AI Conversation
Inverter

Inverters can convert DC power from sources like solar panels into AC power, which is used by most household appliances, enabling the integration of renewable energy into everyday life.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1rxSapfp4Hs
roof mount
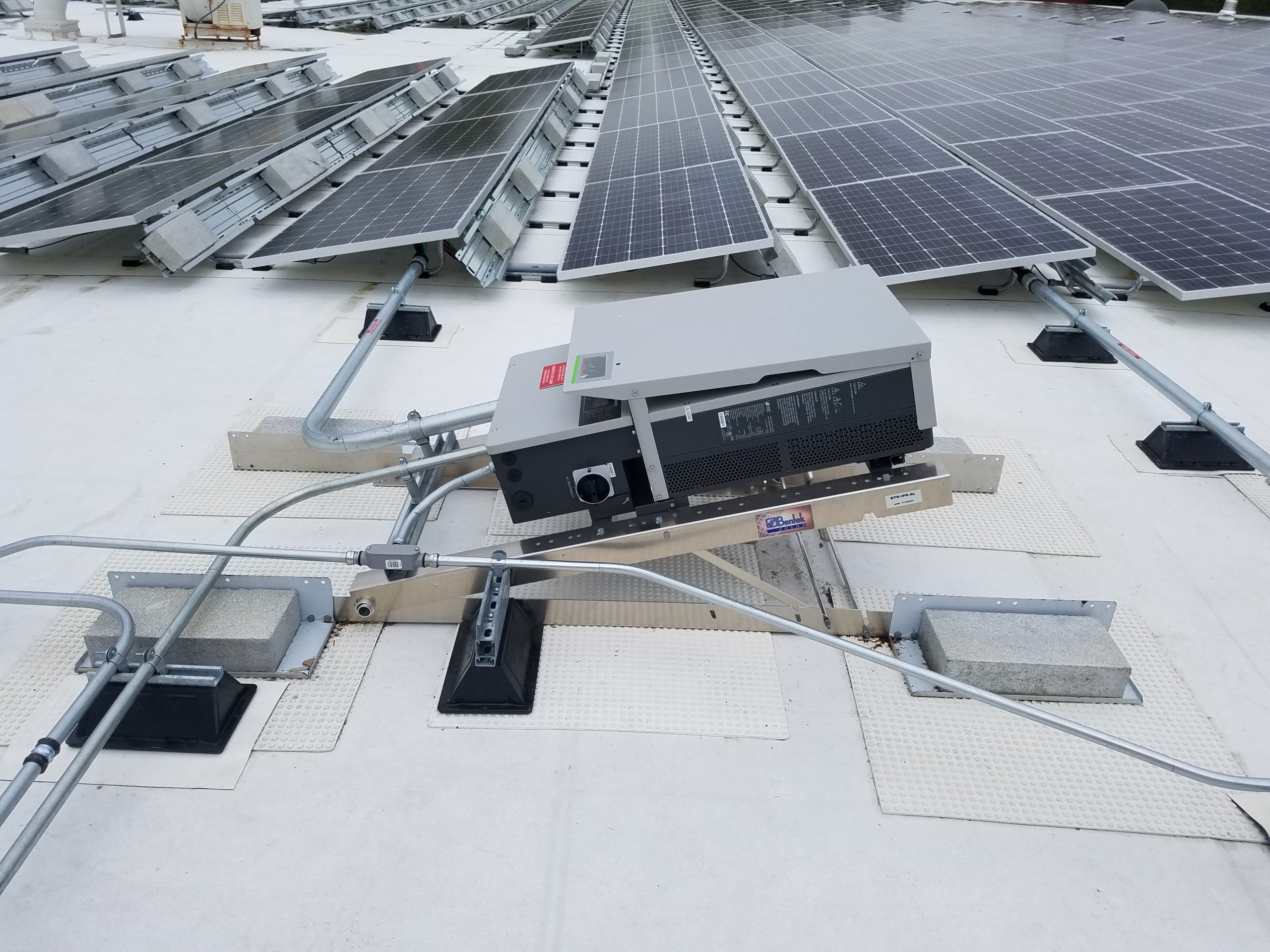

Roof-mounted inverters are integral to solar energy systems, converting DC from solar panels into AC for home use. Positioned on rooftops, they optimize space and energy efficiency, reduce transmission losses, and enhance system performance. Their installation requires careful consideration of roof structure and weatherproofing to ensure durability.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wLoF9rMlmWk
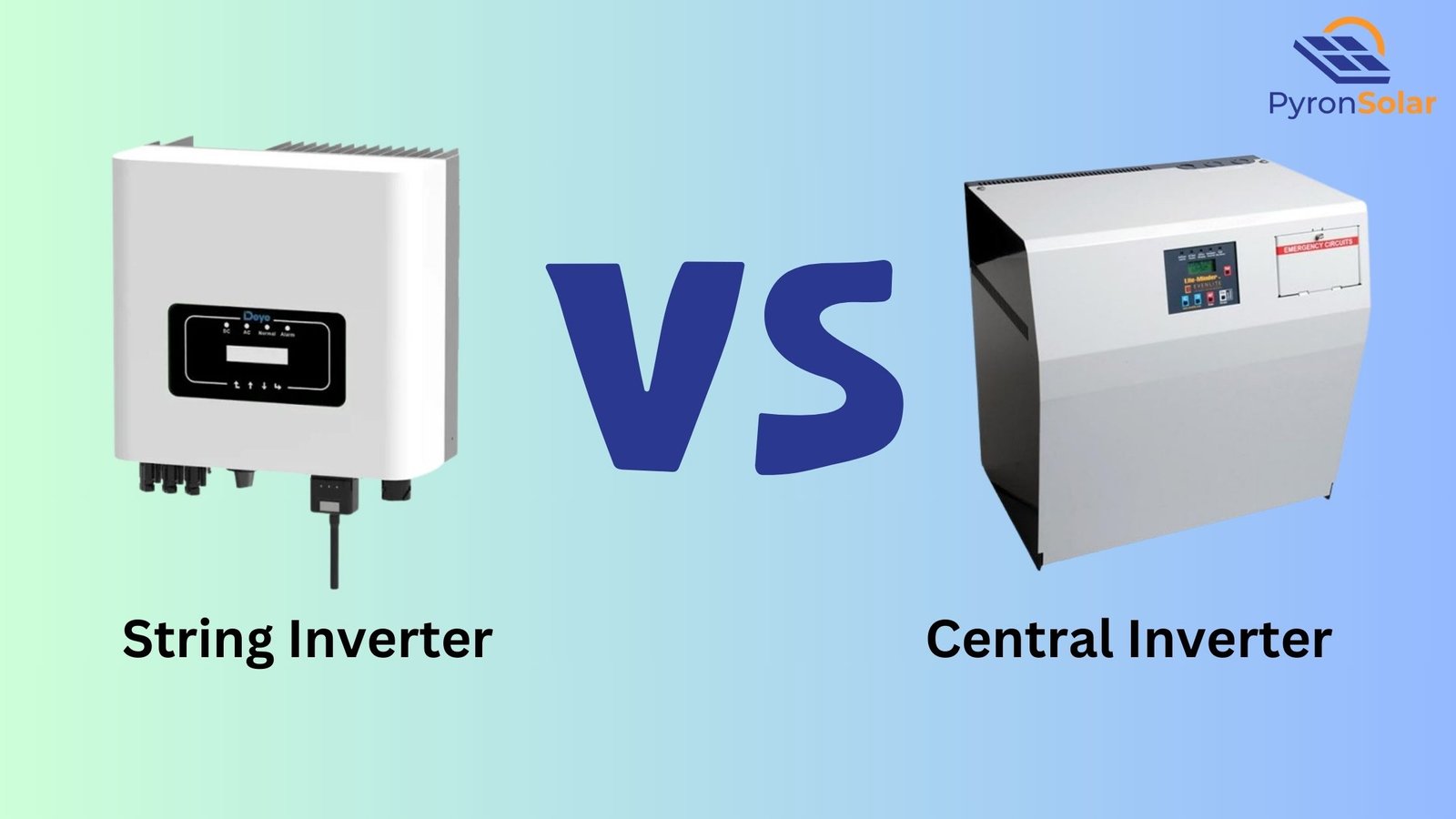
string inverter
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g8nP1B3Zeso
A string inverter is a device used in solar energy systems to convert direct current (DC) from solar panels into alternating current (AC) for home or grid use. It connects multiple panels in series, optimizing performance and cost-effectiveness, but may be less efficient in shaded conditions compared to microinverters.
microinverter
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hVzAKJvxRjM
Microinverters are small, individual inverters attached to each solar panel, converting DC to AC electricity. Unlike traditional string inverters, they optimize each panel's output independently, enhancing efficiency and reliability. This setup improves performance in shaded conditions and simplifies system monitoring, making microinverters ideal for residential solar installations.
power optimizer
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I4czBPobtg0

A power optimizer is a device used in solar energy systems to maximize the energy output of each solar panel. It works in conjunction with inverters by performing maximum power point tracking (MPPT) at the panel level, enhancing system efficiency, reducing losses, and improving overall energy yield.
pole mount

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=abfXLujggBo
A pole mount for inverters is a structural solution used to elevate and secure inverters above ground level. This setup enhances cooling, protects against flooding, and optimizes space in solar installations. Ideal for areas with limited ground space, it ensures efficient energy conversion and system longevity.
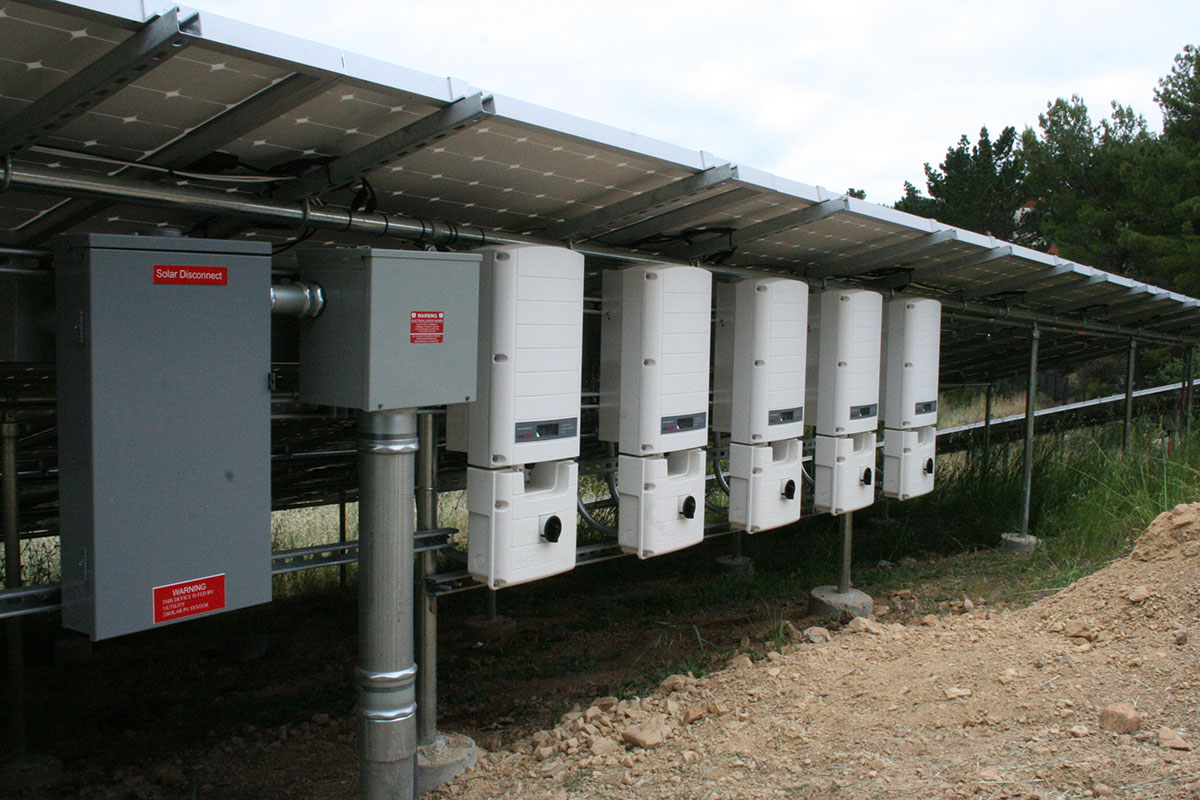
ground mount
Ground mount systems in the context of inverters refer to solar installations where panels are affixed to the ground rather than rooftops. These systems often utilize string or central inverters to convert DC to AC power efficiently, optimizing energy output and facilitating maintenance in large-scale solar projects.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eRPYImCht-s

tracking mount
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zZ8Dq207Szk
Tracking mounts in inverters are mechanisms that adjust the orientation of solar panels to follow the sun's path, maximizing energy capture. By optimizing the angle of incidence, these mounts enhance the efficiency and output of solar inverters, ensuring consistent energy production throughout the day and improving overall system performance.
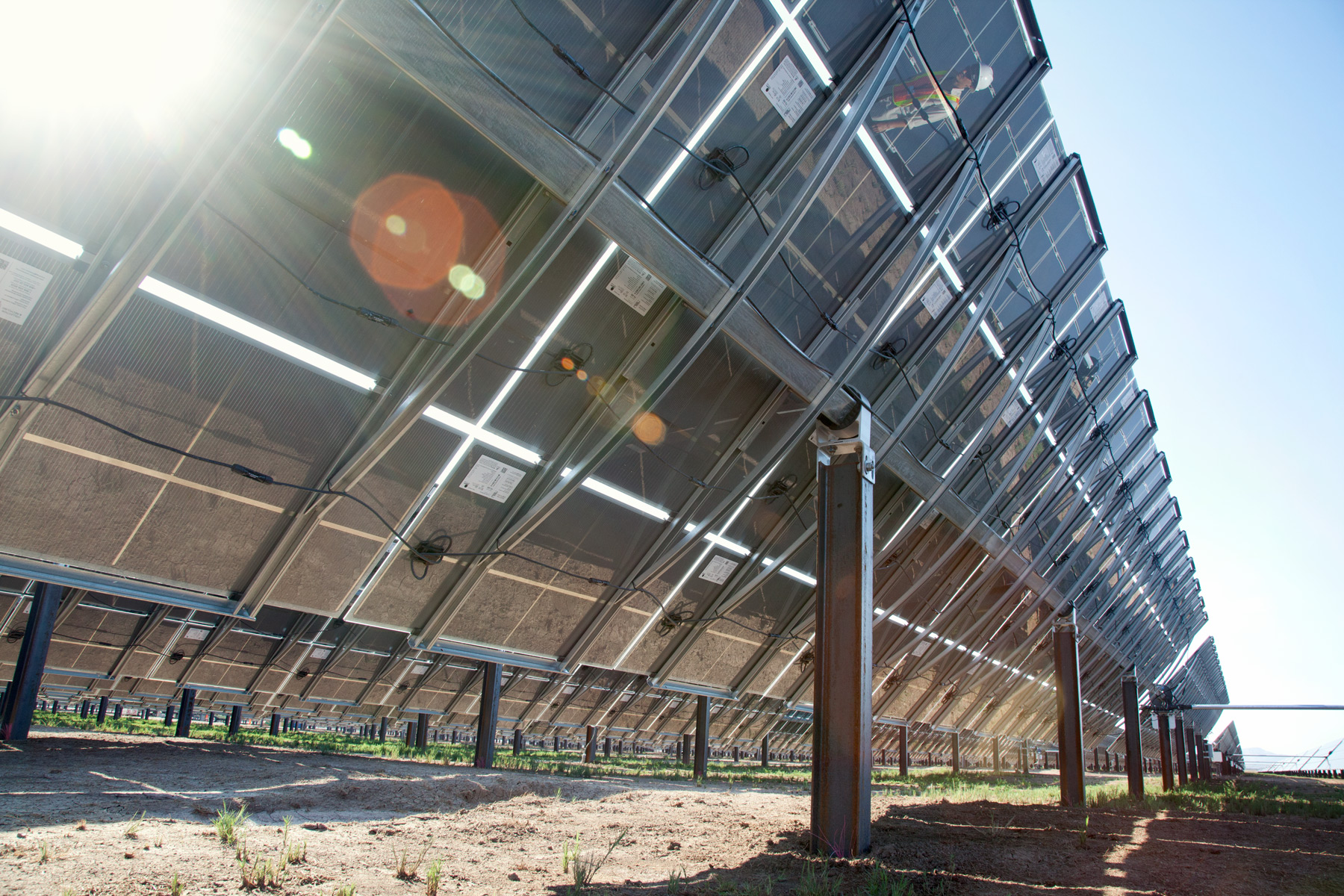

fixed tilt mount
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o9YxpK_Sf8o
A fixed tilt mount is a solar panel installation method where panels are set at a constant angle, optimizing energy capture based on geographic location. In the context of inverters, it ensures consistent energy flow by maintaining optimal panel orientation, enhancing inverter efficiency and overall solar system performance.
Solar energy and types of solar panel mounts
Solar energy is abundant; in just one hour, the sun provides enough energy to power the entire world for a year. Solar panel mounts come in various types, including fixed, adjustable, and tracking mounts, each designed to optimize sunlight capture.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SbwPfoJm8b0
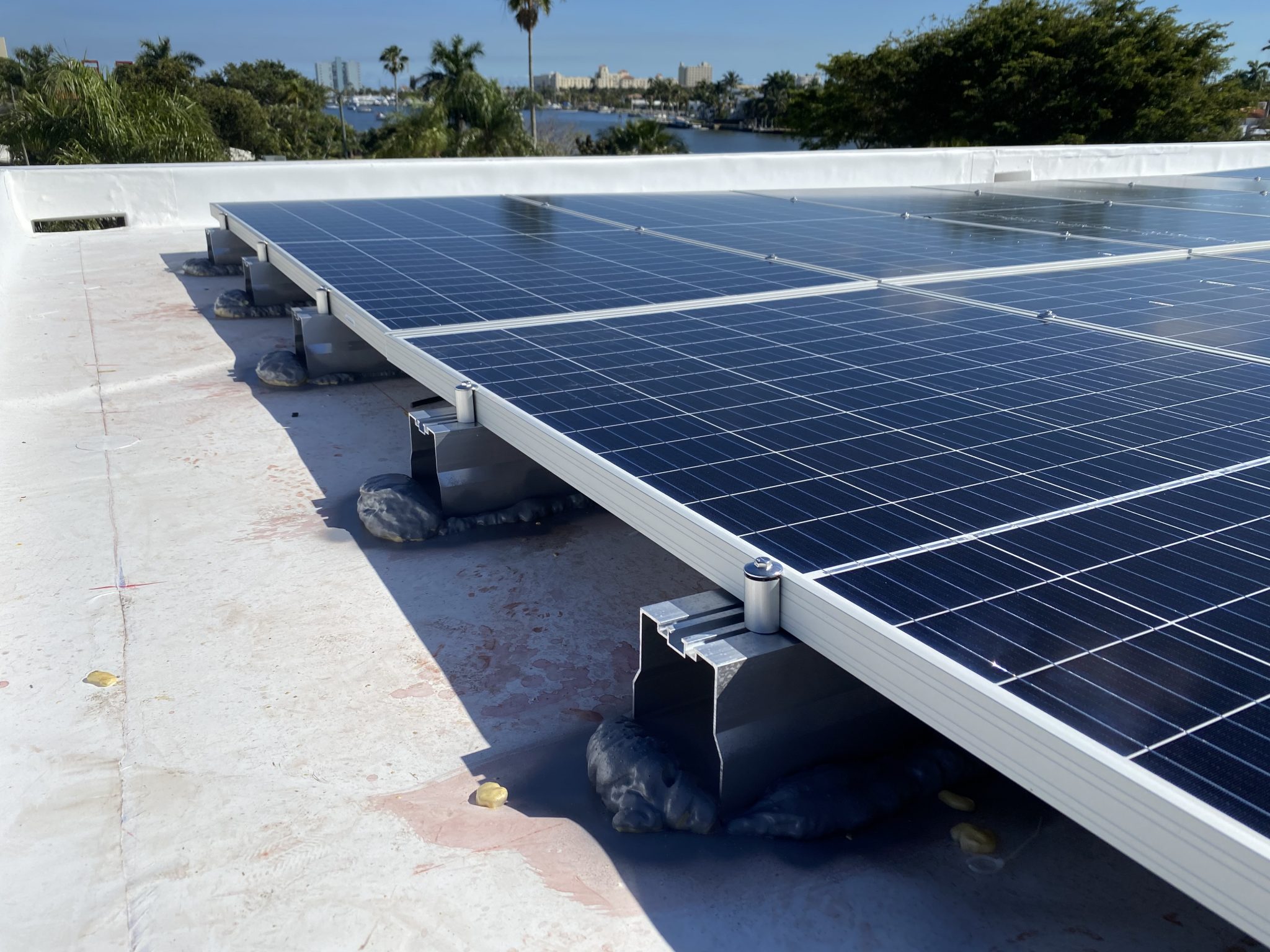
mounting system

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LjrY4fLdVBc
Mounting systems in solar energy secure panels to surfaces like roofs or the ground, optimizing sun exposure. Key types include roof mounts (fixed, adjustable, and flush), ground mounts (standard and pole), and tracking systems that follow the sun's path, enhancing efficiency and energy capture.
battery storage
/GettyImages-1270012506-3d1791e86fee42498c8bb4cdd9c3bff4.jpg)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EZWJVsn2D3A
Battery storage enhances solar energy systems by storing excess power for use during low sunlight. It ensures a reliable energy supply and maximizes efficiency. Solar panel mounts, including roof, ground, and pole mounts, optimize panel orientation and exposure, enhancing energy capture and system performance in various settings.
photovoltaic cells

Photovoltaic cells convert sunlight into electricity, forming the core of solar energy systems. They are integrated into solar panels, which can be mounted using various methods: fixed mounts for stability, adjustable mounts for seasonal optimization, and tracking mounts that follow the sun for maximum efficiency.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jneaauRjI8I
inverter
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DIkCQ1NU1E0
In solar energy systems, inverters convert direct current (DC) from solar panels into alternating current (AC) for home use. Types of solar panel mounts include fixed mounts, which are stationary; adjustable mounts, allowing angle changes; and tracking mounts, which follow the sun's path for optimal energy capture.
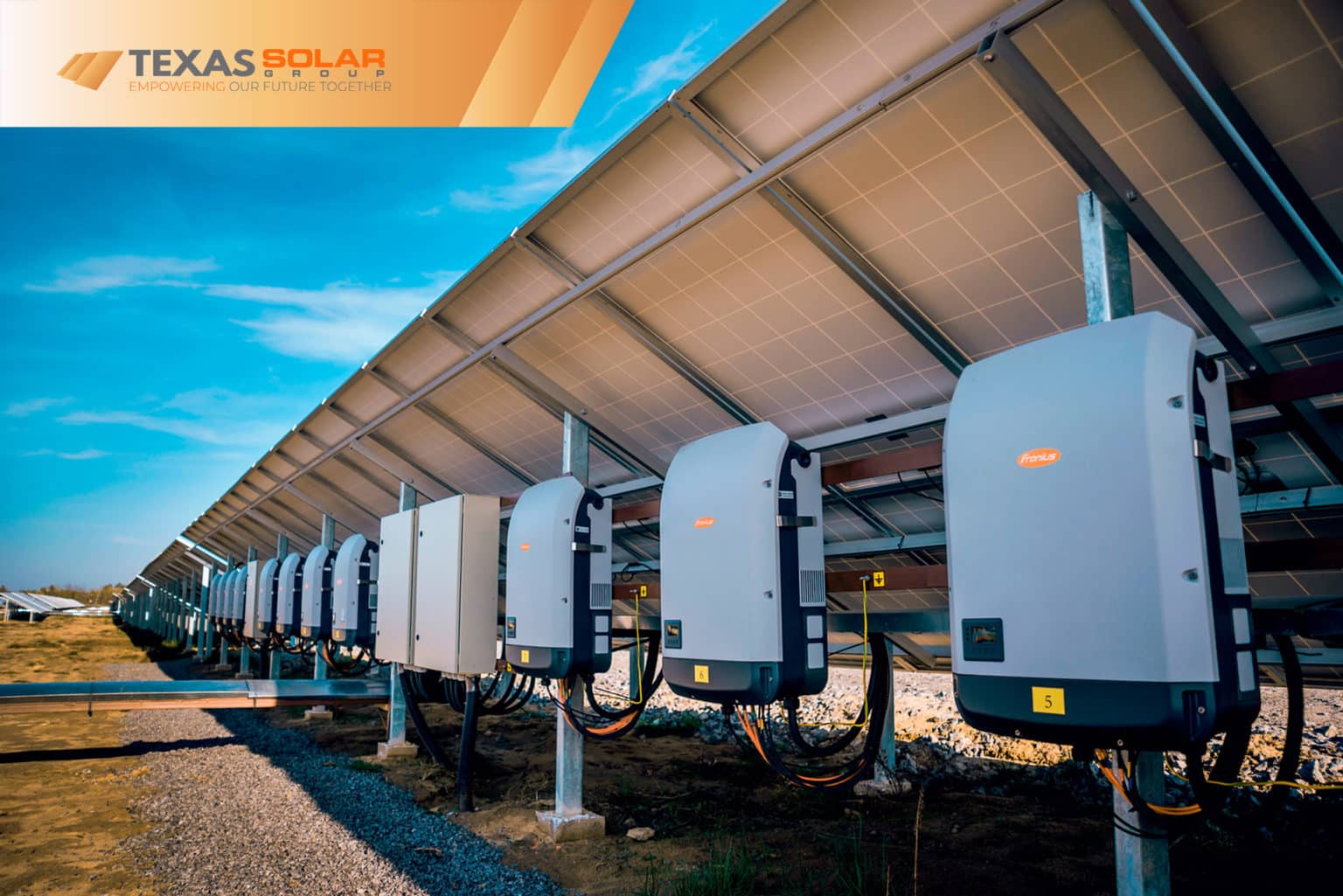

charge controller
A charge controller regulates voltage and current from solar panels to batteries, preventing overcharging and prolonging battery life. Solar panel mounts include fixed mounts, which are stationary; adjustable mounts, allowing angle changes; and tracking mounts, which follow the sun's path for optimal energy capture.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kF_cVEYxj3E
ground mount

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B_kaIiYAY4Q
Ground mounts are a type of solar panel installation where panels are affixed to a framework anchored to the ground. Ideal for large, open spaces, they offer optimal sun exposure and cooling. Other types include roof mounts, which are installed on rooftops, and pole mounts, which elevate panels on single poles.
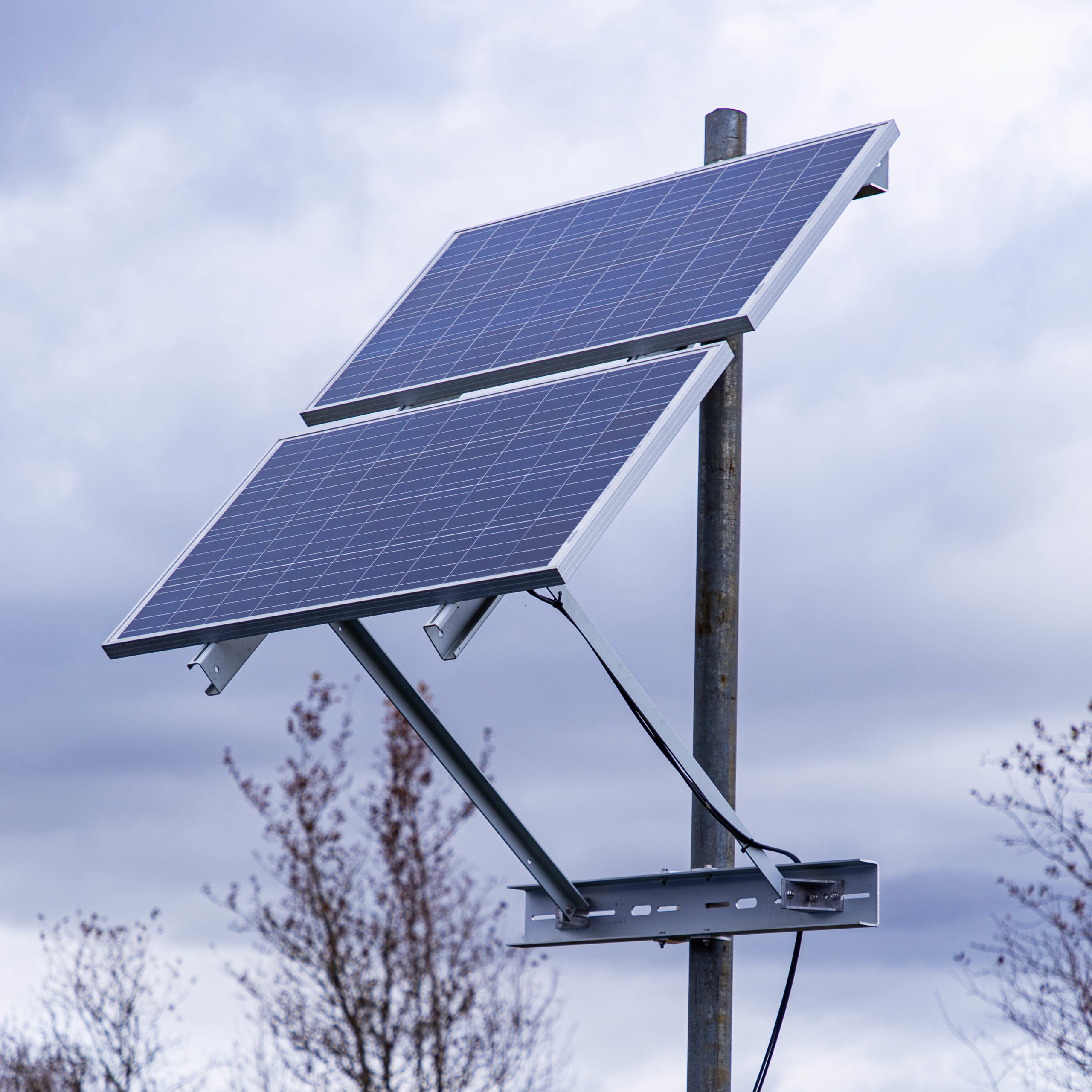
pole mount

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gZvLsO7Ow3M
Pole mounts are a type of solar panel mounting system used in solar energy installations. They elevate panels on a single pole, optimizing sun exposure and minimizing ground space usage. Ideal for uneven terrain, pole mounts can be fixed or adjustable, complementing other types like roof and ground mounts.
roof mount
Roof mounts are a popular method for installing solar panels, utilizing existing roof space to maximize sunlight exposure. They come in various types, including flush mounts, which are parallel to the roof, and tilt mounts, which adjust angles for optimal sun capture, enhancing energy efficiency in solar energy systems.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wzsSZhk7Lz0
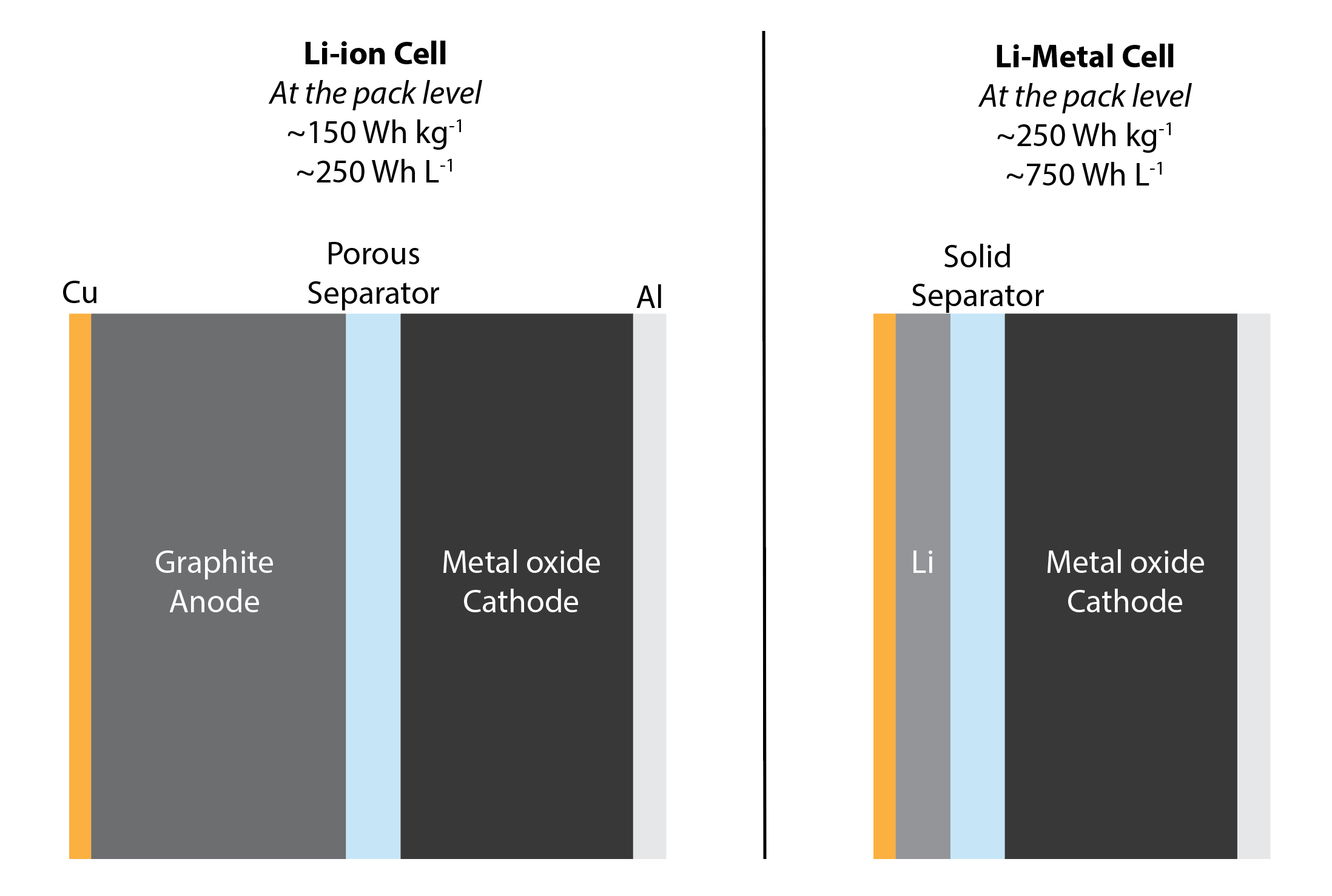
lthium batteries

Lithium batteries were first commercialized in the 1990s and have since revolutionized portable electronics, powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles due to their high energy density and lightweight design.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UDkJ7Sq21Qw
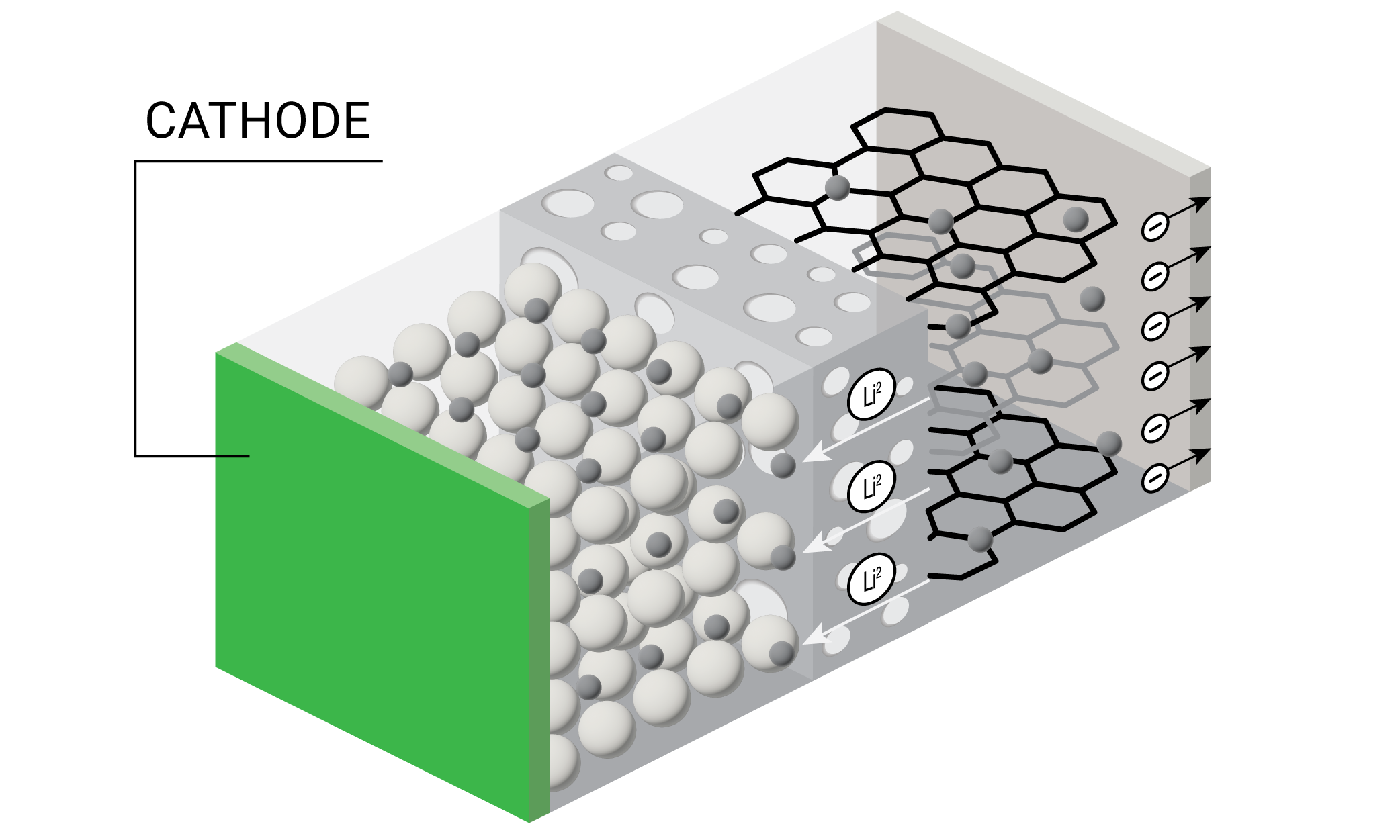
cathode
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oCK_uq2riB8
In lithium batteries, the cathode is a crucial component that determines capacity, voltage, and performance. Typically made from lithium metal oxides, it facilitates lithium-ion movement during discharge and charge cycles. Advances in cathode materials, like NMC and LFP, enhance energy density, stability, and overall battery efficiency.
anode
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j_rNjiIiBKE

In lithium batteries, the anode is a crucial component where lithium ions are stored during charging. Typically made of graphite, it facilitates the flow of electrons through an external circuit, powering devices. Innovations in anode materials, like silicon or lithium metal, aim to enhance battery capacity and longevity.
lithium ions

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G5McJw4KkG8
Lithium ions are crucial in lithium batteries, facilitating energy storage and release. During charging, ions move from the cathode to the anode through an electrolyte. Discharge reverses this flow, generating electricity. Their lightweight and high energy density make lithium-ion batteries ideal for portable electronics and electric vehicles.
current collector

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RQN0CG536JE
In lithium batteries, current collectors are crucial components that facilitate electron flow between the electrodes and the external circuit. Typically made of aluminum (cathode) and copper (anode), they enhance electrical conductivity, structural integrity, and overall battery efficiency, while minimizing energy loss and improving charge-discharge cycles.
electrolyte

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5pws5dnZLrM
In lithium batteries, electrolytes are crucial for conducting ions between the anode and cathode. Typically composed of lithium salts dissolved in organic solvents, they facilitate ion flow, impacting battery efficiency, capacity, and safety. Innovations focus on enhancing stability and conductivity to improve performance and reduce risks like leakage and flammability.
energy density

Energy density in lithium batteries refers to the amount of energy stored per unit weight or volume. High energy density allows for longer-lasting power in compact sizes, making lithium batteries ideal for portable electronics and electric vehicles. Advances in materials and technology continue to enhance their efficiency and performance.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bhAavvZNsdI
separator
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4-1psMHSpKs
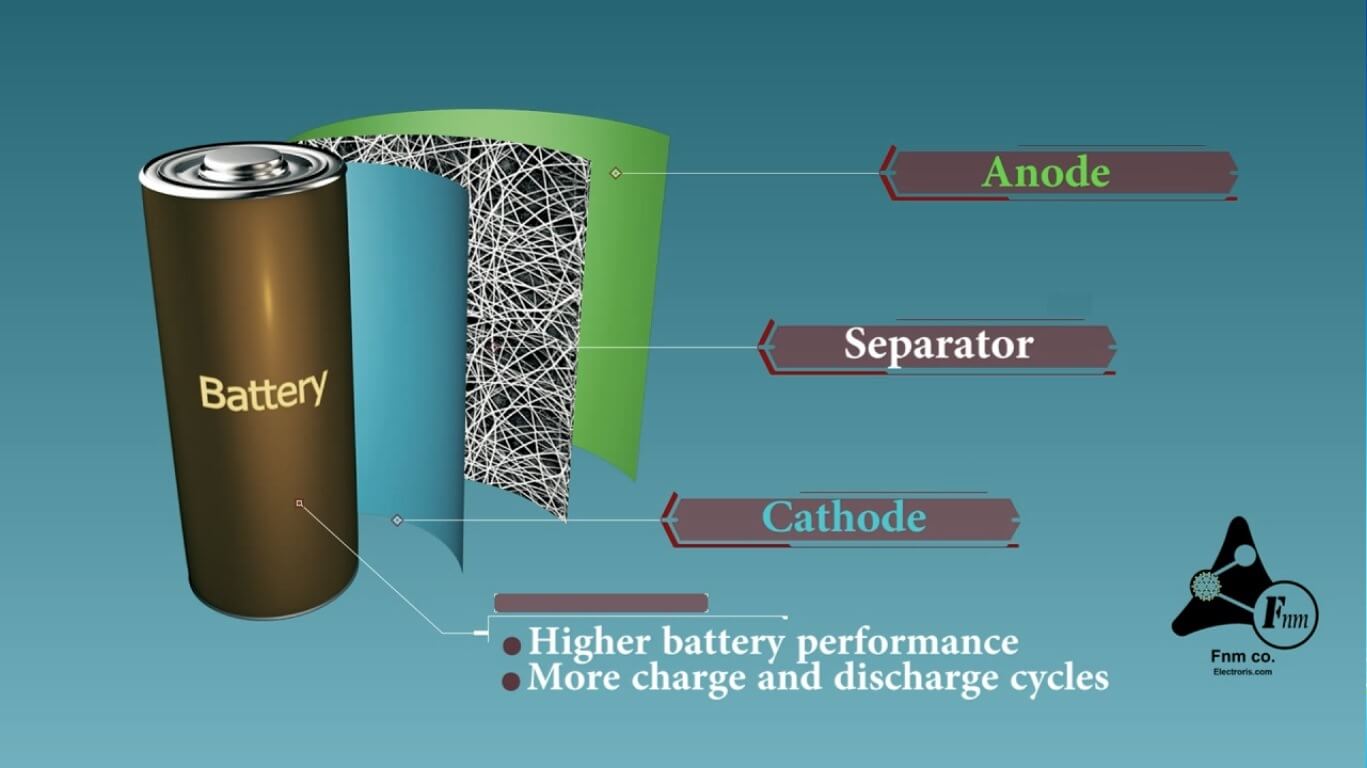
In lithium batteries, separators are critical components that prevent physical contact between the anode and cathode while allowing ion flow. Made from materials like polyethylene or polypropylene, they enhance safety by preventing short circuits and thermal runaway, thus ensuring efficient battery performance and longevity.
charge cycle
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N-yxvZ3Tezg
A charge cycle in lithium batteries refers to the process of charging a battery from 0% to 100% and then discharging it back to 0%. Each cycle contributes to battery wear, gradually reducing capacity over time. Typically, lithium batteries endure hundreds to thousands of cycles before significant performance decline.
lithium ion batteries vs gel batteries

Lithium ion batteries are lighter and have a higher energy density compared to gel batteries, making them more suitable for portable electronic devices and electric vehicles. in addtion lithium ion batteries last longer than gel batteries when purchasing a lithium ion battery the industry warrenty is often 2 years whilst gel batteries are only 6 months
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4JNGQ6hBFNU
AI Report
Essay
**Solar Energy and Types of Solar Panel Mounts**
Solar energy has become an increasingly popular source of renewable energy, harnessing sunlight to generate electricity and heat. This sustainable energy source offers numerous environmental advantages, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and decreasing dependence on fossil fuels. As the world shifts toward cleaner energy alternatives, understanding the technologies that facilitate solar energy utilization, including solar panels and their mounting systems, becomes essential.
There are three primary types of solar panel mounts: fixed mounts, adjustable mounts, and tracking mounts. Fixed mounts are the most common type, securing solar panels in a stationary position at a specific angle. This setup is typically oriented toward the sun's path to optimize energy capture, making it a cost-effective and straightforward option for residential and commercial installations (Green et al., 2020). However, fixed mounts may not maximize energy production throughout the year, as the sun's angle changes with the seasons.
Adjustable mounts offer a solution to the limitations of fixed mounts by allowing users to change the angle of the solar panels seasonally or as needed. This flexibility can significantly enhance the efficiency of solar energy capture, particularly in regions with varying sunlight exposure throughout the year (Kalogirou, 2018). While adjustable mounts can increase energy production, they often require more maintenance and can be more expensive than fixed mounts.
Tracking mounts take energy optimization a step further by automatically adjusting the position of solar panels to follow the sun's trajectory throughout the day. There are two main types of tracking mounts: single-axis and dual-axis. Single-axis trackers rotate on one axis, usually oriented north to south, while dual-axis trackers can adjust on both axes, providing maximum exposure to sunlight (Huld et al., 2019). Although tracking mounts can significantly increase energy output—sometimes by 25% to 40% compared to fixed mounts—they are generally more expensive and require more maintenance due to their mechanical components.
In conclusion, solar energy presents a sustainable alternative to traditional energy sources, and understanding the types of solar panel mounts is crucial for optimizing energy production. Fixed, adjustable, and tracking mounts each have unique advantages and disadvantages, influencing their suitability for various applications. As technology continues to advance, the efficiency and accessibility of solar energy systems are likely to improve, further encouraging their adoption worldwide.
### References
Green, M. A., Emery, K., Hishikawa, Y., Warta, W., & Zou, J. (2020). Solar cell efficiency tables (version 54). *Progress in Photovoltaics: Research and Applications, 28*(1), 3-15. https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.3221
Huld, T., Müller, R., & Gambardella, A. (2019). The role of tracking systems in the performance of solar PV plants. *Renewable Energy, 139*, 1151-1160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.02.015
Kalogirou, S. (2018). Solar Energy Engineering: Processes and Systems (2nd ed.). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-812533-8.00001-4
Lesson Plan
# Lesson Plan: Understanding Solar Energy and Types of Solar Panel Mounts
## Lesson Overview
**Grade Level**: Technical Vocational Students
**Subject**: Renewable Energy Technology
**Duration**: 2 hours
**Objectives**:
- Understand the basic principles of solar energy.
- Identify different types of solar panel mounts.
- Explain how solar panel mounts work.
- Describe maintenance procedures for solar panel mounts.
## Materials Needed
- **Visual Aids**: PowerPoint presentation, videos on solar energy and mounts
- **Handouts**: Diagrams of solar panel mounts, maintenance checklists
- **Tools**: Whiteboard, markers, projectors
- **Sample Equipment**: Different types of solar panel mounts (if available)
- **Safety Gear**: Gloves, goggles (if demonstration involves handling equipment)
## Lesson Outline
### Introduction (15 minutes)
1. **Hook**: Start with a short video showcasing solar energy applications in everyday life (e.g., homes, businesses, and portable devices).
2. **Discussion**: Ask students what they know about solar energy and its importance in the current energy landscape.
3. **Objective Overview**: Present the lesson objectives and what students will learn today.
### Part 1: Understanding Solar Energy (20 minutes)
1. **Definition**: Explain what solar energy is and how it is harnessed from the sun.
2. **Types of Solar Energy Systems**:
- Photovoltaic (PV) systems
- Solar thermal systems
3. **Benefits of Solar Energy**:
- Renewable resource
- Reduces electricity bills
- Low environmental impact
- Energy independence
### Part 2: Types of Solar Panel Mounts (30 minutes)
1. **Introduction to Solar Mounts**:
- Explain the purpose of solar mounts in supporting solar panels.
2. **Types of Solar Panel Mounts**:
- **Fixed Mounts**:
- Description: Static mounts at a fixed angle.
- Pros/Cons: Simple installation, lower cost but less efficiency.
- **Adjustable Mounts**:
- Description: Can be manually adjusted for optimal sun exposure.
- Pros/Cons: More efficient than fixed but require more maintenance.
- **Tracking Mounts**:
- Description: Move to follow the sun throughout the day.
- Pros/Cons: Highest efficiency but more complex and expensive.
3. **Visual Presentation**: Use diagrams and images to illustrate each mount type.
### Part 3: How Solar Panel Mounts Work (20 minutes)
1. **Mechanics of Solar Mounts**:
- Discuss how mounts support solar panels, angles of inclination, and sunlight exposure.
- Explain the importance of proper mounting for energy efficiency.
2. **Demonstration** (if equipment is available):
- Show how to install a fixed mount.
- Explain the adjustment process for adjustable and tracking mounts.
### Part 4: Maintenance of Solar Panel Mounts (25 minutes)
1. **Maintenance Overview**:
- Discuss the importance of regular maintenance for longevity and efficiency.
2. **Maintenance Procedures**:
- Regular inspections (checking for rust, stability, and structural integrity).
- Cleaning panels and mounts to ensure maximum sunlight absorption.
- Lubrication of moving parts in adjustable and tracking mounts.
- Seasonal adjustments (if applicable).
3. **Handout Distribution**: Distribute maintenance checklists and diagrams for students to refer to in the future.
### Conclusion and Q&A (10 minutes)
1. **Recap**: Summarize key points from the lesson.
2. **Q&A Session**: Invite students to ask questions to clarify their understanding.
3. **Closing Thoughts**: Discuss the future of solar technology and its relevance in vocational training.
### Assessment
- **Homework Assignment**: Write a short essay on the benefits of solar energy in their local community and propose a solar installation project.
- **Quiz**: A short quiz at the beginning of the next class covering key concepts from today’s lesson.
### Extensions
- **Field Trip**: Plan a visit to a local solar installation site to see solar mounts in action.
- **Guest Speaker**: Invite a solar energy professional to speak about industry practices.
---
This lesson plan provides a comprehensive framework to engage technical vocational students in the topic of solar energy and solar panel mounts, ensuring a balance of theoretical knowledge and practical insights.
Class Syllabus Outline
# Syllabus for Solar Energy and Types of Solar Panel Mounts
**Course Title:** Solar Energy and Types of Solar Panel Mounts
**Course Code:** SE-101
**Instructor:** [Instructor Name]
**Contact Information:** [Email Address]
**Office Hours:** [Days and Times]
**Course Duration:** [Start Date] to [End Date]
**Class Schedule:** [Days and Times]
**Location:** [Classroom/Online Platform]
---
## Course Description
This course provides an in-depth understanding of solar energy, its applications, and the various types of solar panel mounts used in installations. Students will explore the fundamentals of solar energy, its benefits, challenges, and the technical specifications of different mounting systems. The course will combine theoretical knowledge with practical applications to prepare students for careers in renewable energy, engineering, or environmental science.
## Course Objectives
By the end of this course, students will be able to:
1. Understand the fundamentals of solar energy and photovoltaic technology.
2. Analyze the benefits and challenges of solar energy systems.
3. Identify and describe different types of solar panel mounts.
4. Evaluate the best mounting solutions for various installation scenarios.
5. Design a basic solar energy system incorporating the appropriate mounting techniques.
## Required Texts and Materials
- **Textbook:** [Title of Textbook, Author, Edition, Publisher, Year]
- **Additional Readings:** Articles and case studies as assigned throughout the course.
- **Materials:** Access to a computer with internet, solar energy simulation software (if applicable), and any materials specified by the instructor.
## Course Outline
### Week 1: Introduction to Solar Energy
- Overview of renewable energy
- History and development of solar energy
- Types of solar energy systems (photovoltaic, thermal)
### Week 2: Photovoltaic Technology
- Understanding photovoltaic cells and their function
- Components of a solar panel system
- Efficiency and performance metrics
### Week 3: Benefits of Solar Energy
- Environmental impacts
- Economic benefits and incentives
- Social implications and community solar projects
### Week 4: Challenges in Solar Energy
- Intermittency and energy storage solutions
- Initial costs and financial considerations
- Policy and regulatory frameworks
### Week 5: Introduction to Solar Panel Mounting Systems
- Importance of mounting systems in solar installations
- Overview of mounting options
### Week 6: Fixed Mounts
- Characteristics and advantages
- Applications and limitations
- Design considerations
### Week 7: Adjustable Mounts
- Types of adjustable mounts (seasonal, tilt)
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Case studies on adjustable mount installations
### Week 8: Tracking Systems
- Single-axis vs. dual-axis trackers
- Benefits of tracking systems
- Economic analysis of tracking vs. fixed systems
### Week 9: Roof Mounts
- Types of roof mounts (flush, ballasted, penetrative)
- Roof types and their compatibility with solar panels
- Installation considerations
### Week 10: Ground Mounts
- Types of ground mounts (pole, rack-mounted)
- Site assessments for ground installations
- Soil and environmental considerations
### Week 11: Hybrid and Custom Mounts
- Overview of innovative and custom mounting solutions
- Case studies of unique installations
### Week 12: Practical Applications
- Hands-on installation workshop (if applicable)
- Site visit to a local solar installation (if possible)
- Group project presentations
### Week 13: Future Trends in Solar Energy and Mounting Systems
- Emerging technologies in solar energy
- The future of solar panel mounting systems
- Global trends and innovations
### Week 14: Review and Final Assessment
- Course review
- Final project presentations
- Final exam
## Assessment and Grading
- Participation: 10%
- Quizzes: 15%
- Midterm Exam: 25%
- Group Project: 20%
- Final Exam: 30%
## Attendance Policy
Regular attendance is expected. Students are allowed [number] of unexcused absences. Excessive absences may result in a lower grade.
## Academic Integrity
Students are expected to adhere to the highest standards of academic integrity. Any form of cheating or plagiarism will result in disciplinary action.
## Accommodations
Students requiring accommodations due to disabilities should contact [Institution's Disability Services] to arrange for appropriate support.
---
**Note:** This syllabus is subject to change. Any changes will be communicated in class and via email.
Learning Objectives
### Learning Objectives for a Course on Solar Energy and Types of Solar Panel Mounts
1. **Understand the Fundamentals of Solar Energy**
- Explain the basic principles of solar energy, including how solar panels convert sunlight into electricity.
- Identify the environmental benefits and challenges associated with solar energy utilization.
2. **Identify Different Types of Solar Panels**
- Compare and contrast the various types of solar panels, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film technologies.
- Describe the advantages and disadvantages of each type of solar panel in terms of efficiency, cost, and application.
3. **Explore Solar Panel Mounting Systems**
- Define the different types of solar panel mounts, including fixed, adjustable, and tracking mounts.
- Evaluate the suitability of each mounting system based on specific site conditions and energy production needs.
4. **Assess Site Conditions for Solar Installation**
- Conduct a site assessment to determine the optimal location for solar panel installation considering factors such as sunlight exposure, shading, and roof orientation.
- Analyze local zoning regulations and permits required for solar installation.
5. **Design a Solar Panel System**
- Calculate the energy needs of a residential or commercial building to determine the appropriate size and number of solar panels required.
- Create a basic design layout for a solar panel system, including the selection of mounting systems and orientation.
6. **Implement Safety Practices**
- Identify safety precautions and best practices for working with solar panels and electrical components during installation and maintenance.
- Demonstrate proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and tools while handling solar energy systems.
7. **Evaluate System Performance and Maintenance**
- Monitor and analyze the performance of solar panel systems using appropriate tools and metrics.
- Develop a maintenance schedule for solar panel systems, including cleaning, inspections, and performance assessments.
8. **Explore Emerging Trends and Technologies**
- Investigate current advancements in solar technology and innovative mounting solutions that enhance energy efficiency and system performance.
- Discuss the future of solar energy and the potential impact of new technologies on the industry.
By the end of this course, students will have a comprehensive understanding of solar energy principles and the knowledge required to choose and implement different types of solar panel mounts effectively.
Quiz Questions
Sure! Here are five multiple-choice questions about solar energy and types of solar panel mounts, along with the correct answers:
### Question 1:
What is the primary source of energy for solar panels?
A) Wind
B) Sunlight
C) Water
D) Geothermal
**Answer:** B) Sunlight
---
### Question 2:
Which type of solar panel mount is fixed in place and does not allow for any movement?
A) Adjustable mount
B) Ground mount
C) Fixed mount
D) Tracking mount
**Answer:** C) Fixed mount
---
### Question 3:
What is the main advantage of a tracking solar panel mount?
A) It is cheaper to install.
B) It maximizes sunlight exposure by following the sun's path.
C) It is easier to maintain.
D) It requires no electrical components.
**Answer:** B) It maximizes sunlight exposure by following the sun's path.
---
### Question 4:
Which type of solar panel mount is typically used for residential installations on rooftops?
A) Ground mount
B) Pole mount
C) Roof mount
D) Ballasted mount
**Answer:** C) Roof mount
---
### Question 5:
What is a key benefit of using a ground mount for solar panels?
A) It is more aesthetically pleasing.
B) It allows for easier access for maintenance and cleaning.
C) It can be adjusted seasonally for optimal sun exposure.
D) It eliminates the need for structural roof modifications.
**Answer:** D) It eliminates the need for structural roof modifications.
---
Feel free to use or modify these questions as needed!