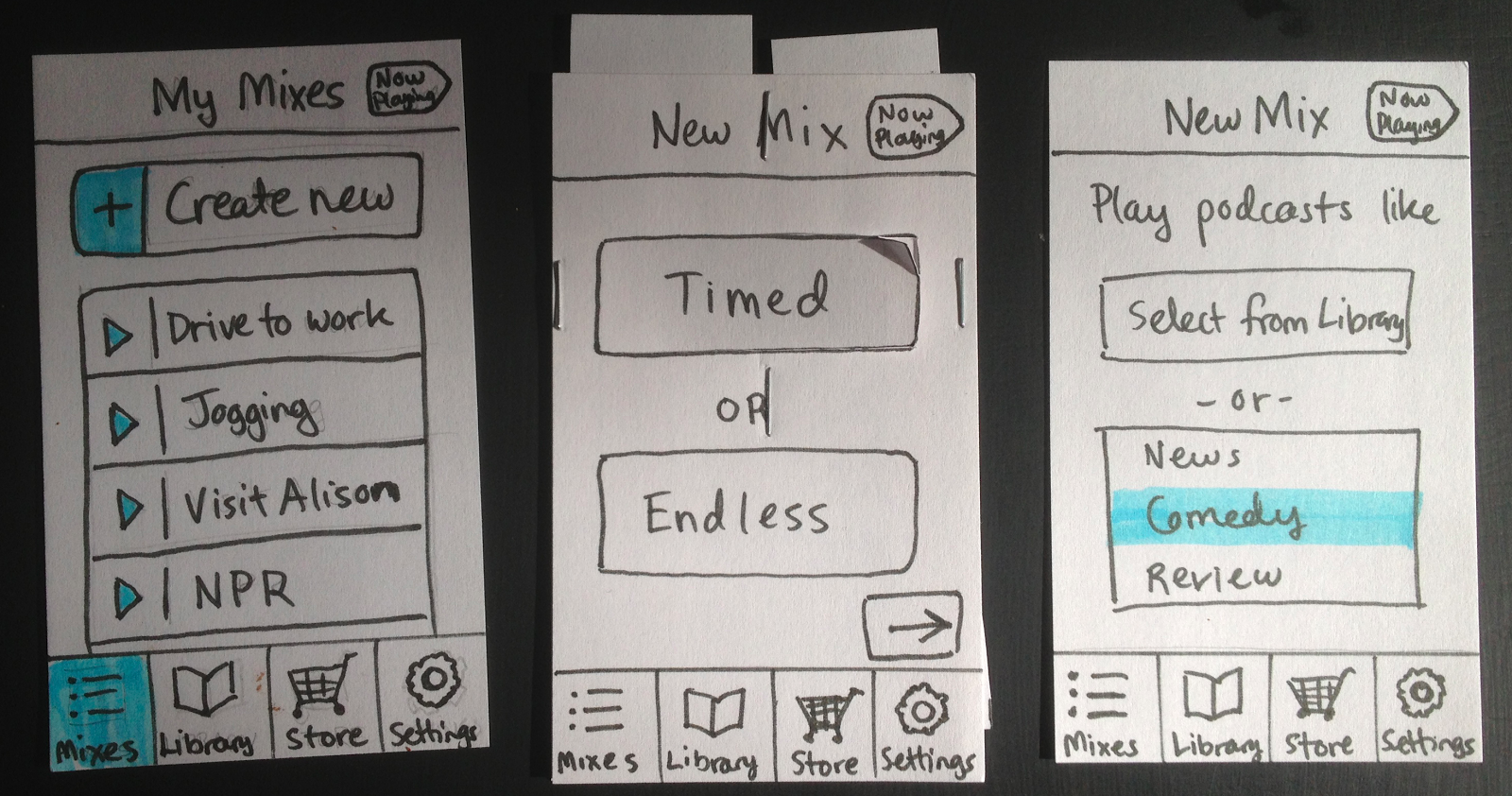
Prototype

The word "prototype" comes from the Greek words "protos," meaning "first," and "typos," meaning "impression" or "model," essentially meaning the first model of something.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uqhJfjbNuQg
empathy
Empathy in prototyping involves understanding and addressing user needs and emotions. By incorporating empathy, designers create more user-centric products, ensuring solutions resonate with real-world experiences. This approach fosters innovation, enhances user satisfaction, and drives meaningful connections between the product and its users.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZbFTVbLfbZA
iteration

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AbXBqppoSYw
Iteration in prototyping involves repeatedly refining and improving a design based on feedback and testing. This cyclical process enhances functionality and user experience, ensuring the final product meets requirements and expectations. Each iteration brings the prototype closer to the optimal solution, fostering innovation and reducing development risks.
feedback

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pijzYKAOluw
Feedback in the context of prototyping is crucial for iterative improvement. It involves collecting user and stakeholder input on early versions of a product to identify strengths and weaknesses. This process helps refine design, functionality, and usability, ensuring the final product meets user needs and expectations effectively.
ideation
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zL8IznEjSCE
Ideation in prototyping involves brainstorming and generating creative ideas to develop initial models of a product. It focuses on exploring diverse concepts, testing feasibility, and refining solutions. This iterative process helps identify potential issues early, ensuring the final prototype effectively addresses user needs and project goals.
usability

Usability in prototype design focuses on ensuring the product is user-friendly, efficient, and intuitive. It involves testing and refining the prototype to enhance user experience, identify potential issues, and gather feedback. This iterative process aims to create a final product that meets user needs and expectations effectively.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SCGDBPa6pNU
functionality
Functionality in the context of a prototype refers to the practical aspects and features that demonstrate how the final product will operate. It involves testing and refining core functions to ensure they meet user needs and performance standards, providing a tangible preview of the final design's capabilities.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8Ome0BKLgqQ
feasibility
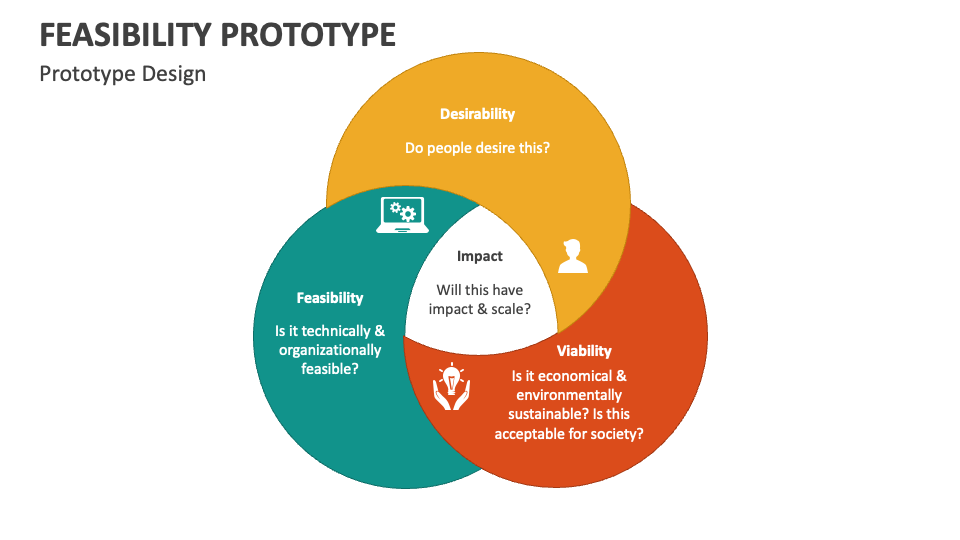
Feasibility in the context of a prototype assesses whether the proposed design is practical and achievable. It involves evaluating technical, economic, and operational aspects to ensure the prototype can be developed, functions as intended, and meets user needs within resource constraints. This step is crucial before full-scale production.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cqunaD4_QEQ
visualization
Visualization in prototyping involves creating visual representations of concepts or designs to communicate ideas effectively. It aids in identifying potential issues, refining features, and enhancing user understanding. Techniques include sketches, wireframes, and 3D models, facilitating iterative development and stakeholder feedback for improved final products.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tbQggGXf1ms
lego

The name "LEGO" is derived from the Danish words "leg godt," which mean "play well."
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P5Qfshfjer0
minifigures

Minifigures, iconic to LEGO, are small, articulated figures introduced in 1978. They enhance play and storytelling, representing various characters from everyday life to fantasy and licensed themes. With interchangeable parts and accessories, minifigures foster creativity and engagement, becoming a beloved aspect of LEGO's imaginative building experience.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iX1M9tvoI9Q
baseplates

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nlLNI7Ex6ig
Lego baseplates are flat, sturdy platforms used as foundations for building Lego structures. They provide stability and a starting point for creative constructions, ranging from simple houses to complex cities. Available in various sizes and colors, baseplates enhance play by offering a reliable surface for assembling and displaying Lego creations.
sets

In the context of LEGO, sets are pre-packaged collections of LEGO bricks and pieces designed to build specific models. Each set includes instructions and themed elements, fostering creativity and problem-solving. They range from simple builds to complex structures, catering to various age groups and skill levels.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9pfq19lUz3I
instructions

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S5y29ptlGtU
Lego instructions are step-by-step visual guides that help builders assemble Lego sets accurately. They use clear, pictorial representations to illustrate each stage of construction, ensuring even complex models can be built with ease. These instructions foster creativity, problem-solving, and spatial awareness, making Lego both educational and entertaining.
mocs

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ry_gvOeUo0o
MOCs (My Own Creations) in the context of LEGO refer to custom-built models designed by enthusiasts, showcasing creativity and engineering skills. These unique creations go beyond official LEGO sets, allowing builders to innovate and share their imaginative designs within the LEGO community.
bricks

LEGO bricks are interlocking plastic pieces used to construct various models and structures. Renowned for their versatility and durability, they foster creativity and problem-solving skills. Each brick's precise design ensures compatibility, enabling endless building possibilities, from simple shapes to intricate designs, making them a beloved educational and recreational tool.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6NL2k3mOi1I
technic

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qdp7rLy9q84
LEGO Technic is a specialized line of LEGO sets designed for advanced builders, featuring complex mechanisms and realistic functions. It includes gears, axles, and motors, enabling the creation of intricate models like vehicles and machinery, offering a hands-on experience in engineering and mechanics.
themes

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=esFqkJIiUVA
LEGO themes encompass creativity, imagination, and problem-solving. They promote learning through play, encouraging spatial awareness and fine motor skills. Themes range from fantasy and adventure to real-world scenarios, fostering storytelling and collaboration. LEGO also emphasizes innovation, engineering, and perseverance, making it a versatile educational tool for all ages.
AI Report
Essay
Lego, a popular toy company founded in 1932, has become a household name for children and adults alike. The company's success can be attributed to its innovative concept of interlocking plastic bricks that can be assembled to create various structures. The versatility and creative freedom of Lego have captured the imagination of generations, making it one of the most beloved toys in the world. In this essay, we will discuss the history, impact, and future of Lego.
The history of Lego can be traced back to the small town of Billund, Denmark, where the founder, Ole Kirk Christiansen, started a business making wooden toys in 1932. The name "Lego" is derived from the Danish phrase "leg godt," which means "play well." It was not until 1949 that the company started producing the interlocking plastic bricks that we know today. These bricks were an instant hit, and by the 1960s, Lego had expanded its production to include a variety of sets, including the iconic Lego train set. In the 1980s, Lego faced financial difficulties, but with the introduction of new themes and licensed products, such as Star Wars and Harry Potter, the company's popularity skyrocketed.
The impact of Lego goes far beyond just being a toy. It has been recognized as a valuable tool for children's learning and development. Studies have shown that playing with Lego can improve problem-solving abilities, spatial awareness, and fine motor skills. Moreover, the open-ended nature of Lego allows for endless possibilities, encouraging creativity and imagination. Lego has also been used in therapy for children with autism and other developmental disorders, helping them with social and communication skills. Additionally, Lego has a strong community following, with adult fans creating intricate and elaborate builds, showcasing the toy's versatility and appeal to all ages.
The future of Lego looks promising with the company's commitment to sustainability and innovation. In 2018, Lego announced its goal to use 100% sustainable materials for its products by 2030. This includes using plant-based plastic and investing in renewable energy sources. Lego has also embraced technology with the introduction of Lego Boost, which combines traditional brick building with coding and robotics. This allows children to learn coding skills while playing with their Lego sets. Furthermore, Lego continues to collaborate with popular franchises, such as Marvel and Disney, to create new and exciting sets that appeal to a wide audience.
In conclusion, Lego's success can be attributed to its rich history, impact on children's development, and innovative approach to sustainability and technology. The company's commitment to providing a high-quality, educational, and entertaining product has made it a beloved brand worldwide. Whether it's a child building their first Lego set or an adult creating a complex masterpiece, Lego has something for everyone. As the company continues to evolve and adapt to the changing times, one thing is for sure, Lego will continue to inspire and bring joy to people of all ages.
Lesson Plan
Lesson Title: Exploring LEGO: How They Work and How to Maintain Them
Grade level: 9-12 (Technical Vocational Students)
Learning Objectives:
- Students will be able to identify the components of LEGO bricks and understand how they work together.
- Students will learn the basics of LEGO maintenance and how to troubleshoot common issues.
- Students will demonstrate their understanding by building a simple LEGO structure and maintaining it.
Materials:
- LEGO bricks in various sizes and colors
- Instruction manuals for LEGO sets
- LEGO maintenance kit (optional)
- Whiteboard/Chalkboard
- Markers/Chalk
- Handouts with troubleshooting tips
Warm-Up (5 minutes):
- Begin the lesson by asking students if they have ever played with LEGO bricks.
- Write down their responses on the board and ask follow-up questions about their experiences (e.g. What did you build? Did you face any challenges?).
- Explain that today's lesson will focus on understanding how LEGO bricks work and how to maintain them.
Introduction (10 minutes):
- Show students the different components of a LEGO brick (studs, tubes, and baseplate) and explain their functions.
- Use the whiteboard/chalkboard to draw a simple LEGO structure and label the different components.
- Ask students to identify the different parts of the structure and explain how they work together.
Main Activity (25 minutes):
- Divide students into pairs and distribute a LEGO set to each pair.
- Ask them to follow the instruction manual and build the set together.
- As they build, encourage them to pay attention to the different pieces and how they fit together.
- After completing the build, ask students to share any challenges they faced and how they solved them.
- Use this as an opportunity to discuss the importance of following instructions and troubleshooting.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting (10 minutes):
- Explain to students that just like any other equipment, LEGO bricks also require maintenance to keep them in good condition.
- Discuss common issues that may arise with LEGO bricks, such as loose pieces, broken pieces, and dust accumulation.
- Provide students with handouts containing tips on how to troubleshoot these issues.
- Demonstrate how to use the LEGO maintenance kit to fix common problems (e.g. replacing a broken piece, using the cleaning brush to remove dust).
- Ask students to practice using the maintenance kit on their own LEGO sets.
Conclusion (5 minutes):
- Ask students to reflect on what they have learned in today's lesson.
- Give them a few minutes to work on maintaining their LEGO sets using the tips and techniques discussed.
- Ask for volunteers to share their experience and any challenges they faced.
- Conclude the lesson by reminding students of the importance of proper maintenance to keep their LEGO sets in good condition.
Assessment:
- Observe students' participation and engagement during the main activity.
- Ask students to explain the function of different LEGO components and how they work together.
- Evaluate students' understanding by having them troubleshoot a common issue with their LEGO sets.
Extension Activity:
- For students who finish early, provide them with a more complex LEGO set and ask them to build it using the instruction manual.
- Challenge students to design and build their own LEGO structure using the skills and techniques they have learned in this lesson.
Class Syllabus Outline
Course Title: The World of LEGO: Exploring Creativity and Imagination
Course Description:
This course is designed to introduce students to the fascinating world of LEGO. Through hands-on activities, students will learn about the history of LEGO, its impact on society, and the endless possibilities for creativity and imagination. Students will also have the opportunity to design and build their own LEGO creations and participate in group challenges. This class is perfect for both beginners and experienced LEGO enthusiasts.
Course Objectives:
- Understand the history and evolution of LEGO
- Explore the impact of LEGO on society and popular culture
- Develop problem-solving and critical thinking skills through LEGO building challenges
- Cultivate creativity and imagination through LEGO design
- Collaborate and communicate effectively in a group setting
- Gain a deeper appreciation for the versatility and endless possibilities of LEGO bricks
Course Materials:
- LEGO bricks and building sets
- Instruction manuals
- Computer and projector for multimedia presentations
- Whiteboard and markers
- Handouts and worksheets
- Reference books and articles
Course Schedule:
Week 1:
- Introduction to LEGO and its history
- LEGO building techniques and terminology
- Icebreaker activity: Introducing yourself through LEGO
Week 2:
- The impact of LEGO on society and popular culture
- Group discussion: Famous LEGO creations and their significance
Week 3:
- LEGO design and problem-solving
- Building challenge: Design and build a structure using only a limited number of bricks
Week 4:
- Exploring different themes and sets in LEGO
- Group activity: Creating a LEGO city with different zones and buildings
Week 5:
- Building with a purpose: Using LEGO for education and therapy
- Guest speaker: A LEGO expert or educator
Week 6:
- Creative storytelling with LEGO
- Building challenge: Create a scene from your favorite book or movie using LEGO
Week 7:
- The future of LEGO: Technological advancements and new possibilities
- Group activity: Designing and building a futuristic LEGO creation
Week 8:
- Final project: Individual or group LEGO creation based on a theme of choice
- Presentation and critique of final projects
- Course wrap-up and reflection
Assessment:
- Class participation and engagement in activities and discussions
- Completion of individual and group building challenges
- Final project presentation and critique
- Reflection paper on the impact of LEGO on creativity and imagination
Grading:
- Class participation: 20%
- Building challenges: 30%
- Final project: 40%
- Reflection paper: 10%
Note: Attendance is crucial for this course, as many activities and discussions will be done in class. More than three unexcused absences may result in a deduction of points from the participation grade.
Academic Integrity:
All work submitted must be original and created solely by the student. Any plagiarism or cheating will not be tolerated and may result in a failing grade for the assignment or the course.
Accommodations:
If you require any accommodations due to a disability or any other reason, please inform the instructor at the beginning of the course.
Contact Information:
If you have any questions or concerns, please feel free to contact the instructor at [insert email/phone number].
Disclaimer:
The instructor reserves the right to make changes to the syllabus as necessary throughout the course. Any changes will be communicated to the students in a timely manner.
Learning Objectives
1. Identify the basic components of a LEGO set and their functions.
2. Demonstrate proper building techniques and construction methods using LEGO pieces.
3. Apply problem-solving skills to design and build a functional LEGO structure.
4. Analyze the principles of engineering and physics through LEGO building.
5. Collaborate with peers to complete complex LEGO projects.
6. Utilize digital resources and software to enhance LEGO building skills.
7. Evaluate the safety precautions and guidelines for handling LEGO pieces.
8. Create and present a unique LEGO design based on a given theme or challenge.
9. Discuss the history and evolution of LEGO and its impact on the toy industry.
10. Develop critical thinking skills by identifying and troubleshooting issues with LEGO constructions.
11. Apply mathematics concepts, such as measurement and geometry, to build accurate and stable LEGO structures.
12. Demonstrate creativity and innovation by incorporating advanced techniques and unconventional building methods in LEGO projects.
13. Evaluate the environmental impact of LEGO production and explore sustainable alternatives.
14. Practice time management and organization skills to complete LEGO projects within a given timeframe.
15. Communicate effectively through written and verbal presentations, explaining the process and details of a LEGO construction.
Quiz Questions
1. What year was the first LEGO brick patented?
a. 1949
b. 1958
c. 1964
d. 1974
Answer: a. 1949
2. Which of these is not a LEGO theme?
a. Star Wars
b. Jurassic World
c. SpongeBob SquarePants
d. Marvel Super Heroes
Answer: c. SpongeBob SquarePants
3. How many LEGO bricks are produced per minute?
a. 100
b. 500
c. 1,000
d. 2,000
Answer: c. 1,000
4. Which of these is not a LEGO building technique?
a. SNOT
b. Studs Up
c. BURP
d. LEGO Loop
Answer: d. LEGO Loop
5. What is the largest LEGO set ever released?
a. LEGO Star Wars Millennium Falcon
b. LEGO Taj Mahal
c. LEGO Hogwarts Castle
d. LEGO Colosseum
Answer: d. LEGO Colosseum