AI Conversation
Non-verbal communication
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2795397-types-of-nonverbal-communication-5b0db1218023b90036ee686a.png)
Non-verbal communication makes up a significant portion of our daily interactions, with studies showing that it can account for up to 93% of our communication effectiveness.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fLaslONQAKM
appearance

Appearance plays a significant role in non-verbal communication, as it can convey information about a person's personality, status, and emotions. Clothing, grooming, and body language all contribute to how others perceive and interpret an individual. A person's appearance can influence how they are perceived and treated by others.
touch

Touch is a powerful form of non-verbal communication that can convey a wide range of emotions and intentions. It can express affection, support, comfort, or aggression. Touch can create a sense of connection and intimacy between individuals, and is an important aspect of human interaction.
silence

Silence plays a crucial role in non-verbal communication, conveying emotions, intentions, and attitudes. It can signify agreement, disagreement, discomfort, or contemplation. Silence can create tension or provide a sense of calm. Understanding the nuances of silence is essential for effective communication and building strong relationships.
proxemics

Proxemics is the study of how people use and perceive personal space in social interactions. It plays a crucial role in non-verbal communication, as it can convey power dynamics, intimacy levels, and cultural norms. Understanding proxemics can help individuals navigate social situations and communicate effectively without using words.
eye contact
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L8-R0wn9rJ8
Eye contact is a powerful form of non-verbal communication that can convey emotions, intentions, and establish connections between individuals. It can signal interest, attentiveness, and trustworthiness, while also influencing the dynamics of a conversation. Maintaining appropriate eye contact is essential for effective communication and building relationships.
gestures
Gestures are non-verbal cues used to convey messages, emotions, and intentions. They can include hand movements, facial expressions, and body language. Gestures can enhance or contradict verbal communication, providing additional context and meaning to interactions. Understanding and interpreting gestures is essential for effective communication.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fLaslONQAKM
facial expressions
Facial expressions play a crucial role in non-verbal communication, conveying emotions, intentions, and attitudes without the need for words. They can indicate happiness, sadness, anger, fear, and more, helping individuals to understand and connect with others on a deeper level through visual cues.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fLaslONQAKM
posture
Posture plays a crucial role in non-verbal communication, conveying confidence, openness, and attentiveness. A person's posture can indicate their level of interest, engagement, and authority in a conversation. It is important to be mindful of one's posture to effectively communicate messages and establish rapport with others.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fLaslONQAKM
Cultural awareness

Cultural awareness can help individuals understand and appreciate different customs, traditions, and beliefs, leading to increased empathy and respect for diverse cultures.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FNCu1ED0Zsk
time orientation

Time orientation refers to how different cultures perceive and value time. Some cultures prioritize punctuality and efficiency, while others have a more relaxed attitude towards time. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective communication and collaboration across cultures, as it can impact expectations and perceptions of professionalism.
gender roles

Gender roles are societal expectations dictating behaviors and responsibilities based on one's gender. Cultural awareness involves understanding and respecting diverse beliefs and practices. Recognizing and challenging traditional gender roles can promote equality and inclusivity within different cultures, fostering a more accepting and understanding society.
religion

Religion plays a significant role in cultural awareness, shaping beliefs, values, and practices of societies. Understanding different religions fosters tolerance, respect, and appreciation for diverse perspectives. It promotes interfaith dialogue, unity, and cooperation, fostering a more inclusive and harmonious global community.
personal space

Personal space varies across cultures, with some valuing close physical proximity while others prefer more distance. Understanding and respecting these differences is crucial for effective communication and building relationships. Cultural awareness of personal space helps prevent misunderstandings and promotes mutual respect in diverse social interactions.
hospitality
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=my5ezpTnnzA
Hospitality is a universal concept that varies across cultures. Understanding cultural norms and customs is essential for providing excellent hospitality. Respect for differences in communication styles, gestures, and traditions is key to creating a welcoming and inclusive environment for guests from diverse backgrounds.
nonverbal cues
Nonverbal cues play a crucial role in communication, especially in cross-cultural interactions. Understanding and interpreting these cues accurately is essential for effective communication and building relationships across different cultures. Awareness of cultural differences in nonverbal communication can help avoid misunderstandings and promote successful interactions.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YAV4SDgVv-o
language
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CwySb-vRHqA
Language is a crucial aspect of cultural awareness, as it reflects the values, beliefs, and traditions of a society. Understanding different languages can help individuals bridge cultural divides, foster empathy, and promote mutual understanding. By learning and respecting diverse languages, people can deepen their appreciation for different cultures.
hierarchy
Understanding hierarchy is crucial in cultural awareness as it shapes social structures and interactions. It influences power dynamics, decision-making processes, and communication styles within a society. Recognizing and respecting hierarchy can help individuals navigate unfamiliar cultural settings and build positive relationships with people from different backgrounds.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=seCkNSgMrQE
Vocabulary

Vocabulary is essential for effective communication in Arabic. It includes words, phrases, and expressions that convey meaning and help speakers express themselves clearly. Building a strong vocabulary is crucial for improving language skills and fluency in Arabic, enabling individuals to communicate effectively in various social and professional settings.
cultural awareness

Cultural awareness is essential in Arabic communication skills, as it involves understanding and respecting the customs, traditions, and values of Arab societies. By being aware of cultural nuances, individuals can effectively navigate conversations, build relationships, and avoid misunderstandings in their interactions with Arabic speakers.
non-verbal communication

Non-verbal communication plays a significant role in Arabic communication skills, with gestures, facial expressions, and body language conveying messages alongside spoken words. Eye contact, hand gestures, and posture are important aspects of non-verbal communication in Arab culture, influencing the effectiveness of interpersonal interactions and relationships.
grammar

Grammar is essential in Arabic communication skills as it ensures clarity and accuracy in conveying messages. Proper grammar rules help in forming coherent sentences and expressing ideas effectively. Understanding Arabic grammar rules, such as verb conjugation and sentence structure, is crucial for effective communication in both spoken and written forms.
arabic communication skills
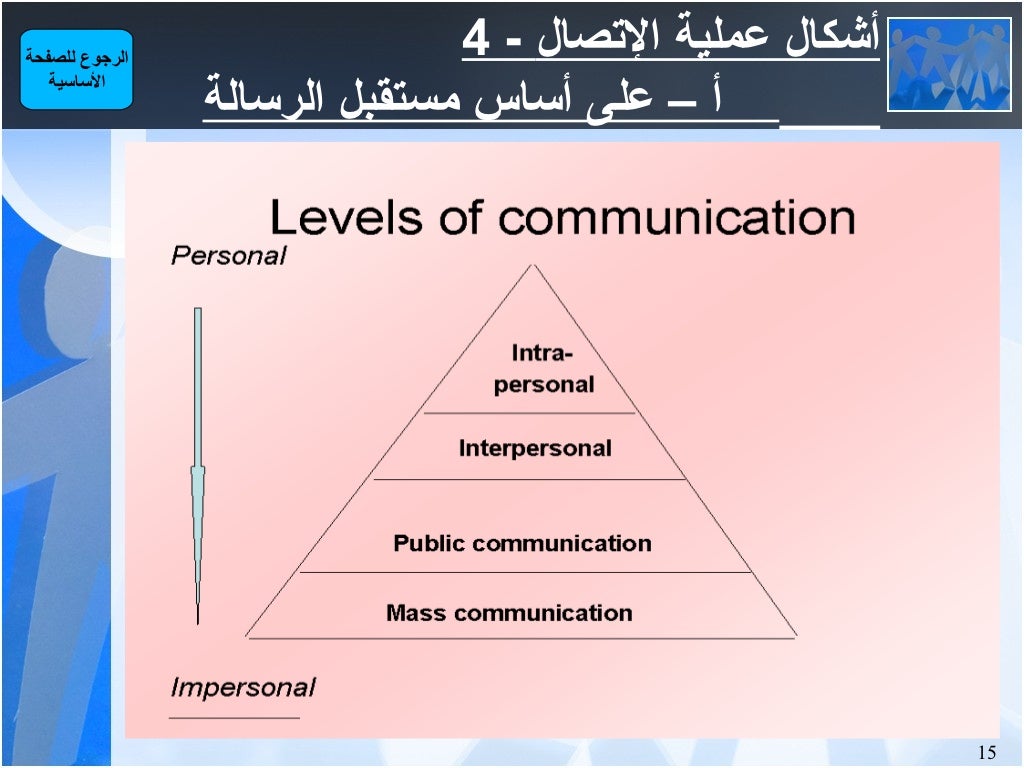
Arabic communication skills often involve the use of gestures and body language to convey meaning, as well as a strong emphasis on tone of voice and intonation to express emotions and emphasis.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X1mC1XY65Kc
reading skills
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AVqu6a1U_jQ
Reading skills are crucial for effective communication in Arabic. Proficiency in reading allows individuals to understand written texts, communicate clearly, and comprehend complex ideas. Strong reading skills enable better comprehension, vocabulary expansion, and overall language proficiency, enhancing communication abilities in both written and spoken Arabic.
listening skills
Listening skills are crucial in Arabic communication, as they demonstrate respect and understanding. Active listening, maintaining eye contact, and avoiding interruptions are key components. Effective listening helps build trust, strengthen relationships, and avoid misunderstandings. It is essential for successful communication in Arabic culture.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ENZE1Knq3nU
speaking skills
Effective speaking skills are crucial in Arabic communication. It involves clear pronunciation, proper intonation, and appropriate use of gestures. Active listening and responding appropriately are also important. Developing these skills can enhance understanding and connection in conversations, making communication more effective and meaningful.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X1mC1XY65Kc
writing skills
Effective writing skills are essential for effective communication in Arabic. Clear and concise writing helps convey ideas accurately and professionally. It is important to use proper grammar, punctuation, and vocabulary to ensure clarity and coherence in written communication. Practice and feedback are key to improving writing skills in Arabic.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=msbIWn54hVk
AI Report
Essay
Arabic communication skills are an essential aspect of effective communication in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. With over 420 million native speakers worldwide, Arabic is the fifth most spoken language in the world (Gordon, 2020). As a result, having proficiency in Arabic communication skills is vital for individuals and businesses operating in this region. In this essay, we will discuss the importance of Arabic communication skills, the unique features of the language, and the impact of culture on communication in the MENA region.
First and foremost, having Arabic communication skills is crucial for building strong relationships in the MENA region. In Arabic culture, communication is not only about exchanging information, but it is also a way of building trust and establishing personal connections (Al-Jenaibi, 2016). By speaking in Arabic, individuals can show respect and understanding towards the local culture, which can significantly improve business opportunities and personal relationships. As stated by Al-Omar and Al-Jenaibi (2015), "speaking the same language creates a sense of unity and belonging, which is highly valued in the MENA region."
Moreover, Arabic communication skills are essential for effective business communication in the MENA region. In this part of the world, personal relationships and trust play a significant role in business transactions (Al-Bargi, 2017). By communicating in Arabic, individuals can establish a personal connection with their counterparts, which is crucial for negotiating and closing deals successfully. Additionally, speaking the language can also help in understanding the business culture and etiquette, which can differ from western cultures (Al-Omar & Al-Jenaibi, 2015).
Arabic is a unique language with its own set of features and characteristics. It is a Semitic language, which means it has a different grammatical structure and vocabulary from languages like English and French (Dahou, 2018). One of the most distinctive features of Arabic is its diglossia, which means there are two forms of the language - formal (Fusha) and colloquial (Amiyya). The formal form is used in written communication and formal settings, while the colloquial form is used in everyday conversation (Al-Jenaibi, 2016). This feature can be challenging for non-native speakers to grasp, but it is essential to understand the differences to communicate effectively in Arabic.
Finally, it is crucial to acknowledge the impact of culture on communication in the MENA region. In Arabic culture, communication is more indirect and relies heavily on nonverbal cues such as tone, body language, and facial expressions (Al-Jenaibi, 2016). Therefore, it is essential for individuals to be aware of these cultural differences and adjust their communication style accordingly. For instance, using a direct approach in negotiations may be perceived as rude or disrespectful in Arabic culture (Al-Bargi, 2017). By understanding and adapting to the local culture, individuals can avoid miscommunication and build stronger relationships.
In conclusion, having proficiency in Arabic communication skills is crucial for individuals and businesses operating in the MENA region. It not only helps in building relationships but also plays a significant role in business communication and understanding the unique features of the language. Additionally, it is vital to be aware of the impact of culture on communication in this region to avoid miscommunication and build stronger connections. Therefore, individuals and businesses should invest in learning Arabic communication skills to succeed in the MENA region.
References:
Al-Bargi, N. (2017). Communication Patterns in the Arab World. Journal of Intercultural Communication Research, 46(6), 545-559. doi: 10.1080/17475759.2017.1351556
Al-Jenaibi, B. (2016). Communication Styles in the Arab World. International Journal of Business Communication, 53(4), 381-403. doi: 10.1177/2329488414534406
Al-Omar, M., & Al-Jenaibi, B. (2015). The Role of Arabic Language in Business Communication in the GCC Region. International Journal of Business Communication, 52(3), 316-334. doi: 10.1177/2329488414562012
Dahou, S. (2018). Arabic Language and Culture. In M. Farooq (Ed.), The Routledge Handbook of Arabic Linguistics (pp. 1-12). New York, NY: Routledge.
Gordon, R. (2020). How Many People Speak Arabic, And Where Is It Spoken? Retrieved from https://www.ethnologue.com/guides/how-many-people-speak-arabic-and-where.
Lesson Plan
Lesson Title: Arabic Communication Skills
Subject: Technical Vocational Education
Grade Level: High School
Time Frame: 45 minutes
Objectives:
Students will be able to:
1. Understand the importance of Arabic communication skills in the workplace.
2. Identify the key elements of effective Arabic communication.
3. Demonstrate the proper use and maintenance of Arabic communication skills.
Materials:
1. PowerPoint presentation
2. Handouts with key vocabulary and phrases
3. Whiteboard and markers
4. Role-playing scenarios
5. Evaluation rubric
Introduction (5 minutes):
1. Begin the lesson by asking students if they have ever been in a situation where they needed to communicate in a language other than their native language.
2. Explain that in today's globalized world, having strong communication skills in multiple languages is becoming increasingly important, especially in the workplace.
3. Introduce the topic of Arabic communication skills and explain that in this lesson, students will learn about the importance and maintenance of these skills.
Direct Instruction (15 minutes):
1. Use the PowerPoint presentation to discuss the importance of Arabic communication skills in the workplace. Highlight the growth of Arabic-speaking countries in the global economy and the demand for employees who can effectively communicate in Arabic.
2. Discuss the key elements of effective Arabic communication, such as tone, body language, and cultural sensitivity.
3. Use examples to demonstrate how these elements can affect the success of communication.
Guided Practice (10 minutes):
1. Provide students with handouts containing key vocabulary and phrases commonly used in Arabic communication.
2. Have students practice pronouncing and using these phrases in pairs.
3. Encourage students to pay attention to tone and body language while practicing.
Independent Practice (10 minutes):
1. Divide students into groups of three and assign them role-playing scenarios involving Arabic communication.
2. Each group will have a chance to act out their scenario while the rest of the class observes and takes notes.
3. After each role-play, have the class provide feedback on the use of key elements of effective Arabic communication.
Closure (5 minutes):
1. Ask students to share their observations from the role-plays and discuss the importance of effective Arabic communication skills in different workplace scenarios.
2. Summarize the key points of the lesson and remind students of the importance of maintaining and continuously improving their Arabic communication skills.
Assessment:
1. During the role-playing activity, use the evaluation rubric to assess students' use of key elements of effective Arabic communication.
2. At the end of the lesson, have students complete a short quiz or writing assignment to assess their understanding of the topic.
Extension:
1. Have students research and present on the cultural norms and communication styles in different Arabic-speaking countries.
2. Encourage students to practice their Arabic communication skills outside of the classroom by engaging with native Arabic speakers or watching Arabic TV shows or movies.
Conclusion:
Effective communication is a crucial skill in any workplace, and having strong Arabic communication skills can give students a competitive edge in the job market. By understanding the key elements and continuously practicing and improving their skills, students can become confident and successful communicators in Arabic.
Class Syllabus Outline
Course Title: Arabic Communication Skills
Course Description:
This course is designed for students who are interested in developing their Arabic communication skills. The course will focus on developing the four main language skills: speaking, listening, reading, and writing. Through a variety of activities and exercises, students will learn how to effectively communicate in Arabic in various situations and contexts. This course is suitable for both beginner and intermediate level students.
Course Objectives:
By the end of this course, students will be able to:
1. Communicate effectively in Arabic in both formal and informal settings.
2. Understand and respond to basic spoken Arabic.
3. Read and write simple Arabic texts.
4. Use appropriate vocabulary and grammar to express themselves in Arabic.
5. Develop cultural sensitivity and awareness when communicating in Arabic.
Course Materials:
- Textbook: "Arabic for Communication" by Ahmed Al-Kadi
- Handouts and worksheets provided by the instructor
- Audio and video materials for listening and speaking practice
- Online resources for reading and writing practice
Course Requirements:
- Regular attendance and active participation in class discussions and activities
- Completion of assigned homework and class assignments
- Midterm and final exams
- A final project or presentation
Grading:
- Attendance and participation: 20%
- Homework and class assignments: 30%
- Midterm exam: 20%
- Final exam: 20%
- Final project or presentation: 10%
Course Outline:
Week 1: Introduction to Arabic communication
- Basic greetings and introductions
- Arabic alphabet and pronunciation
Week 2: Everyday communication
- Asking and answering simple questions
- Expressing likes and dislikes
- Making requests and giving directions
Week 3: Communication in social settings
- Talking about family and friends
- Inviting and accepting/declining invitations
- Making small talk
Week 4: Communication in the workplace
- Introducing oneself and others in a professional setting
- Writing emails and memos in Arabic
- Conducting phone conversations in Arabic
Week 5: Making plans and arrangements
- Discussing schedules and appointments
- Making reservations and bookings
- Canceling or changing plans
Week 6: Describing people and things
- Using adjectives to describe people and things
- Comparing and contrasting
- Giving opinions and feedback
Week 7: Talking about past events
- Using the past tense in Arabic
- Narrating personal experiences and events
- Talking about historical events in Arabic-speaking countries
Week 8: Midterm exam
Week 9: Understanding and responding to spoken Arabic
- Listening comprehension practice
- Understanding different accents and dialects
- Participating in conversations and group discussions
Week 10: Reading and writing in Arabic
- Basic reading comprehension exercises
- Writing simple sentences and paragraphs
- Building vocabulary and using correct grammar in writing
Week 11: Cultural sensitivity and awareness
- Cultural norms and customs in Arabic-speaking countries
- Appropriate behavior and communication in different contexts
- Avoiding cultural misunderstandings
Week 12: Final project or presentation preparation
Week 13: Final project presentations
Week 14: Final exam
Note: This syllabus is subject to change at the discretion of the instructor. Any changes will be communicated to the students in a timely manner.
Learning Objectives
At the end of this course, students will be able to:
1. Communicate effectively in Arabic language in a variety of workplace settings.
2. Demonstrate proficiency in reading, writing, and speaking Arabic.
3. Understand and use basic grammar rules and sentence structures in Arabic.
4. Develop a basic vocabulary of technical terms used in their vocational field.
5. Conduct basic conversations in Arabic with colleagues and clients.
6. Deliver clear and concise presentations in Arabic on technical topics related to their field of study.
7. Interpret and respond appropriately to instructions and requests given in Arabic.
8. Engage in written communication in Arabic through emails, reports, and other workplace documents.
9. Adapt to different communication styles and cultural norms when interacting with Arabic-speaking individuals.
10. Utilize appropriate language and tone to express ideas and opinions in Arabic.
11. Apply effective communication strategies to resolve conflicts and solve problems in the workplace.
12. Develop confidence and fluency in using Arabic for professional communication.
13. Recognize the importance of cross-cultural communication and its impact on their vocational career.
14. Use technology and online resources to enhance their Arabic communication skills.
15. Reflect on their progress and continuously improve their Arabic communication skills through self-evaluation and feedback.
Quiz Questions
1. Which of the following is NOT a common Arabic greeting?
A. Marhaba
B. Salaam
C. Shukran
D. Aloha
Answer: D. Aloha
2. In Arabic communication, it is considered polite to:
A. Make direct eye contact
B. Use gestures to emphasize your point
C. Interrupt others when speaking
D. Use a firm handshake when greeting someone
Answer: D. Use a firm handshake when greeting someone
3. The Arabic language is written and read from:
A. Right to left
B. Left to right
C. Top to bottom
D. Bottom to top
Answer: A. Right to left
4. When addressing someone in a formal setting, it is important to use:
A. First names
B. Last names
C. Titles and last names
D. Nicknames
Answer: C. Titles and last names
5. In Arabic culture, it is considered respectful to:
A. Speak loudly to show enthusiasm
B. Ask personal questions
C. Avoid making direct eye contact
D. Use hand gestures while speaking
Answer: D. Use hand gestures while speaking