Lesson AI Summary
"Ergonomics and Workplace Design" is an immersive augmented and virtual reality experience that educates users on the principles of creating a healthier and more productive work environment. Participants will learn about the critical role of ergonomics in minimizing physical strain and discomfort, which can boost productivity by up to 25%. The experience covers optimal posture, workstation layout, and the importance of ergonomic tools such as adjustable chairs and desks, task lighting, and proper monitor placement. Users will discover how to enhance employee well-being and performance through effective design strategies that reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) and repetitive strain injuries (RSIs). Additionally, the program emphasizes the significance of noise control, temperature regulation, and the structured use of breaks to maintain focus and mental well-being. By engaging with interactive scenarios, participants will gain practical knowledge on creating tailored ergonomic solutions that align with individual needs, fostering a safer and more efficient workplace. This experience is essential for anyone looking to optimize their work environment for improved comfort and operational efficiency.
AI Conversation
Ergonomics and Workplace Design
Ergonomically designed workplaces can increase productivity by up to 25%, as they reduce physical strain and discomfort, leading to fewer breaks and enhanced focus. This optimization not only boosts employee well-being but also contributes to overall operational efficiency.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EgELCpY62jc
posture

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MWfMqTvB6Y0
Posture in ergonomics and workplace design is critical for minimizing musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) and enhancing productivity. Optimal posture involves aligning the spine, neck, and limbs to reduce strain. Ergonomic interventions, such as adjustable chairs and desks, promote neutral postures, thereby mitigating fatigue and improving employee well-being and performance.
noise control
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SjY9fbHtyjw
Noise control in ergonomics and workplace design focuses on minimizing auditory distractions to enhance productivity and employee well-being. It involves strategic use of sound-absorbing materials, spatial layout optimization, and acoustic engineering. Effective noise management reduces stress, prevents hearing loss, and fosters a conducive work environment, aligning with occupational health standards.
equipment design

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oBkGxMV6UEE
Equipment design in ergonomics focuses on optimizing workplace tools and environments to enhance user comfort, efficiency, and safety. It involves anthropometric data analysis, minimizing repetitive strain, and ensuring intuitive interfaces. Effective design reduces fatigue, prevents injuries, and improves productivity by aligning equipment functionality with human capabilities and limitations.
lighting

In workplace ergonomics, optimal lighting is crucial for enhancing productivity and reducing eye strain. Proper illumination minimizes glare, supports visual tasks, and aligns with circadian rhythms. Adjustable lighting solutions, such as task lighting and ambient controls, cater to individual preferences, promoting comfort and overall well-being in the work environment.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gHbiJtnbSh4
workstation layout
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dVFtAEDlnRA
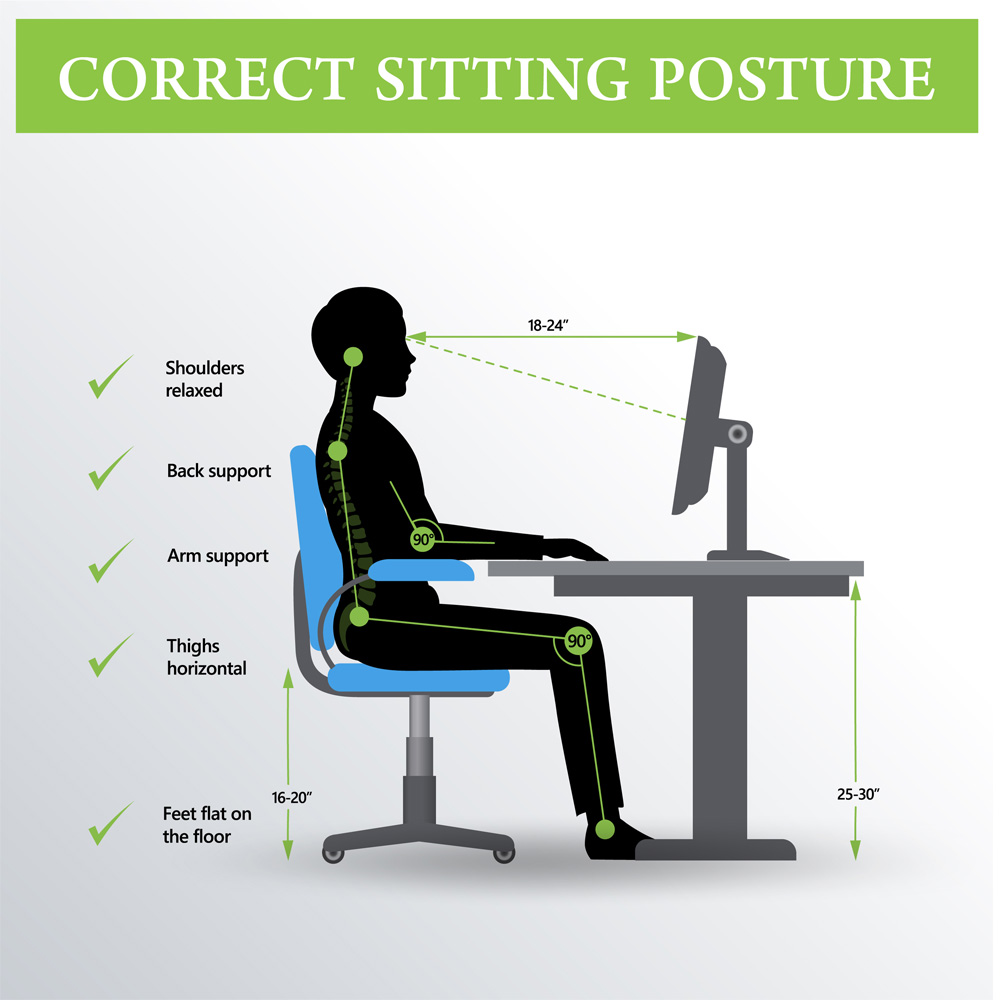
Workstation layout in ergonomics and workplace design focuses on optimizing employee comfort and productivity. Key elements include adjustable chairs, desks at appropriate heights, and monitor positioning to reduce strain. Proper lighting and minimal clutter enhance focus and efficiency, while ergonomic tools mitigate repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) and musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs).
training

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O6FAz4F1j2k
Training in ergonomics and workplace design focuses on optimizing employee well-being and productivity by educating staff on proper posture, equipment use, and workspace arrangement. It aims to reduce musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) and enhance efficiency through tailored programs, fostering a safer and more comfortable work environment.
temperature

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dTlHpnctRuw
Temperature is a critical factor in ergonomics and workplace design, impacting employee comfort, productivity, and health. Optimal thermal conditions, typically between 20-24°C (68-75°F), minimize thermal stress and enhance cognitive performance. Effective HVAC systems and adaptive clothing policies are essential to maintain thermal comfort and comply with occupational health standards.
breaks
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K88q_oEwRS8
In ergonomics and workplace design, breaks are essential for mitigating musculoskeletal strain and enhancing productivity. Regular intervals, such as micro-breaks and scheduled pauses, facilitate physical movement, reduce cognitive fatigue, and promote mental well-being. Implementing structured break schedules aligns with occupational health guidelines, optimizing employee performance and workplace safety.
Workstation Layout

A well-designed workstation layout can reduce musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) by up to 60%, enhancing both safety and productivity by ensuring ergonomic alignment and minimizing repetitive strain.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dVFtAEDlnRA
chair

In workstation layout, the chair is pivotal for ergonomic design, impacting user comfort and productivity. Key features include adjustable height, lumbar support, and swivel capability, promoting optimal posture and reducing strain. Proper chair selection enhances employee well-being, minimizes musculoskeletal disorders, and aligns with occupational health standards.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CCTRWARIBDs
desk

In workstation layout, a desk serves as the primary surface for task execution, influencing ergonomics, productivity, and space utilization. It accommodates essential equipment like computers and peripherals, and its design—considering factors such as height, size, and material—affects user comfort and workflow efficiency within the office environment.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XZMXdlg3yhQ
footrest

A footrest in workstation layout enhances ergonomic comfort by promoting proper posture and reducing strain on the lower back and legs. It supports optimal blood circulation and aligns the body ergonomically, mitigating fatigue. Adjustable footrests accommodate various user heights, ensuring compliance with occupational health standards and improving overall productivity.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9ql_KKFsFwk
keyboard

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Es66Y2z6S28
The keyboard is a critical component in workstation ergonomics, influencing user comfort and productivity. Optimal placement involves aligning the keyboard with the user's elbows at a 90-degree angle, minimizing wrist strain. Adjustable keyboard trays and ergonomic designs, such as split or tented keyboards, further enhance posture and reduce repetitive strain injuries (RSIs).
monitor

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l1N3jlgqcQ4
In workstation layout, the monitor is pivotal for ergonomic efficiency and productivity. Optimal placement involves aligning the top of the screen at or slightly below eye level, maintaining a 20-40 inch distance from the user. This minimizes eye strain and supports a neutral neck posture, enhancing overall user comfort and performance.
lighting

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Jp654JD5pg
Effective workstation lighting enhances productivity and reduces eye strain. Optimal layouts incorporate adjustable, glare-free lighting, balancing natural and artificial sources. Task lighting should be directed and dimmable, complementing ambient illumination. Consideration of color temperature and luminance levels ensures visual comfort, aligning with ergonomic standards and promoting a conducive work environment.
mouse
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rt95mpTGBRA
In workstation layout, the mouse is a critical input device, influencing ergonomics and productivity. Optimal placement minimizes strain, ideally positioned close to the keyboard at elbow height. Consideration of mouse type—wired, wireless, ergonomic—affects user comfort and efficiency, impacting overall workstation effectiveness and user health.
document holder

A document holder in workstation layout is an ergonomic accessory designed to position documents at eye level, reducing neck strain and enhancing productivity. It facilitates seamless transitions between screen and paper, optimizing workspace efficiency. Proper placement aligns with ergonomic principles, promoting a comfortable and organized work environment.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EVdRMWogTOc
image of wrong posture

A fun fact about images depicting incorrect posture in safety training is that they often use exaggerated poses to highlight risks, making them memorable and engaging, which enhances retention and awareness among employees.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OyK0oE5rwFY
head tilt
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kt-jibhaPYA
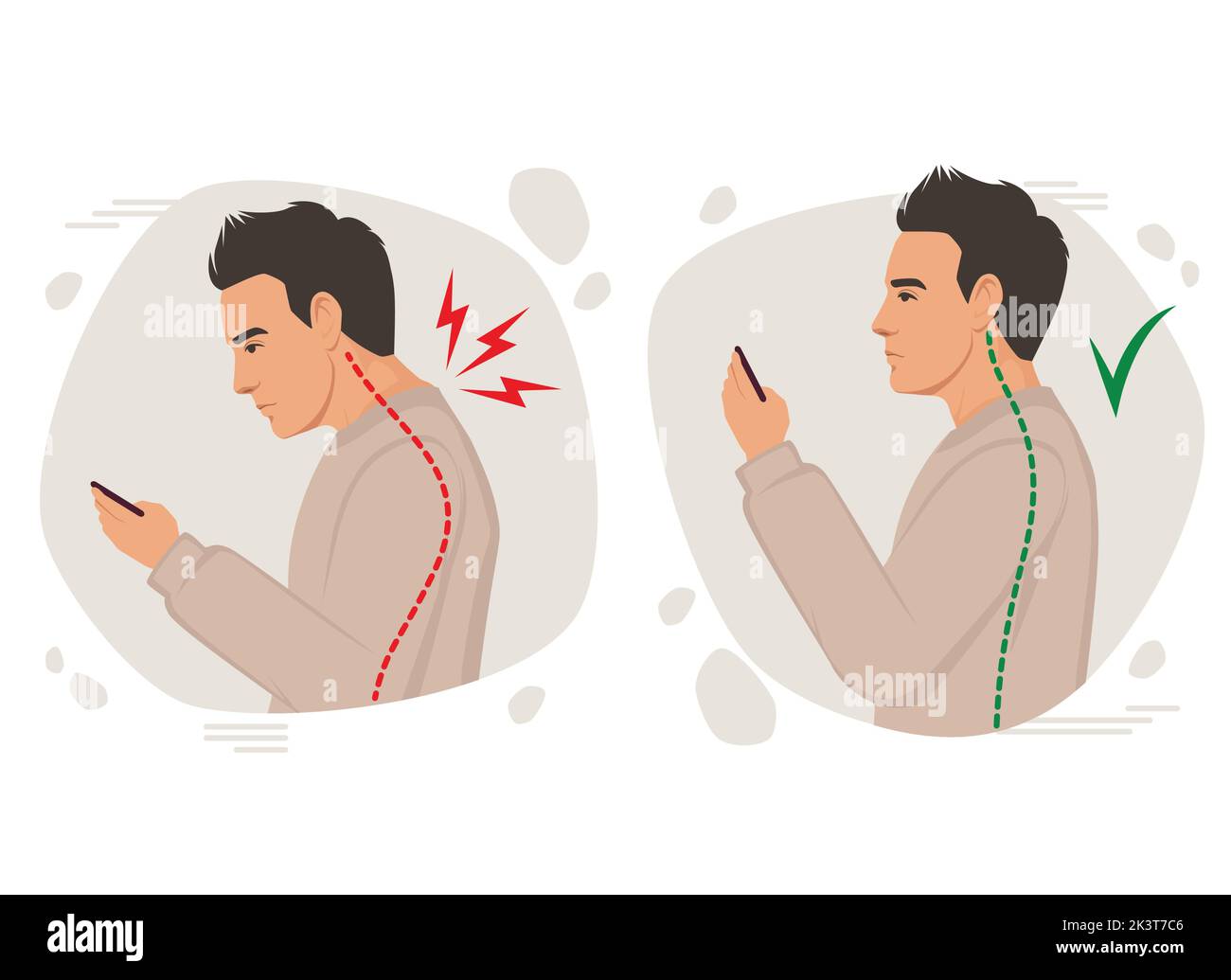
Head tilt in images of incorrect posture often indicates musculoskeletal strain, particularly in the cervical region. This misalignment can lead to discomfort, reduced ergonomic efficiency, and potential long-term health issues. Identifying and correcting head tilt is crucial for maintaining proper posture and preventing associated complications in workplace settings.
rounded shoulders

Rounded shoulders, a common postural deviation, occur when the shoulders are positioned forward, often due to prolonged sitting or improper ergonomics. This misalignment can lead to muscular imbalances and discomfort. In images depicting poor posture, rounded shoulders are a key indicator of potential musculoskeletal issues and ergonomic inefficiencies.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LkaIim4Zdhw
curved spine

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3tiQWwNcu_I
A curved spine, often resulting from poor posture, can be visually identified in images depicting incorrect postural alignment. This condition, known as postural kyphosis or scoliosis, manifests as an abnormal curvature, potentially leading to discomfort, musculoskeletal strain, and long-term spinal health issues if not addressed through corrective measures and ergonomic adjustments.
arm position
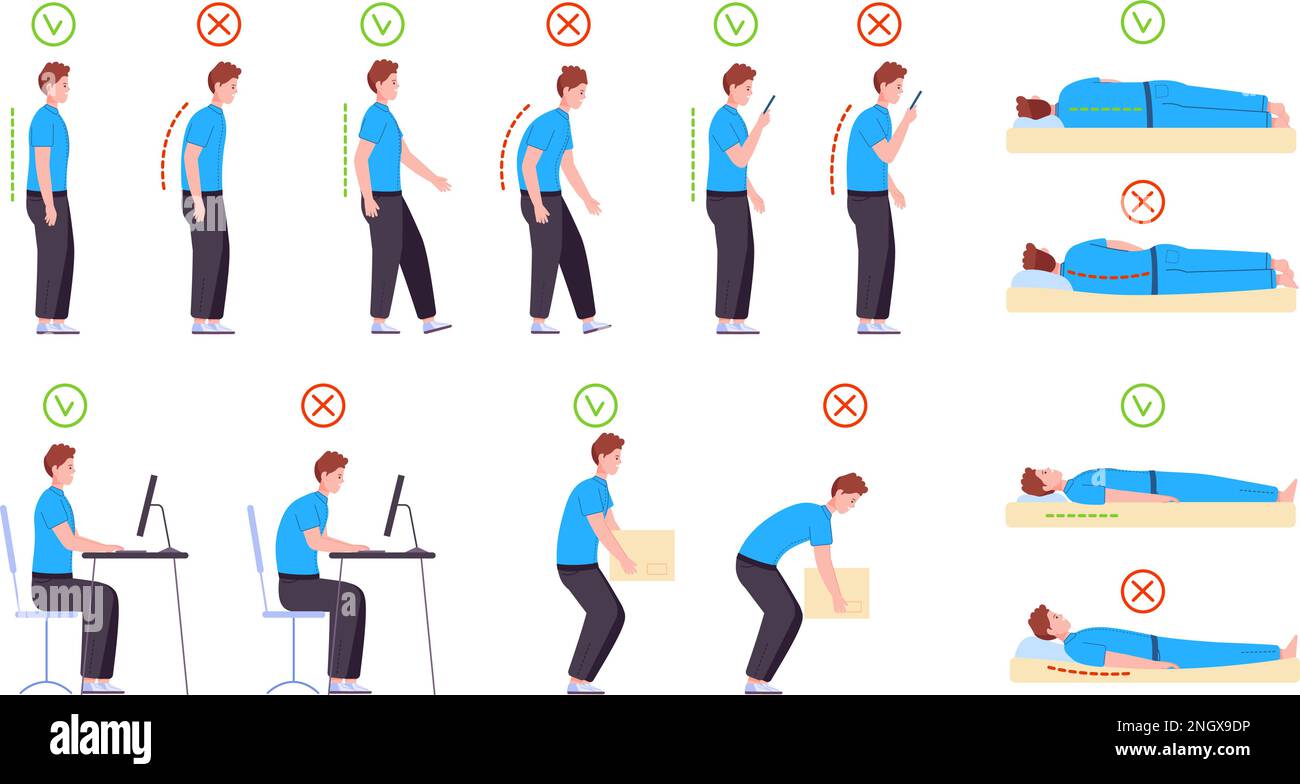
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=riD8Xt8r1MQ
In images depicting incorrect posture, arm positioning often contributes to musculoskeletal strain. Misaligned arms, such as those elevated or extended awkwardly, can lead to shoulder tension and discomfort. Proper ergonomic alignment, ensuring arms are relaxed and parallel to the torso, is crucial to mitigate stress and promote optimal posture.
foot placement

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k9kVD7ACdtA
Foot placement is crucial in maintaining proper posture. Incorrect foot positioning can lead to misalignment of the body, causing strain on muscles and joints. In images depicting poor posture, improper foot placement often results in uneven weight distribution, contributing to discomfort and potential long-term musculoskeletal issues.
back support

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CXUtOm6cDC8
Improper posture, often depicted in images, can lead to significant back strain and discomfort. Back support solutions, such as ergonomic chairs and lumbar cushions, are essential in mitigating these issues. They promote spinal alignment, reduce pressure on the vertebrae, and enhance overall comfort, thereby preventing long-term musculoskeletal disorders.
pelvic tilt
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pdKyaLe5R5A
Pelvic tilt, often depicted in images illustrating poor posture, refers to the misalignment of the pelvis, either anteriorly or posteriorly. This misalignment can lead to compensatory postural deviations, affecting spinal alignment and contributing to discomfort or musculoskeletal issues. Correcting pelvic tilt is crucial for maintaining optimal posture and preventing related health problems.

knee position

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0hhmjhgUghg
In analyzing images of incorrect posture, knee positioning is critical. Misalignment, such as hyperextension or inward collapse (valgus), can indicate poor posture. These deviations can lead to increased stress on the knee joint, contributing to discomfort or injury. Proper knee alignment is essential for maintaining overall musculoskeletal health and posture integrity.
ergonomic keyboard

Ergonomic keyboards are designed to reduce strain by promoting a natural hand, wrist, and forearm position, which can decrease the risk of repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) and enhance typing comfort and efficiency.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GSacX1gzU8c
tent angle

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pUKoB95aEc4
Tent angle refers to the vertical inclination of an ergonomic keyboard, designed to reduce wrist strain by aligning the forearms and wrists in a more natural, neutral position. This ergonomic adjustment minimizes ulnar deviation and promotes comfort, potentially reducing the risk of repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) in users.
curved layout

Curved layouts in ergonomic keyboards are designed to align with the natural curvature of the human hand, reducing strain and enhancing comfort. By minimizing wrist deviation and promoting a neutral typing posture, these keyboards aim to alleviate repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) and improve typing efficiency and user experience.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XScUYxLFt-U
compact size
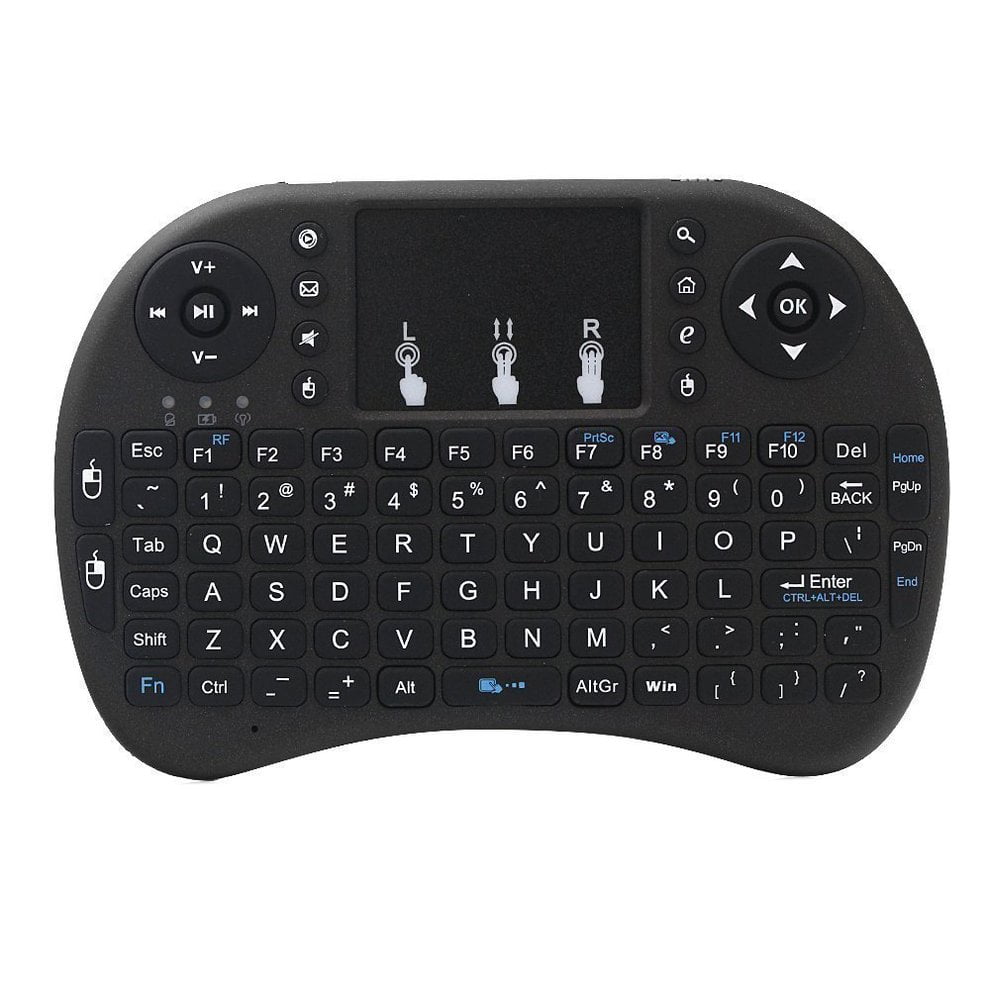

Compact-sized ergonomic keyboards are designed to minimize desk space usage while promoting user comfort and reducing strain. By integrating ergonomic principles, such as split layouts and tenting, these keyboards enhance typing posture and efficiency. Their reduced footprint facilitates portability and adaptability, making them ideal for dynamic work environments.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lKYrCjB8B6A
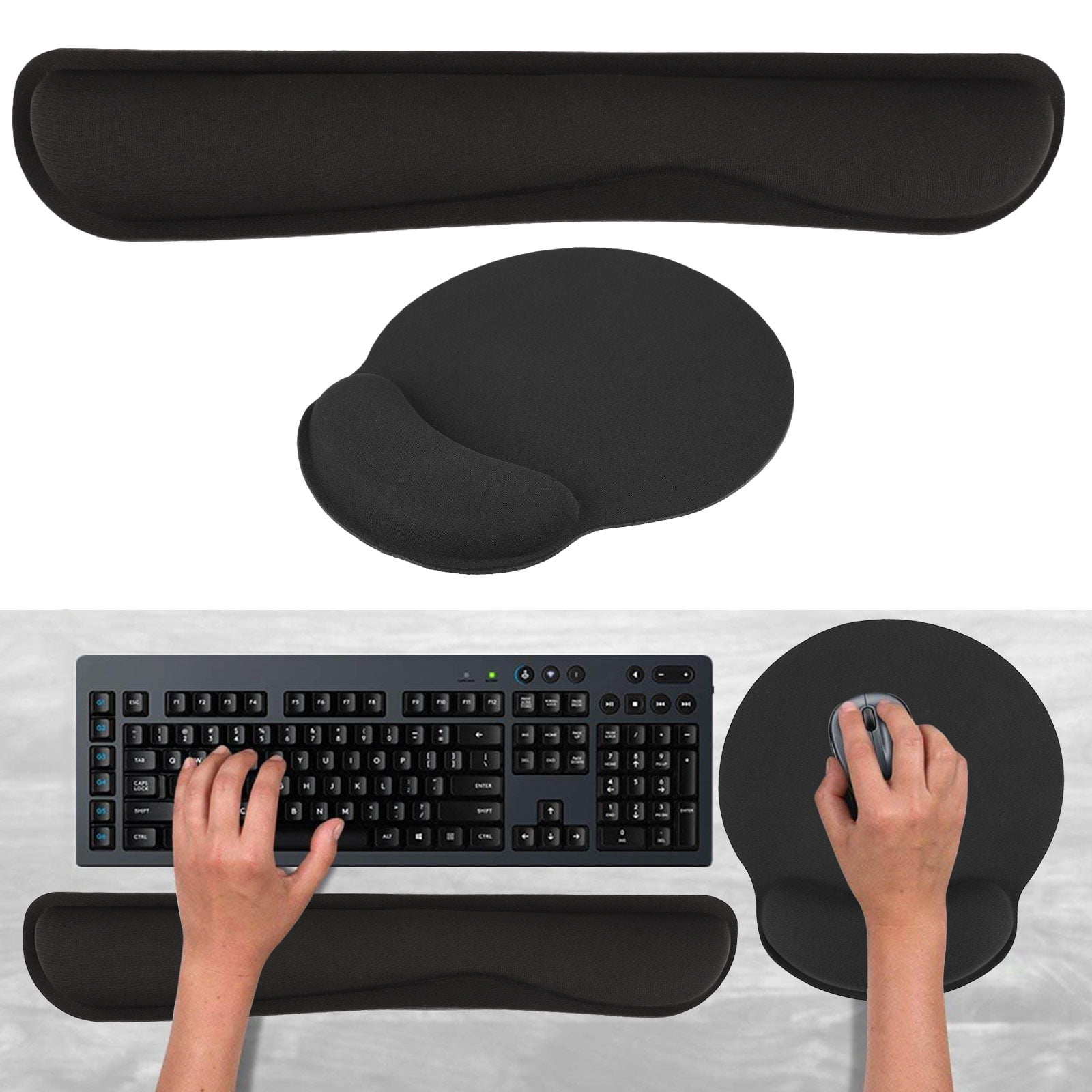
wrist rest

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZiHnbJ7w9EY
A wrist rest is an ergonomic accessory designed to support the wrists while typing on a keyboard. It helps maintain a neutral wrist position, reducing strain and preventing repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) such as carpal tunnel syndrome. Proper wrist alignment enhances comfort and productivity in prolonged computer use.
split design
A split design in ergonomic keyboards refers to a configuration where the keyboard is divided into two separate sections. This design promotes natural hand positioning, reduces ulnar deviation, and minimizes strain on the wrists and forearms, thereby enhancing user comfort and reducing the risk of repetitive strain injuries (RSIs).
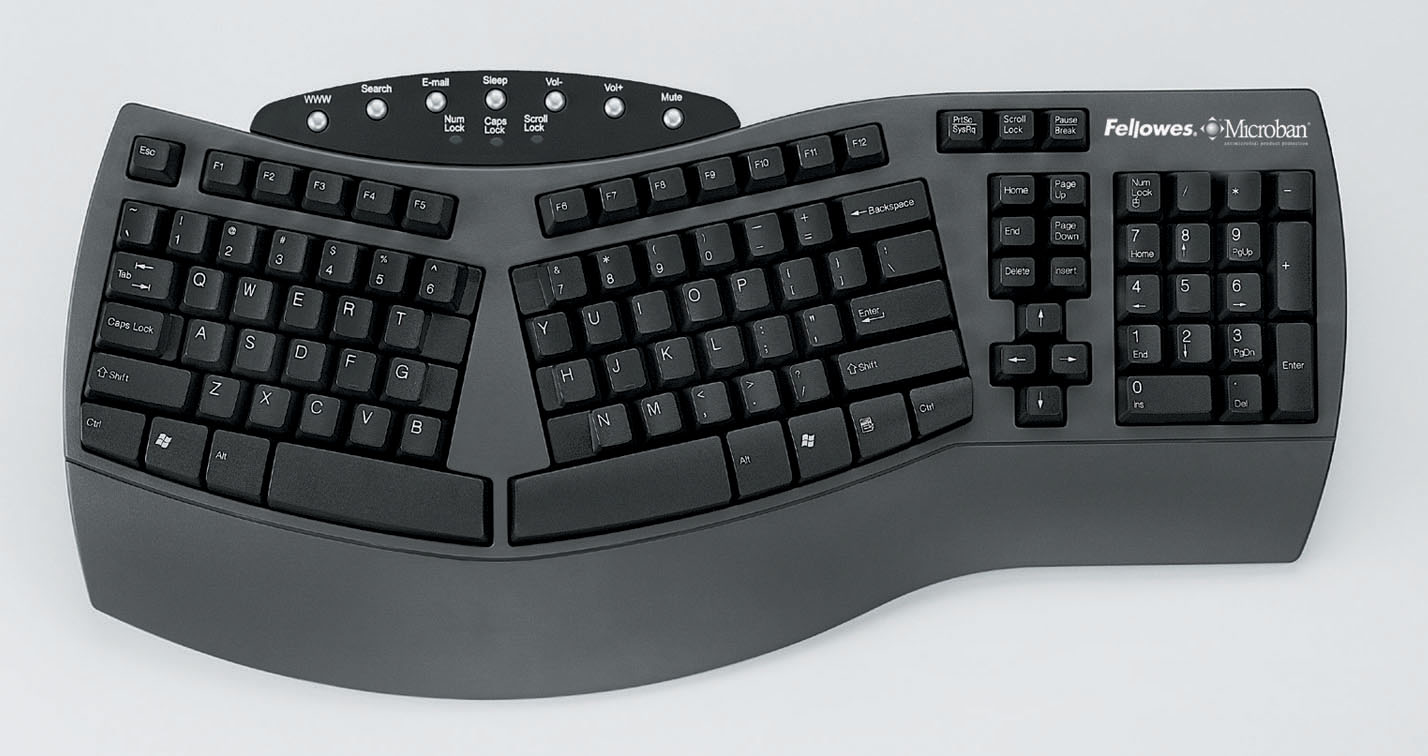

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q8FeBPREzZA
adjustable height

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZgJOxlD11xM
Adjustable height in ergonomic keyboards enhances user comfort by allowing customization to individual ergonomic needs. It reduces strain on wrists and forearms, promoting a neutral typing posture. This feature supports prolonged use, minimizes repetitive strain injuries (RSIs), and aligns with occupational health standards for workplace ergonomics.
key travel

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=czwX1BdepdM
Key travel refers to the distance a key moves when pressed on an ergonomic keyboard. Optimal key travel enhances typing comfort and reduces strain by providing tactile feedback and minimizing finger fatigue. Ergonomic keyboards typically feature a key travel distance of 1.5 to 2.0 mm for improved user experience.
tactile feedback
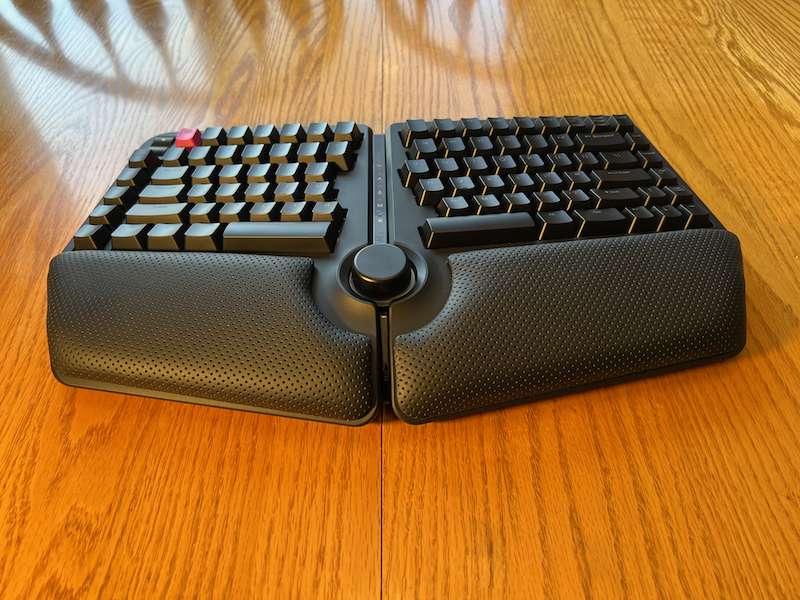

Tactile feedback in ergonomic keyboards enhances user experience by providing physical sensations upon keypress, improving typing accuracy and speed. This haptic response reduces strain and fatigue, promoting comfort during extended use. By simulating mechanical switch actuation, it aids in minimizing repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) and optimizing ergonomic efficiency.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=REgaiV831iU