Lesson AI Summary
Data backup is an essential aspect of data management that involves creating a duplicate copy of important data in case the original data is lost or becomes inaccessible. In today's digital age, where data is the backbone of most businesses and individuals, the importance of data backup cannot be overstated. This essay will discuss the importance of data backup, the different types of data backup, and the best practices for ensuring effective data backup.
One of the main reasons why data backup is crucial is the potential risk of data loss. Data loss can occur due to various reasons such as hardware failure, natural disasters, cyber-attacks, or human error. According to a study by the Ponemon Institute, the average cost of a single data breach in 2020 was $3.86 million (Ponemon Institute, 2020). This cost includes not only the financial losses but also the damage to a company's reputation. Data backup can help mitigate these risks by providing a secondary copy of data that can be used to restore the original data in case of a disaster.
There are several types of data backup methods available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common types of data backup are full backup, incremental backup, and differential backup. Full backup involves creating a complete copy of all the data, while incremental backup only backs up the changes made since the last backup. Differential backup, on the other hand, backs up all the changes made since the last full backup. The best data backup strategy is to combine these methods to create a comprehensive backup plan. This approach ensures that data is backed up regularly and can be restored quickly in case of a disaster.
To ensure effective data backup, it is essential to follow best practices. One of the best practices is to create multiple copies of data and store them in different locations. This approach provides an extra layer of protection in case one copy is lost or becomes inaccessible. Another best practice is to regularly test the backup data to ensure its integrity and reliability. This testing should be done on a schedule to identify any potential issues and address them promptly. Additionally, it is crucial to have a clear data backup policy in place and train employees on how to follow it. This will help ensure that data is backed up consistently and securely.
In conclusion, data backup is a critical aspect of data management that helps mitigate the risks of data loss. The different types of data backup methods, such as full, incremental, and differential backup, can be combined to create an effective backup plan. By following best practices such as creating multiple copies of data and regularly testing backups, organizations can ensure the integrity and reliability of their data backups. In today's digital world, where data is invaluable, it is essential to have a robust data backup strategy in place to safeguard against potential disasters and ensure business continuity.
Reference List:
Ponemon Institute. (2020). 2020 Cost of a Data Breach Report. https://www.ibm.com/security/digital-assets/cost-data-breach-report/#/worldwide/Average%20Total%20Cost%20of%20Data%20Breach%20by%20Country
Lesson Title: Understanding Data Backup and Maintenance
Grade Level: Technical Vocational Students (High School)
Objectives:
- Students will be able to define data backup and understand its importance in computer systems.
- Students will learn about different types of data backup methods and their advantages and disadvantages.
- Students will understand the process of maintaining data backups and the importance of regular backups.
- Students will be able to identify potential risks and challenges in data backup and maintenance.
- Students will demonstrate their understanding by creating a data backup plan for a hypothetical scenario.
Materials:
- Computer with internet access
- Projector
- Handouts with key terms and definitions
- Examples of different backup methods (external hard drive, cloud storage, etc.)
- Data backup plan template (one per student)
- Whiteboard and markers
Introduction (10 minutes):
1. Begin the lesson by asking students if they have ever lost important files on their computer or phone.
2. Explain that data backup is a method of creating a copy of important files to prevent loss in case of a computer or system failure.
3. Ask students to share their experiences with data backup or if they have any knowledge about it.
Direct Instruction (20 minutes):
1. Use a projector to display a presentation or use the whiteboard to discuss the importance of data backup in computer systems.
2. Define key terms such as data backup, data loss, and system failure.
3. Discuss the different types of data backup methods, such as external hard drives, cloud storage, and network drives.
4. Explain the advantages and disadvantages of each method, including cost, accessibility, and security.
5. Use examples and visuals to help students understand the concepts better.
Guided Practice (15 minutes):
1. Divide the class into small groups of 3-4 students.
2. Distribute handouts with key terms and definitions.
3. Provide each group with a scenario, such as a company losing important financial data due to a system failure.
4. Ask students to discuss and come up with a data backup plan for the given scenario, considering the type of data, backup method, and frequency of backups.
5. Encourage students to ask questions and provide guidance as needed.
Independent Practice (15 minutes):
1. Ask students to individually complete the data backup plan template provided.
2. Remind them to consider the different types of data and backup methods discussed in class.
3. Walk around the class and provide individual feedback and assistance as needed.
Closure (10 minutes):
1. Ask students to share their data backup plans with the class.
2. Discuss any challenges or potential risks they identified in the process.
3. Summarize the key points and emphasize the importance of regular data backups and maintenance.
4. Allow time for students to ask any final questions.
Assessment:
1. Observe students during the independent practice and provide feedback.
2. Assess students' data backup plans for their understanding of different types of data and backup methods.
3. Use a rubric to assess their knowledge and understanding of the topic.
Extension:
1. For advanced students, have them research and present on the latest data backup technologies and methods.
2. Have students create a step-by-step guide or tutorial on how to backup and maintain data for a specific device or software.
3. Invite a guest speaker, such as an IT professional, to share their experience and best practices for data backup and maintenance.
References:
- Data Backup and Recovery. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.techopedia.com/definition/23364/data-backup-and-recovery
- Pettey, C. (2015, August 20). Gartner Says Backup as a Service Is a Critical Offering for Channel Partners. Retrieved from https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2015-08-20-gartner-says-backup-as-a-service-is-a-critical-offering-for-channel-partners
I. Course Title: Data Backup: Best Practices and Strategies
II. Course Description:
This course is designed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of data backup and its importance in today's digital world. Students will learn the fundamentals of data backup, including different methods and tools for backing up data, as well as best practices for creating a reliable backup system. The course will also cover disaster recovery planning and strategies for protecting data from potential threats.
III. Course Objectives:
- Understand the importance of data backup in safeguarding valuable information.
- Identify the different methods of data backup and their advantages and disadvantages.
- Learn the best practices for creating a reliable backup system.
- Develop skills in creating and implementing a disaster recovery plan.
- Gain knowledge of data encryption and security measures for protecting data during backup and recovery.
- Explore the latest trends and technologies in data backup.
IV. Course Outline:
Week 1:
- Introduction to Data Backup: Importance and Benefits
- Types of Data: Understanding the Different Types of Data and their Backup Requirements
- Data Backup Methods: Full, Incremental, and Differential Backups
Week 2:
- Backup Tools: Overview of Backup Software and Cloud Storage Solutions
- Planning for Data Backup: Factors to Consider and Creating a Backup Schedule
- Hands-on: Setting up a Backup Schedule using Backup Software
Week 3:
- Best Practices for Data Backup: Data Redundancy, Offsite Backup, and Testing Backups
- Data Recovery: Understanding the Recovery Process and Types of Recovery Strategies
- Hands-on: Restoring Data from Backups using Backup Software
Week 4:
- Disaster Recovery Planning: Importance and Steps for Creating a Disaster Recovery Plan
- Backup Security: Encryption and Other Security Measures for Protecting Data
- Hands-on: Implementing Encryption for Backup Data
Week 5:
- Automation and Monitoring: Using Automation and Monitoring Tools for Efficient Backup Management
- Backups in the Cloud: Advantages, Disadvantages, and Best Practices
- Hands-on: Setting up Automated Backups and Monitoring for Backup Systems
Week 6:
- Data Backup Trends: Latest Technologies and Innovations in Data Backup
- Disaster Recovery Testing: Importance and Methods for Testing Disaster Recovery Plans
- Final Project: Students will create a Backup and Disaster Recovery Plan for a hypothetical business.
V. Grading Policy:
- Class participation and attendance: 20%
- Assignments and quizzes: 40%
- Final project: 40%
VI. Textbook:
There is no required textbook for this course. All course materials will be provided by the instructor.
VII. Additional Resources:
- Online articles and case studies
- Backup software and tools (provided by the instructor)
- Webinars and videos on data backup best practices
VIII. Prerequisites:
There are no prerequisites for this course. Basic computer skills are recommended.
IX. Course Policies:
- Attendance and participation are crucial for success in this course.
- Late assignments will not be accepted unless prior arrangements have been made with the instructor.
- Plagiarism and academic dishonesty will not be tolerated and will result in disciplinary action.
X. Instructor Information:
[Insert Name]
[Insert Email Address]
[Insert Office Hours and Location]
XI. Disclaimer:
The course outline and schedule are subject to change at the discretion of the instructor. Any changes will be communicated to the students in a timely manner.
XII. Conclusion:
This course will provide students with the necessary knowledge and skills to effectively backup and protect data. By the end of the course, students will have a thorough understanding of data backup best practices and strategies, as well as practical experience in implementing them.
1. Understand the importance of data backup in the technical vocational field.
2. Identify different types of data and the appropriate backup methods for each type.
3. Learn how to implement a backup plan and schedule for efficient data storage and retrieval.
4. Familiarize with various backup devices and software used in the industry.
5. Gain knowledge on disaster recovery strategies and their role in data backup.
6. Learn how to troubleshoot and resolve common issues related to data backup.
7. Develop skills in selecting the right backup solution based on organizational needs and budget.
8. Understand the concept of data encryption and its role in securing backed-up data.
9. Learn how to test and validate backups to ensure data integrity.
10. Develop a comprehensive understanding of backup best practices and industry standards.
11. Gain hands-on experience in implementing data backup solutions in real-world scenarios.
12. Learn how to create and maintain backup logs and documentation for compliance and auditing purposes.
13. Develop skills in disaster management and contingency planning to minimize data loss.
14. Understand the importance of regular backups and how to automate the process for increased efficiency.
15. Learn how to troubleshoot and recover data from failed backups.
1) What is the primary purpose of data backup?
a) To save storage space
b) To protect against data loss
c) To improve data organization
d) To increase internet speed
Answer: b) To protect against data loss
2) What is the recommended frequency for backing up important data?
a) Once a year
b) Once a month
c) Once a week
d) Once a day
Answer: d) Once a day
3) Which of the following is NOT a type of data backup?
a) Full backup
b) Incremental backup
c) Duplicate backup
d) Differential backup
Answer: c) Duplicate backup
4) What is the difference between a local backup and a cloud backup?
a) Local backup requires an internet connection, while cloud backup does not
b) Local backup is more secure than cloud backup
c) Local backup is stored on physical devices, while cloud backup is stored remotely
d) Local backup is more expensive than cloud backup
Answer: c) Local backup is stored on physical devices, while cloud backup is stored remotely
5) Which of the following is NOT a factor to consider when choosing a data backup solution?
a) Cost
b) Speed of backup and restore
c) Security measures
d) Type of data being backed up
Answer: d) Type of data being backed up
AI Conversation
Cyber Security - design
One fun fact about cyber security is that the first known computer virus was created as an experiment in 1982 by a high school student named Rich Skrenta. The virus, called "Elk Cloner," infected Apple II computers by spreading through floppy disks.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jq_LZ1RFPfU
antivirus software

Antivirus software is a crucial component of cyber security, designed to detect, prevent, and remove malicious software from computer systems. It acts as a protective shield against viruses, malware, and other cyber threats, ensuring the safety and integrity of digital data.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1_rXO2Es5B8
firewall

Firewalls are essential components of cybersecurity design. They act as a barrier between internal networks and external threats, filtering and monitoring incoming and outgoing network traffic to prevent unauthorized access and protect against malicious activities.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9GZlVOafYTg
authentication

Authentication in cyber security is the process of verifying the identity of a user or system. It ensures that only authorized individuals or devices can access sensitive information or resources, protecting against unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jq_LZ1RFPfU
encryption

Encryption is a vital component of cybersecurity, safeguarding sensitive data by converting it into unreadable code. It ensures confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity, making it difficult for unauthorized individuals to access or manipulate information.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jq_LZ1RFPfU
intrusion detection system (ids)

Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are crucial components of cyber security, designed to identify and prevent unauthorized access or malicious activities within computer networks. They monitor network traffic, analyze patterns, and raise alerts to protect against potential threats.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfVAi87BSEs
patch management
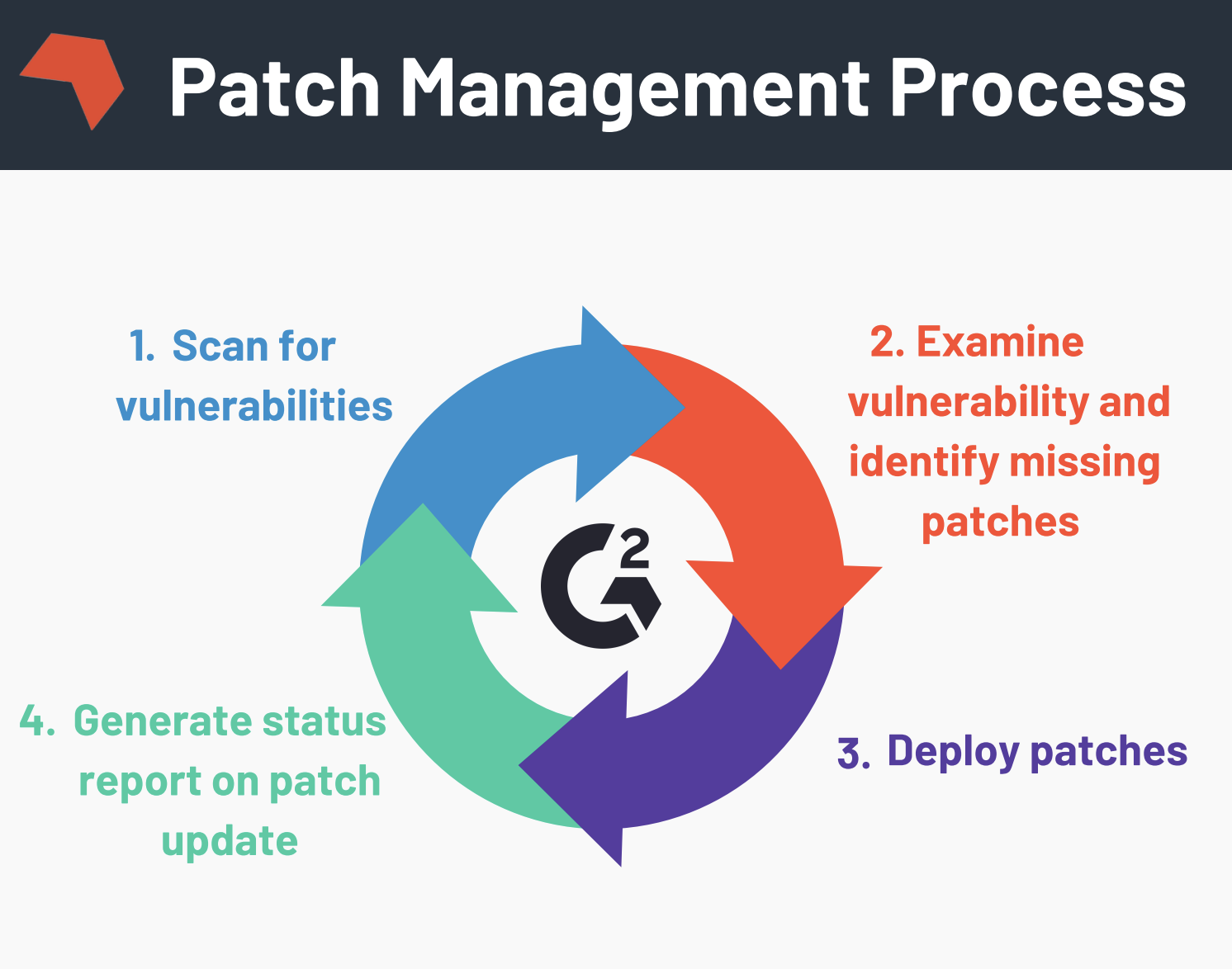
Patch management is a crucial aspect of cybersecurity, involving the regular updating and maintenance of software to fix vulnerabilities. It ensures systems are protected against potential threats and reduces the risk of cyberattacks.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vIDG-O_17qA
phishing

Phishing is a cyber security threat where attackers deceive individuals into revealing sensitive information through fraudulent emails or websites. It aims to steal personal data, such as passwords or credit card details, by exploiting human vulnerabilities. Vigilance and awareness are crucial to prevent falling victim to these scams.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XBkzBrXlle0
data backup

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uEP9GTs1lZs
Data backup is a crucial aspect of cyber security design. It involves creating copies of important information to protect against data loss or breaches. By regularly backing up data, organizations can ensure quick recovery and minimize the impact of cyber attacks or system failures.
Firewall
One fun fact about firewalls is that they were originally named after the physical walls that were built to prevent the spread of fire in buildings. The concept of a digital firewall was inspired by this idea of creating a barrier to protect computer networks from unauthorized access and potential threats.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kDEX1HXybrU
stateful inspection

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M2tm5xTSt-o
Stateful inspection is a firewall technique that monitors and analyzes the state of network connections. It examines the context of data packets to determine if they are part of an established connection, providing enhanced security by allowing only authorized traffic.
packet filtering

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jkYVRtiUmJ0
Packet filtering is a firewall technique that examines data packets based on predefined rules. It allows or blocks packets based on factors like source/destination IP, port numbers, and protocols.
proxy server
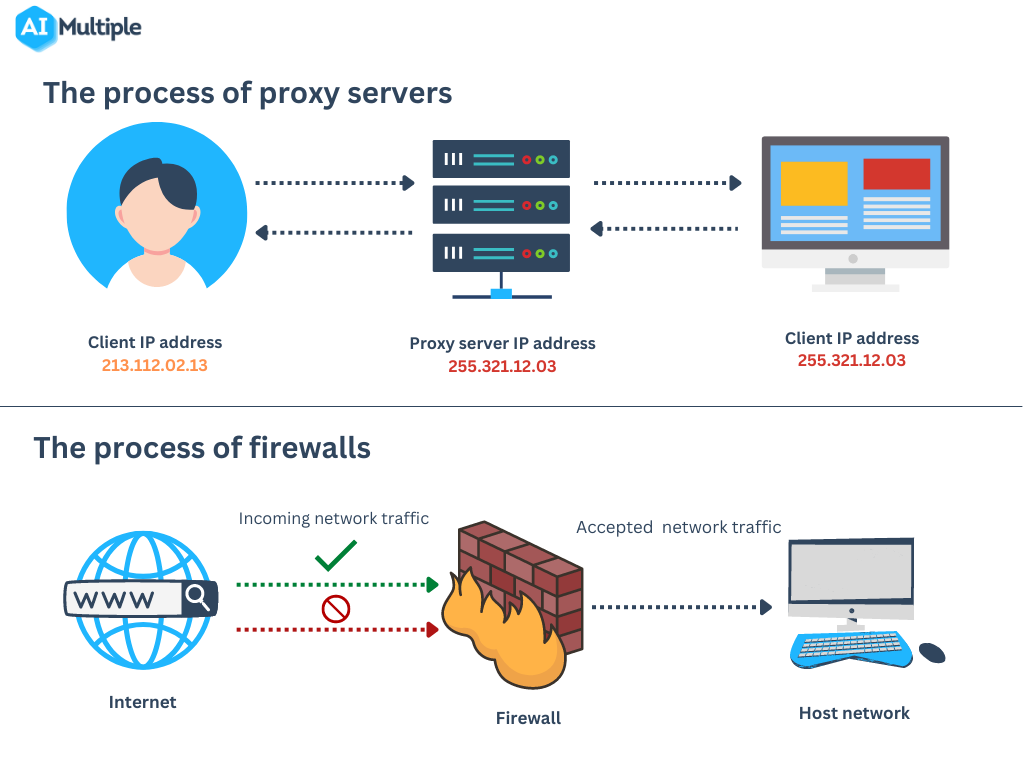
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between a user and the internet, providing an additional layer of security and privacy. It can be used within a firewall to filter and monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic, enhancing network security.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j9-Y0KWVJ1k
intrusion detection system

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kDEX1HXybrU
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a security tool that works alongside a firewall to monitor network traffic and identify potential threats or unauthorized access attempts. It enhances the firewall's capabilities by providing an additional layer of protection against intrusions.
network address translation

Network Address Translation (NAT) is a firewall technique that allows multiple devices on a private network to share a single public IP address. It masks internal IP addresses, enhancing security and conserving IP addresses.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HazLGg_pgEQ
application-level gateway
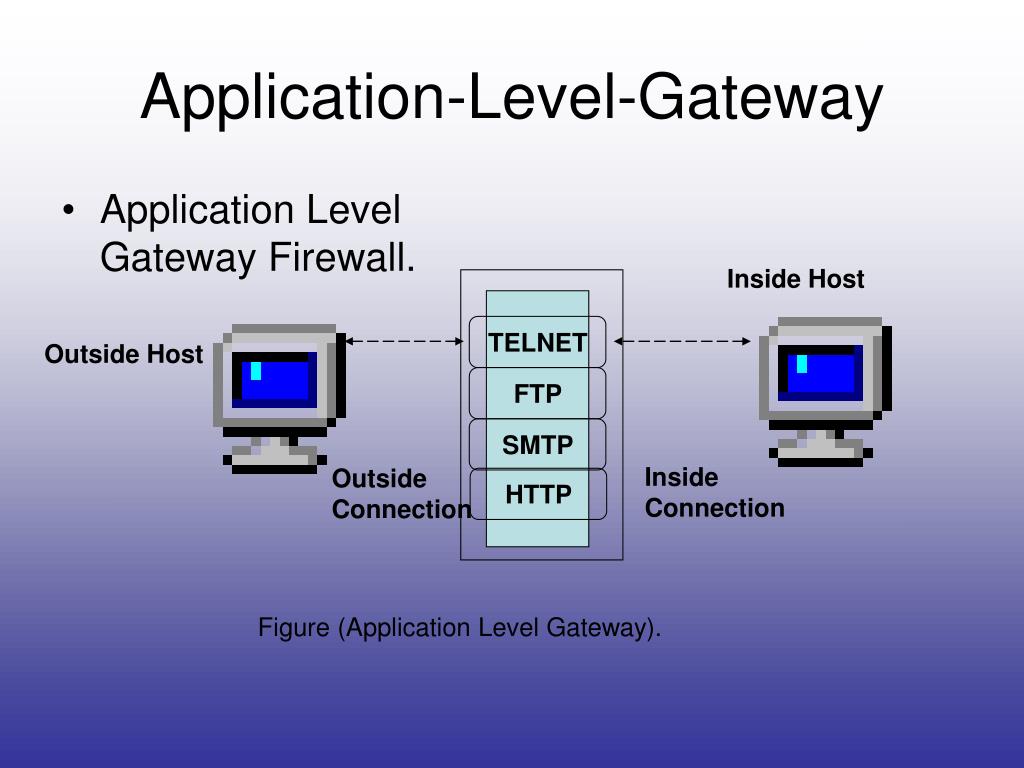
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uGaERP4Npys
An application-level gateway is a firewall component that monitors and filters network traffic at the application layer. It provides enhanced security by inspecting and controlling specific application protocols, ensuring protection against potential threats.
logging and auditing

Logging and auditing in the context of firewalls involve the recording and analysis of network traffic and security events. It helps monitor and track unauthorized access attempts, identify potential threats, and ensure compliance with security policies.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z57e4vs_CQE
virtual private network
A virtual private network (VPN) is a secure connection that allows users to access a private network over a public network. It enhances firewall protection by encrypting data and providing anonymity, ensuring secure communication and preventing unauthorized access.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R-JUOpCgTZc
Data backup

One fun fact about data backup is that the world's largest backup and recovery software company, Acronis, offers a service called "CyberFit Score" which assesses the cyber protection level of an organization and provides recommendations to improve their data backup and security measures.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FIL6L7f32Bs
backup frequency

Backup frequency refers to the regularity with which data is copied and stored to prevent loss or damage. It determines how often backups are performed, ensuring data is protected and recoverable in case of system failures, disasters, or human errors.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VmgE3vQG3lc
backup method
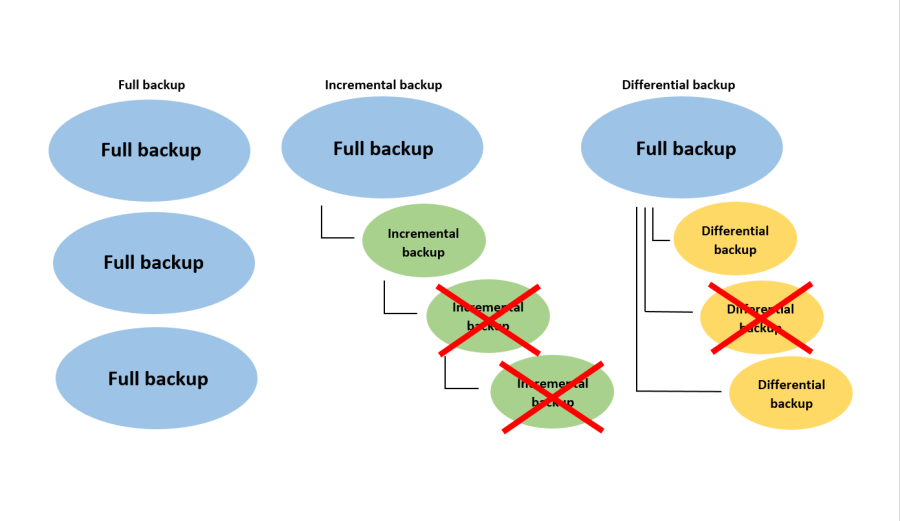
Backup methods are techniques used to create copies of data for safekeeping. They ensure data protection by duplicating files and storing them in separate locations, minimizing the risk of data loss.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o-83E6levzM
backup retention

Backup retention refers to the length of time that backup data is stored and available for recovery. It ensures that data can be retrieved in case of data loss or system failure.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CkSmo9WIjfA
backup testing
Backup testing is the process of evaluating the effectiveness and reliability of data backup systems. It ensures that backups are functioning correctly and can be restored when needed, minimizing the risk of data loss.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LZydDFT8Bx0
backup encryption

Backup encryption is the process of securing data backups by converting them into unreadable formats, ensuring protection against unauthorized access.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Crpv6bYUpFc
backup location

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Up8ufhCToFE
Backup location refers to the physical or virtual space where copies of data are stored for protection against loss or damage. It ensures data redundancy and enables quick recovery in case of emergencies, providing a secure and reliable solution for data backup.
backup automation

Backup automation is the process of automatically creating and managing data backups. It eliminates the need for manual intervention, ensuring that backups are consistently performed, reducing the risk of data loss, and improving overall efficiency.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-wXeQ3T497A
backup monitoring

Backup monitoring is the process of overseeing data backup operations to ensure their effectiveness and reliability. It involves tracking backup progress, identifying errors or failures, and taking corrective actions.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YU-4j7-sOXk